Chemistry Chapter 1 Outline
advertisement

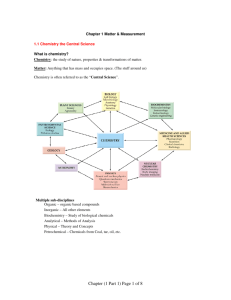
Chemistry I Chapter 1 Outline MATTER AND CHANGE For graded assessments, you will need to be familiar with the following terms: chemistry, chemical, mass, matter, atom, element, compound, extensive properties, intensive properties, physical property, physical change, change of state, solid, liquid, gas, plasma, chemical property, chemical change/chemical reaction, reactants, products, mixture, homogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous mixtures, solutions, pure substances, groups/families, periods, metal, nonmetal, & metalloid. I. CHEMISTRY IS A PHYSICAL SCIENCE A. What are the 6 major branches (sub disciplines) of chemistry listed in your textbook on page 4? II. MATTER AND ITS PROPERTIES A. Compare and contrast extensive and intensive properties. B. Describe the molecular consistencies of matter in the solid state, liquid state and gaseous state. C. Compare and contrast physical changes, physical properties, chemical changes and chemical properties. D. Review and be familiar with the flow chart on page 11 regarding classification of matter. Figure 8. E. Distinguish between a mixture, a solution, homogeneity, & heterogeneity. F. Know how a pure substance differs from a mixture (page 13). Any sample of pure substance is ____________________________________. III. Elements A. Review table 2 on page 16. Omit learning the “older name” column but please learn the symbol and the “modern name” of the element. For example, antimony is Sb, copper is Cu, etc… B. Distinguish and recognize elements from the periodic table and how they are classified. For example, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and phosphorus are nonmetals; boron, silicon, germanium and arsenic are metalloids; lithium, zirconium, vanadium and cobalt are metals. Figure 12 on page 17 is very helpful in accomplishing this objective. C. Distinguish the following properties of metals: malleability, ductility, tensile strength, conductivity & luster. D. What state of matter are most nonmetals at room temperature? Which nonmetal is a liquid at room temperature? E. At room temperature, what state of matter are all metalloids? What property makes metalloids useful in engineering and technological manufacturing such as computers, digital watches, televisions and radios? F. What makes noble (or inert) gases unique among the elements on the periodic table?