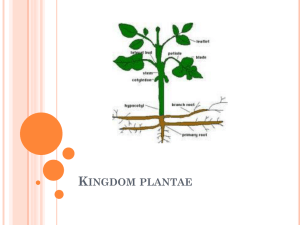
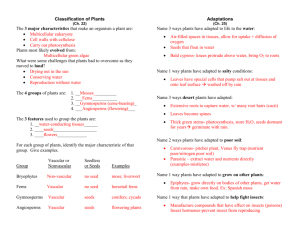
Section 1: Intro to plants. Summarize how plants are adapted to
advertisement

Section 1: Intro to plants. 1. Summarize how plants are adapted to living successfully on land. What were the obstacles they had to overcome? List and describe the main 3. Being able to absorb nutrients, prevent water loss, and reproduce on land. 2. Define vascular and non-vascular plants. Describe 2 differences between vascular and non-vascular plants. Vascular = those with xylem & phloem. Non-vascular = those that circulate water and nutrients cell-to-cell, without the assistance of veins. Vascular plants can be much larger and have many more specialized cells, including those responsible for reproduction. 3. Describe the adaptation of the seed. What are the 4 benefits of having seeds? Describe each of them. A seed is a structure that contains an embryo. These appear only in vascular plants. The benefits are: 1) they protect the seed from damage and disease. 2) they provide nutrients for the seedling 3)they allow for a variety of methods of dispersal 4) they can allow for delayed growth, ensuring the environment is suitable for development. 4. Describe the adaptation of the flower. What is its benefit? This adaptation, one that produces pollen and seeds, is beneficial as it is designed to attract organisms, such as insects, to help pollinate them. 5. List and describe the 3 main types of non-vascular plants. What are the 3 key features of them? Mosses – leafy green plants with conductive cells that transport water short distances Liverworts – grow in mats but lack conducting cells. Hornworts – no conducting cells 3 features: Small, larger gametophyte (the haploid cells that forms a gamete (sperm or egg)), require water for sexual reproduction. 6. List and describe the kinds of seedless vascular plants. What are the 3 key features of seedless vascular plants? Key features: vascular system, larger sporophyte (stage that produces the gametophyte), drought resistant spores (not seeds though) Ferns – large sporophyte (what we commonly know as a fern) Club mosses – roots, stems, and leaves (unlike true mosses that are non-vascular plants) Horsetails – form cone-like structures for spores Whisk ferns – no stems, roots, or leaves. Short branches produce spores. 7. List and describe the phylum Pterophyta. Ferns 8. What are gymnosperms? List and describe the 3 key features. Seed plants where seeds don’t produce in fruit. Cone trees = conifers. Features = Seeds, much smaller gametophyte, wind pollination 9. List and describe the phylum Coniferophyta. Most familiar gymnosperm. Redwoods, pine trees, these plants are adapted to reduce water loss by having very small, tough leaves called needles. 10. What are angiosperms? List and describe the 3 key features. Plants that produce seeds within fruit. Flowers – site where male & female gametophytes are produced = promotes fertilization more efficiently Fruit – body that promotes seed dispersal Endosperm – stored food that supplies the seed with energy for initial germination (growth) 11. What are the 2 kinds of angiosperms? Describe the differences in seed leaves, flower structure, and leaf structure. Monocots = one seed leaf, flowers have petals in multiples of three, narrow leaves with parallel veins Dicots = two seed leaves, flower petals in multiples of 2, 4, or 5, leaves with branching veins. 12. List and describe 5 ways we incorporate plants as food in our lives. Fruits & veggies, root crops, legumes, cereals, wheat, corn, rice 13. List and describe 3 ways we incorporate plants as nonfood in our lives. Wood, medicines, fibers Plant Vocabulary. Define these terms on a separate sheet of paper. 1. angiosperm 2. cuticle 3. endosperm 4. nonvascular plant 5. phloem 6. seed 7. vascular plant 8. vascular tissue 9. woody tissue 10. xylem 11. cotyledon 12. dicot 13. monocot Construct a word search for the terms as per group assignments. 1. 1-10 2. 3-12 3. 7-16 4. 10-19 5. 14-23 6. 15-26 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. ovary apical meristem epidermis meristem vascular cambium cortex endodermis root cap root hair taproot guard cells spongy mesophyll stomata