LO wk 4Muscular System - PBL-J-2015
advertisement

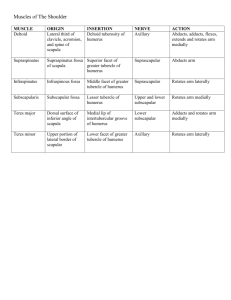
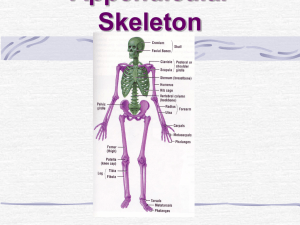
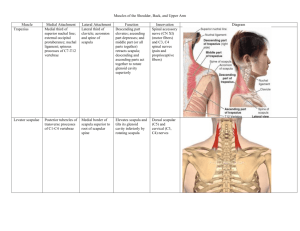
PBL Night Starvation Muscular System & Muscles of the Upper Limb Understand the concepts & associated principles, functional & clinical applications of muscle structure, tendons and attachments. Be able to identify the major muscles in the upper limb. Comprehend the organisation of muscles within different compartments of the upper limb, their nerve supply and actions. The upper limb is designed for its’ mobility and ability to grasp, strike and conduct fine motor skills. The upper limb is characterised into four segments. Shoulder: includes the pectoral, scapular and lateral supraclavicular regions. The pectoral girdle is formed posteriorly by the scapulae and clavicles and anteriorly by the manubrium of the sternum. Arm: between shoulder and elbow and is centred around the humerus. Includes posterior and anterior regions. Forearm: is between the elbow and wrist and contains the ulna and radius. Consists of anterior and posterior regions of the forearm. Hand: distal to forearm and contains carpus, metacarpus and phalanges. It is composed of the wrist, palm, dorsum of hand and digits (fingers, including the opposable thumb). The hand is richly supplied with sensory endings for touch, pain and temperature. ANTERIOR AXIOAPPENDICULAR MUSCLES Muscle Medial attachment Lateral attachment Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor Clavicular head: anterior surface of medial half of clavicle. Sternocostal head: anterior surface of sternum, superior six costal cartilages, aponeurosis of external oblique muscle. 3rd-5th ribs near their costal cartilages. Lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus (groove) of humerus. Innervation Lateral and medial pectoral nerves; clavicular head (C5, C6 ), sternocostal head (C7, C8, T1). Main actions Adducts and medially rotates humerus; draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly. Acting alone, clavicular head flexes humerus and sternocostal head extends it from the flexed position. Medial border and Medial pectoral Stabilizes scapula by drawing superior surface of nerve (C8, T1). inferiorly and anteriorly coracoid process of against thoracic wall. scapula. Subclavius Junction of 1st rib and Inferior surface of Subclavian nerve Anchors and depresses its costal cartilage. middle third of (C5, C6). clavicle. clavicle. Serratus External surfaces of Anterior surface of Long thoracic Protracts scapula and holds anterior lateral parts of 1st-8th medial border of nerve (C5, C6, against thoracic wall; rotates ribs. scapula. C7). scapula. NB: bolded spinal cord segmented innervations refers to main innervation to that region. POSTERIOR AXIOAPPENDICULAR MUSCLES Muscle Trapezius Medial attachment Medial third of superior nuchal line; external Lateral attachment Lateral third of clavicle; acromion Innervation Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) Main actions Descending (superior) part elevates; ascending (inferior) PBL Night Starvation occipital protuberance; and spine of scapula nuchal ligament; spinous processes of C7T12 vertebrae (motor fibres) and C3, C4 spinal nerves (pain and proprioceptive fibres). part depresses; and middle part(or all parts together) retracts scapula; descending and ascending parts act together to rotate glenoid cavity superiorly Latissimus dorsi Spinous processes of inferior 6 thoracic vertebrae, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inferior 3 or 4 ribs Floor of intertubercular sulcus (groove) of humerus Thorocodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8) Extends, adducts, and medially rotates humerus; raises body toward arms during climbing. Levator scapulae Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1-C4 vertebrae Medial border of scapula superior to root of spine Dorsal scapular (C5) and cervical (C3, C4) nerves Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula Rhomboid minor and major Minor: nuchal ligament; spinous processes of C7 and T1 vertebrae Major: spinous processes of T2T5 vertebrae minor: triangular Dorsal scapular area at medial end of nerve (C4, C5) scapular spine Major: medial border of scapula from level of spine to inferior angle SCAPULOHUMERAL (INTRINSIC SHOULDER) MUSCLES Muscle Medial attachment Lateral attachment Deltoid Lateral third of Deltoid tuberosity of Retract scapula and rotate it to depress glenoid cavity; fix scapula to thoracic wall Innervation Main actions Axillary nerve (C5, Clavicular (anterior) part flexes PBL Night Starvation clavicle; acromion and spine of scapula humerus C6) and medially rotates arm; acromial (middle) part abducts arm; spinal (posterior) part extends and laterally rotates arm Suprapinatus Supraspinous fossa of scapula Superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus Suprascapular