File - Miss S. Harvey

Vocabulary Word Definition
CHAPTER 2
Nuclear membrane surrounds the nucleus and allows certain materials to pass into and out of the nucleus
DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid) a long molecule that provides instructions for making, running, and repairing a cell; made of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base molecules
Nucleolus an organelle in the nucleus of a cell that produces and assembles ribosomes
Centrioles organelles made of special microtubules; they are active during cell division in most animal cells
Nucleotide molecule made up of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base
Nitrogenous base there are four different bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G); pairs of these molecules form each rung of the DNA ladder
Amino acids small molecules that make up proteins; there are 20 different amino acids
Gene a short section of DNA on a chromosome that contains the instructions to make a specific protein
Genome all of an organism’s genes (thus its entire DNA)
Trait one version of a characteristic
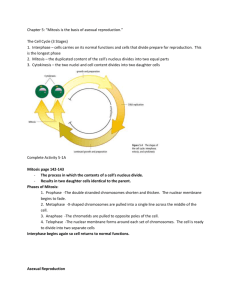
Cell cycle the sequence of events in the cell from one cell division to another; includes interphase and cell division
Interphase phase of the cell cycle in which cells grow and work
Sister chromatids a chromosome and its copy; chromosomes make copies of themselves during interphase
Parent cell a cell before it divides
Daughter cells one of two genetically identical cells produced when a parent cell divides
Mitosis the process that divides the nuclear material during cell division
Cytokinesis the process that divides the cytoplasm and the rest of the organelles in half during cell division; it usually begins before mitosis is finished
Prophase the first stage of mitosis
Spindle moves the chromatids during the later phases of cell division; made of spindle fibres
Metaphase the second stage of mitosis
Anaphase the third stage of mitosis
Telophase the final stage of mitosis
Mutation a change in the DNA, or the genetic code of a cell
Cancer a disease in which cells divide very rapidly and uncontrollably; caused by a mutation in the genes that control cell division
Benign tumours a mass of cells that grows but stays in one place and usually does not interfere with the normal functioning of the surrounding tissue or organ
Malignant tumours mass of cells that invades the surrounding tissues and interferes with the normal functioning of the tissues and organs
Metastasis the spread of cancer cells away from their original location
Carcinogen any substance that can cause cancer
Sexual reproduction two separate organisms (parents) contribute genetic information to produce offspring that are genetically different from both parents
Zygote the first cell of a new organism; a fertilized egg cell
Asexual reproduction one parent produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
Clone an offspring of asexual reproduction; genetically identical to the parent and to other offspring produced asexually by the parent
Binary fission a form of asexual reproduction used by single-celled organisms to produce two genetically identical daughter cells
Budding
Vegetative reproduction
Fragmentation
Spore a type of asexual reproduction in which the offspring begins as a small growth (called a bud) on the parent asexual reproduction in plants; includes producing runners, bulbs, tubers, and cuttings a type of asexual reproduction in which a small part of an animal breaks off and grows into a new organism cell with thick cell walls similar to seeds, but is produced by cell division and grows into organisms genetically identical to the parent organism