Modeling with Real Data: Linear Model Activity & Guide
advertisement

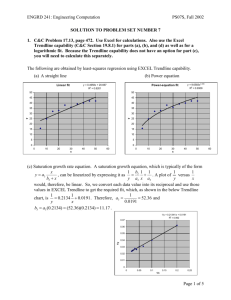
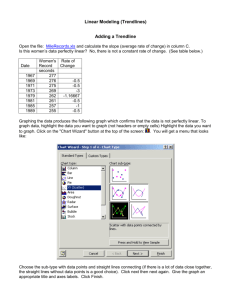
Modeling with Real Data: Linear Model Activity & Guide 2011 1) Create a table using the data provided. 2) Use the table to create a Scatter Plot. Use graph paper to plot the coordinates. Create appropriate intervals. Label the x- and y- axis. Title your graph. Make a legend. 3) Do the coordinates on the graph appear to be approximately a straight line? Explain your reasoning as to why or why not. 4) Connect the two endpoints you plotted on your graph with a line. Use a ruler if necessary. Compute the ratio of changes from each coordinate pair to the next. Do the ratios seem relatively the same? 5) The line you drew in problem #4 is called a trendline. Write a conjecture explaining what you think the trendline tells us. Justify your reasoning. Do you think that a “better” trendline can be drawn to better explain our data? Draw a new trendline that passes through two different coordinates on your graph. 6) Compare and contrast the two trendlines’ predictability. Which trendline do you think is going to explain our data more accurately? Make a prediction for the number of cars that will be in the US in 2010. Which trendline is more aligned with your prediction? 7) Find the line of best fit. Remember, you will need to identify two coordinates in your data in order to build this model. 8) Using the model equation in question #7, estimate how many automobiles will be in the US in 2020. To do this, you will need to make a table relating years to the models prediction. 9) How good was your estimate? Using any research method, compare the actual data with the prediction from your model. Do you feel confident about the predictability of the model now that you compared it with the actual data? 10) Using excel, find the equation of the line that you calculated by hand. Were you correct and accurate? Remember that models can be perfected. Can you manipulate your equation in the same method as re-drawing a trendline on your graph? Try and find another trendline using two different coordinates and repeat questions #7-9. Created by: Vanessa Garza & Paul Rodriguez Page 1 Modeling with Real Data: Linear Model Activity & Guide 2011 Math Dictionary Compare & Contrast Excel Checklist Table Set Up Algebraic Review Prediction Analysis Scatter Plot Guide 11th grade—Activity using Linear Models. Find an Polynomial Models of degree 2, 3, and 4. Compare models and choose best fit to data and explains effect on Global Warming accurately. Line of Best Fit Goals: 6th grade—Questions 1-3; Explore-based activity; Carbon Dioxide caused by automobiles? Why? Why not? Cars in Year 2020 7th grade—Questions 1-6; Make conjectures; Carbon Dioxide caused by automobiles truly affecting global warming? Trendline & Ratios To Reflect & Conject Compare & Contrast 8th grade—Questions 110; Reasonableness of conjectures; answer question of Carbon Dioxide—Causing Global Warming? Excel Set Up 9th grade—Activity using Linear Models. Find an Exponential Model. Compare models and choose best fit to data and explains effect on Global Warming accurately. Created by: Vanessa Garza & Paul Rodriguez 10th grade—Activity using Linear Models. Find an Quadratic Model. Compare models and choose best fit to data and explains effect on Global Warming accurately. Suggestions: Accompany guide/activity with PowerPoint presentation Do activity with students using a different set of data Use activity as an assessment of overall understanding Review skills necessary to complete activity Materials: Excel Data Set Activity Handout Graphing Calculator PowerPoint Graphic Organizers (if necessary) Vocabulary List Page 2