nerve (C4, C5, C6) Initiates and assists deltoid in abduction of arm and acts with rotator cuff muscles Infraspinatus Infraspinous fossa of scapula Middle facet of greater tubercle of humerus Suprascapula nerve (C5, C6) Laterally rotates arm: and acts with rotator cuff muscles. Teres minor Middle part of lateral Inferior facet of border of scapula greater tubercle of humerus Axillary nerve (C5, C6) Laterally rotates arm: and acts with rotator cuff muscles. Teres Major Posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula Medial lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus Lower Adducts and medially rotates subscapular nerve arm (C5, C6) Subscapularis Subscapular fossa (most anterior surface of scapula) Lesser tubercle of humerus Upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5, C6, C7) Medially roates arm; as part of roator cuff, help hold head of humerus in gelnoid cavity PBL Night Starvation MUSCLES OF THE ARM Muscle Proximal attachment Distal attachment Innervation Tuberosity of radius and fascia of forearm via bicipital aponeurosis Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6 ) Middle third of medial surface of humerus Muscle action Supinates forearm and, when it is supinated, flexes forearm; flexes arm; short head resists dislocation of shoulder Distal half of anterior surface of humerus Coronoid process and tuberosity of ulnar Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6 ) and radial nerve (C5, C7) Flexes forearm in all positions Triceps brachii Long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula Lateral head: posterior surface of humerus, superior to radial groove Medial head: posterior surface of humerus, inferior to radial groove Proximal end of olecranon of ulnar and fascia of forearm Radial nerve (C6, C7, C8) Chief extensor of forearm; long head extends arm and resists dislocation of humerus (especially important during abduction) Anconeus Lateral epicondyle of humerus Lateral surface of olecranon and superior part of posterior surface of ulnar Radial nerve (C7, C8, T1) Assists triceps in extending forearm; stabilizes elbow joint; abducts ulna during pronation Biceps brachii Short head: tip of coracoid process of scapula Long head: supraglenoid tubercle of scapula Coracobrac hialis Tip of coracoid process of scapula Brachialis Helps flex and adduct arm; resists dislocation of shoulder PBL Night Starvation MUSCLES OF ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF FOREARM Muscle Medial attachment Lateral attachment Superficial (first) layer Innervation Main actions Median nerve (C6, C7) Pronates and flexes forearm (at elbow) Pronator teres Coronoid process Ulnar head Middle of convexity of lateral surface of radius Humeral head Flexor carpi radialis Medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor origin) Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Humeral head Ulnar head Olecranon and posterior border (via aponeurosis) Base of 2nd metacarpal Flexes and abducts hand (at wrist) Distal half of flexor retinaculum and apex of palmar aponeurosis Median nerve (C7, C8) Flexes hand (at wrist) and tenses palmar aponeurosis) Pisiform, hook of hamate, 5th metacarpal Ulnar nerve (C7, C8) Shafts of middle phalanges of medial four digits Median nerve (C7, C8, T1) Flexes middle phalanges at proximal interphalangeal joints of middle four digits; acting more strongly, it also flexes proximal phalanges at metacarpophalangeal joints Bases of distal phalanges of 4th and 5th digits Ulna nerve (C8, T1) Flexes distal phalanges 4 and 5 at distal interphalangeal joints Bases of distal phalanges of 2nd and 3rd digits Anterior interosseous nerve, from median nerve (C8, Flexes distal phalanges 2 and 3 at distal interphalangeal joints Flexes and adducts hand (at wrist) Intermediate (second) layer Flexor digitorum superficialis Humeroulnar head Radial head Medial epicondyle (common flexor origin and coronoid process) Superior half of anterior border Deep (third) layer Flexor digitorum profundus Medial part Proximal ¾ of medial and anterior surfaces of ulna and interosseous membrane Lateral part Flexor pollicis Anterior surface of radius and adjacent Base of distal phalanx of Flexes phalanges of 1st digit PBL Night Starvation longus interosseous membrane thumb T1) Pronator quadratus Distal quarter of anterior surface of ulna Distal quarter of anterior surface of radius (thumb) Pronates forearm; deep fibers bind radius and ulna together TENDONS Tendons and muscles work together. A tendon is a tough yet flexible band of fibrous connective tissue connecting muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Ligaments are similar (both made of collagen) except ligaments join one bone to another. PBL Night Starvation MUSLCE OF POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF FOREARM Muscle Proximal Distal Attachment Attachment Superficial layer Brachioradialis Proximal 2/3 of