Plate Tectonics Unit Study Guide
advertisement
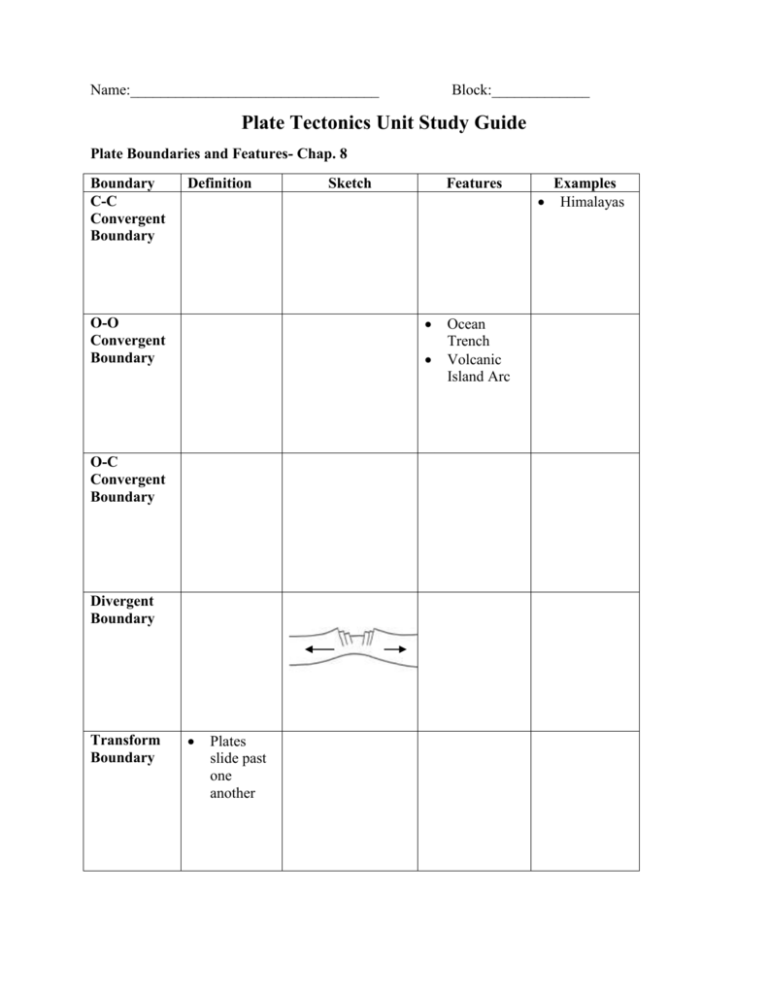
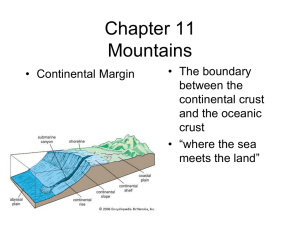
Name:_________________________________ Block:_____________ Plate Tectonics Unit Study Guide Plate Boundaries and Features- Chap. 8 Boundary C-C Convergent Boundary Definition Features O-O Convergent Boundary O-C Convergent Boundary Divergent Boundary Transform Boundary Sketch Plates slide past one another Ocean Trench Volcanic Island Arc Examples Himalayas Earth’s Layers- Chap 4 1. Compare and contrast oceanic crust to continental crust. 2. What layer of the earth is liquid? 3. Why is the asthenosphere important to plate tectonics? 4. What layer of earth makes up the plates? Plate Tectonics History- Chap. 8 1. What evidence did Alfred Wegener use to support continental drift? a. b. c. d. e. 2. What was Pangaea? 3. What causes the plates to move? 4. What evidence did Harry Hess use to support sea-floor spreading? Explain this phenomenon. 5. How does the theory of plate tectonics differ from continental drift? Earthquakes- Chap. 10 1. What types of boundaries result in earthquakes? 2. Sketch a reverse fault, a normal fault, and a strike-slip fault. Label the hanging wall and foot wall. Fault: Stress: Fault: Stress: Fault: Stress: 3. Fill in the graphic organizer. Seismic Waves Surface Waves (L) S-Wave Primary, Compressional, fastest wave 4. Compare and contrast the Richter scale and the Modified Mercalli Scale on how they measure an earthquake’s magnitude. 5. How many seismographs are needed to determine the epicenter? 6. Compare and contrast the focus and epicenter of an earthquake? 7. How do earthquakes help geologists study the interior of the earth? Volcanoes- Chap. 9 1. What is pyroclastic material and how does it differ from lava flows? 2. What is a caldera? 3. What types of plate boundaries result in volcanoes? 4. Compare and contrast volcano types using the chart. Magma Shape Shield Cinder Cone lava flow or pyroclastic material Example Basaltic, mafic, high silica content, viscous Cone shaped Composite Lava flows and Mt. St. Helens violent, gaseous pyroclastic clouds Mountain Building and Continental Margins- Chap 11 1. Label the following folds anticline or syncline. 2. What type of stress causes folds in rock? 3. What type of boundary will result in folded mountains? What type of boundary will result in volcanic mountains? 4. What is a continental margin? What makes a passive margin different from an active margin? 5. Give one example of an active continental margin and a passive continental margin.