Dermatomes and Myotomes
Dermatomes are areas on the surface of the skin that are control by specific nerve roots from the spinal
cord
Myotomes correspond to muscles that are controlled by specific nerve roots from the spinal cord
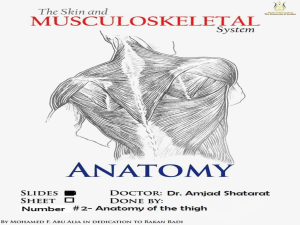
Cranial Nerves branch out off the brain (12)
Nerve Roots branch out off the spinal cord (31)
info.med.yale.edu/ caim/cnerves/
www.informeddecision.com/options/ lowback/dclmlama.htm
These nerve roots branch out to form a plexus which is a network of intersecting nerves which travel to
different parts of the body, they are both motor and sensory
Cervical Plexus1
C1-C4 nerve roots innervate the diaphragm, shoulder and neck.
Brachial Plexus2
C5-T1 nerve roots innervate the upper limbs
Lumbosacral Plexus3 L1- L5, S2 nerve roots innervate the lower extremity
1. http://instruct.westvalley.edu/granieri/cervical%20plexus.jpg
2. www.medical-look.com/.../Brachial_Plexus.jpg
3. "LifeART (and/or) MediClip image copyright (2005) Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. All rights reserv
Skin (sensation) is innervated by a single nerve roots called the dermatomes
Muscles (movement) are innervated by singe nerve roots called myotomes
Nerves and nerve roots are typically injured by compression or stretching forces
When a nerve root is damaged a deficit may occur in the corresponding limb
The evaluation of nerve root damage can be done by testing dermatomes and myotomes
Nerve root trauma should always be inspected by a physician
Dermatomes
Test for abnormalities in sensitivity by using a pinwheel, paper clip or finger nail
The athlete should close his/her eyes and give the therapist feedback with regards to various
stimuli
All tests should be compared bilaterally
Nerve Root
Dermatome Patterns
Upper Extremity
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
T1
Top of head
Temporal & occipital regions of head
Neck and posterior cheek
Superior shoulder and clavicle
Deltoid patch & lateral arm
Lateral forearm, thumb and index finger
Posterior lateral forearm & middle finger
Medial forearm, ulna border & ring/little fingers
Medial side of forearm & upper arm
Lower Extremity
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
S1
S2
Back, hip and groin
Anterior superior thigh, medial thigh above knee
Back, anterior thigh and medial knee
Lateral thigh/knee, anterior medial lower leg to medial aspect of big toe
Lateral knee and lateral lower leg and top of foot
Buttocks, posterior lateral thigh and lateral plantar surface of foot
Buttocks, posterior medial thigh and medial plantar surface of foot
Figure 24-4 Dermatome distribution of the spinal nerves.From Thibodeau GA,
Patton KT: Anatomy and Physiology,ed 6, St. Louis, 2006, Mosby.
(Cameron, Michelle H.. Physical Rehabilitation: Evidence-Based Examination, Evaluation, and
Intervention. W.B. Saunders Company, 032007.).
<vbk:978-0-7216-0361-2#B9780721603612500272_f4>
Myotomes
Test with resistive exercises
The clinician will check for weakness in strength
All tests should be compared bilaterally
Upper Extremity
Nerve Root
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
T1
Muscle
Upper traps
Deltoids, Biceps
Biceps, Wrist Ext
Wrist Flexors, Elbow Ext
Thumb Ext, Flexors
Hand Intrinsics
Test
tested with resisted shoulder shrugs/elevation
tested with resisted shoulder abduction
tested with resisted elbow flexion, wrist extension
tested with resisted wrist flexion, elbow extension
tested with resisted thumb extension
fingers abduction & adduction
Lower Extremity
Nerve Routes
L1-L2
L3
L4
L5
S1/S2
Muscle
Test
Iliopsoas, hip adductors
tested with resisted hip flexion
Quadriceps
tested with resisted knee extension
Anterior Tibialis,
tested with resisted foot dorsiflexion
Extensor Hallucis, Glut Medius
tested with resisted great toe extension
Gastrocnenius
tested with plantar flexion