Lateral surface of supraepicondylar distal end of ridge of humerus radius proximal to styloid process Extensor carpi radialis longus Lateral supraepicondylar Dorsal aspect of base of 2nd metacarpal Extensor carpi radialis brevis Lateral epicondyle of humerus (common extensor origin) Lateral epicondyle of humerus (common extensor origin). Dorsal aspect of base of 3rd metacarpal Extensor digitorum Extensor digit minimi Extensor carpi ulnaris Deep layer Supinator Extensor indicis Innervation Main Action Radial nerve (C5, C6, C7) Weak flexion of forearm; maximal when forearm is in mid-pronated position Extend and abduct hand at the wrist joint; ECRL active during first clenching Radial nerve (C6, C7) Extensor expansions of medial 4 digits Extensor expansion of 5th digit Deep branch of radial nerve (C7, C8) Extends medial 4 digits primarily at metocarpophalangeal joints Extends 5th digit primarily at metacarpophalangeal joint, secondarily at interphalangeal joint Extends and adducts hand at wrist joint (also active during fist clenching) Lateral epicondyle of humerus; posterior border of ulna via a shared aponeurosis Dorsal aspect of base of 5th metacarpal Lateral epicondyle of humerus; radial collateral and anular ligaments; supinator fossa; crest of ulna Posterior surface of distal third of ulna and interosseous membrane Lateral, posterior, and anterior surfaces of proximal third of radius. Deep branch of radial nerve (C7, C8) Supinates forearm; rotates radius to turn palm anteriorly or superiorly (if elbow is flexed) Extensor expansion of 2nd digit Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8), continuation of deep branch of radial nerve Extends 2nd digit (enabling its independent extension); helps extend hand at wrist. Base of 1st metacarpal Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8), continuation of deep branch of radial nerve. Abducts thumb and extends it at carpometacarpal joint Outcropping muscles of deep layer Abductor pollicis Posterior surface longus of proximal halves of ulna, radius, and interosseous membrane Extensor pollicus Posterior surface longus of middle third of ulna and interosseous Dorsal aspect of base of distal phalanx of thumb Extends distal phalanx of thumb at interphalangeal joint; extends PBL Night Starvation membrane Extensor pollicis brevis Posterior surface of distal third of radius and interosseous membrane INTRINSIC MUSCLES OF HAND Muscle Proximal Attachment metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints Extends proximal phalanx of thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint; extends carpometacarpal joint Dorsal aspect of base of proximal phalanx of thumb Distal attachment Innervation Main Action Thenar muscles Opponens pollicis Abductor Lateral side of 1st metacarpal To oppose thumb it draws 1st metacarpal medially to center of palm and rotates it medially Recurrent branch Abducts thumb, PBL Night Starvation pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis brevis Superficial head of median nerve (C8, T1) Flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium helps oppose it Lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb Flexes thumb Deep head Adductor pollicis Oblique head Transverse head Bases of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals, capitate and adjacent carpals Anterior surface of shaft of 3rd metacarpal Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1) Adducts thumb toward lateral border of palm Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb Hypothenar muscles Abductor digiti minimi Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit Flexor digiti minimi brevis Opponens digiti Abducts 5th digit; assists in flexion of its proximal phalanx Pisiform Hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1) Flexes proximal phalanx of 5th digit Draws 5th metacarpal anterior and rotates it, bringing 5th digit into opposition with thumb Medial border of 5th metacarpal Short Muscles Lumbricals 1st and 2nd Lateral two tendons of flexor digitorum profundus 3rd and 4th Medial three tendons of flexor digitorum profundus Dorsal interossei, 1st4th Adjacent sides of two metacarpals Bases of proximal phalanges; extensor expansions of 2nd4th digits Palmar Palmar surfaces of Bases of proximal Lateral sides of extensor expansions of 2nd5th digits Median nerve (C8, T1) Branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1) Flex metacarpophalangeal joints; extend interphalangeal joints of 2nd-5th digits Abducts 2nd-4th digits from axial line; act with lumbricals in flexing metacarpophalangeal joints and extending interphalangeal joints Adducts 2nd, 4th and PBL Night Starvation interossei, 1st3rd 2nd, 4th, 5th metacarpals phalanges; extensor expansions of 2nd, 4th, 5th digits 5th digits toward axial line; assist lumbricals in flexing metacarpophalangeal joints and extending interphalangeal joints; extensor expansions of 2nd-4th digits