worksheet demo: Intensive corn farming
advertisement
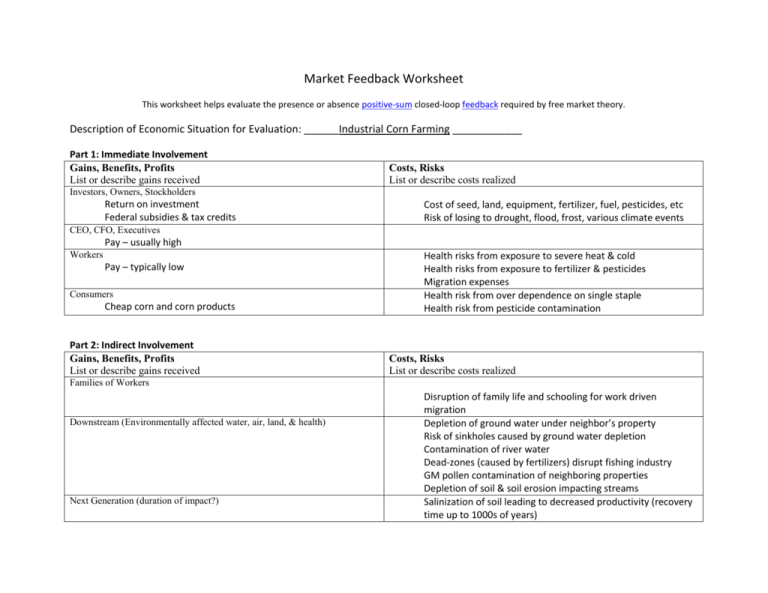
Market Feedback Worksheet This worksheet helps evaluate the presence or absence positive-sum closed-loop feedback required by free market theory. Description of Economic Situation for Evaluation: ______Industrial Corn Farming ____________ Part 1: Immediate Involvement Gains, Benefits, Profits List or describe gains received Costs, Risks List or describe costs realized Investors, Owners, Stockholders Return on investment Federal subsidies & tax credits Cost of seed, land, equipment, fertilizer, fuel, pesticides, etc Risk of losing to drought, flood, frost, various climate events CEO, CFO, Executives Pay – usually high Workers Pay – typically low Consumers Cheap corn and corn products Part 2: Indirect Involvement Gains, Benefits, Profits List or describe gains received Health risks from exposure to severe heat & cold Health risks from exposure to fertilizer & pesticides Migration expenses Health risk from over dependence on single staple Health risk from pesticide contamination Costs, Risks List or describe costs realized Families of Workers Downstream (Environmentally affected water, air, land, & health) Next Generation (duration of impact?) Disruption of family life and schooling for work driven migration Depletion of ground water under neighbor’s property Risk of sinkholes caused by ground water depletion Contamination of river water Dead-zones (caused by fertilizers) disrupt fishing industry GM pollen contamination of neighboring properties Depletion of soil & soil erosion impacting streams Salinization of soil leading to decreased productivity (recovery time up to 1000s of years) Depletion of aquifers (recovery time up to 1000s of years) Sediment banks downstream concentrated with pesticides & fertilizers affect fish and stream health (decades for recovery) Increase of super-pests in environment (pesticide resistant, etc.) Probable combined effects mean decreased food production Depletion of fossil fuels (permanent) Part 3: Source of Resource & Impact Value Added List work for which the producer owners should rightfully be paid All farm related activities Value Taken List value derived from sources other than the producer Pre-existing resource Soil quality (depleted & contaminated) ground water (depleted) Resources derived from other properties Ground water Depletion rate vs. replenishment rate Ground water & soil (100s to 1000s of years to replenish) Fossil fuels (millions of years to replenish) Evaluation In a perfect free market, profit is made by those who do the actual work and take the risks, and all parties involved are properly compensated. All person’s and properties affected are appropriately compensated for their involvement. The further an economic situation deviates from these relationships the less the market is functioning according to the free market ideal. If entries in the profit and cost columns (Parts 1 & 2) correlate strongly the transaction is working close to the market ideal. If they are highly different the transaction does not represent a free market. If the producer is appropriately compensated for value added and value is only taken with consensual agreement and compensation (part 3) then the market is working as a free market. If value is taken without consensual agreement and compensation then the transaction does not represent free market action. Is this situation strongly characteristic of a free market, or not characteristic of free market ideals? (i.e.: do the profit columns and cost columns highly correlate? Modern methods for corn farming are not consistent with free market ideals Industrialized corn farming has very large long-term downstream impacts, and large impacts on local ground water and soil. No method exists to compensate those downstream for these impacts nor future generations Health impacts for workers are potentially high but compensation is low











