No conformation change of secondary structure due to Ebola GP
advertisement

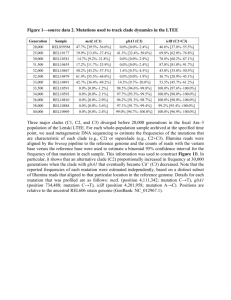
Received by Qing Received on 2014-10-29 ID No. APJTD-2014-0260 First revised on Second revised on Third revised on Pages 3 埃博拉 GP-F88A 突变引起的次生结构无结构改变 No conformation change of secondary structure due to Ebola GP-F88A mutation Beuy Joob1 1. Sanitation 1 Medical Academic Center, Bangkok Thailand Viroj Wiwanitkit2 2. Visiting professor, Hainan Medical University, China Correspondence Beuy Joob Sanitation 1 Medical Academic Center, Bangkok Thailand Email: beuyjoob@hotmail.com Dear editor, the Ebola virus outbreak is the serious problem at present. An interesting concern is on the mutation of the virus that might lead to alteration of clinical pattern. An interesting reported mutation is the F88A mutation of Ebola viral glycoprotein. Martinez et al. reported that this mutation could restrict viral entry in a host species- and cell-type-specific manner [1]. Basically, the sense mutation might cause a change in conformation due to secondary structure aberration. For the mentioned F88A mutation, it is still no data on the resulted structural aberration. Here, the authors tried to predict the secondary structure change due to the mutation. The standard bioinformatics analysis (APSSP2 [2]) was done and the result showed no secondary structure change due to the mutation (Figure 1). This method is confirmed for efficacy and used in previous published paper by Zhou et al [3]. The position 88 still preserved “coil” appearance in both wild and mutated (F88A) type of Ebola viral glycoprotein. This can imply that the observed clinical pattern alteration by Martinez et al. should not be due to the alteration of secondary structure. References 1. Martinez O, Ndungo E, Tantral L, Miller EH, Leung LW, Chandran K, Basler CF. A mutation in the Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein restricts viral entry in a host species- and cell-type-specific manner. J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(6):3324-34. 2. Raghava GPS. APSSP2 : A combination method for protein secondary structure prediction based on neural network and example based learning. CASP5.2002: A-132. 3. Zhou HZ, Xu HF, Xin XM, Guan XR, Zhou J. Position 22 of the V3 loop is associated with co-receptor usage and disease progression in HIV-1 subtype B isolates. Curr HIV Res. 2011 Dec 1;9(8):636-41. Figure 1. The predicted secondary structure in wild and mutated (F88A) showing the position 82 – 95 (H = helix, C = coil). Wild Mutated KH RC WC GH AH RH SC GC VC PC PC KC VC VC KH RC WC GC FC RC SC GC VC PC PC KC VC VC secondary Wild Mutated 88 --- coil