Appendicular Skeleton
advertisement
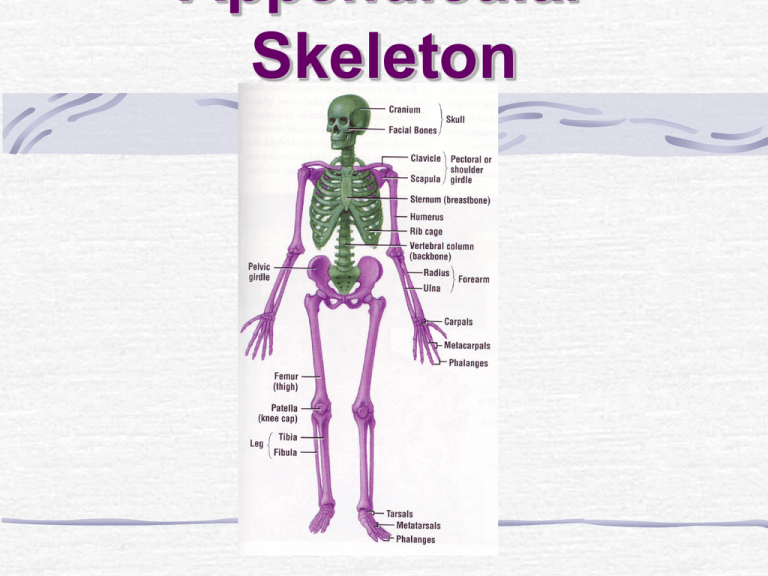
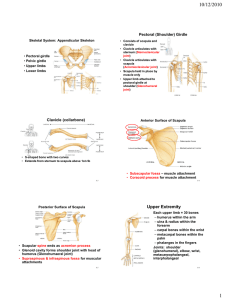
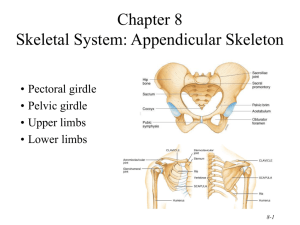
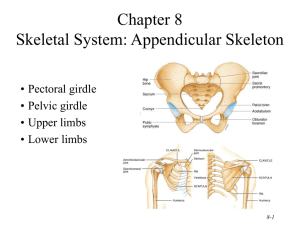
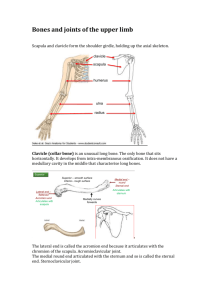
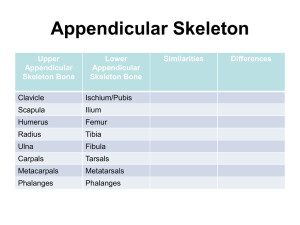
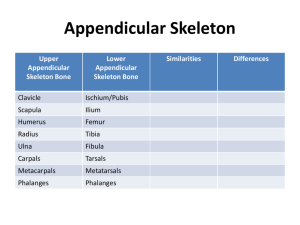
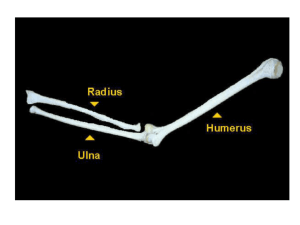
Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Pectoral Girdle Attach the bones of the upper limbs to the axial skeleton Consist of two bones: clavicle and scapula The joints are freely movable in many directions Clavicle Also known as the collarbone Long, slender Sshaped bone that is horizontally above the first rib Transmits mechanical force from the upper limb to the trunk Scapula Also known as the shoulder blade Large, flat triangular bone situated in the posterior part of the thorax A sharp ridge, the spine, runs diagonally across the back portion of the scapula body The lateral end of the spine is the acromion, where the scapula articulates with the clavicle The glenoid cavity is a depression inferior to the acromion. It articulates with the humerus head to form the shoulder joint. The coracoid process is where muscles attach. Upper Limb Upper Limb Consists of 30 bones (all paired up) Humerus in the arm Ulna and radius in the forearm 8 carpals, 5 metacarpals, and 14 phalanges in the hand Humerus Longest and largest bone of the upper limb Articulates with the scapula at the shoulder and both the ulna and radius at the elbow Ulna Located on the medial side of the forearm (pinky side) Longer than the radius Radius Located on the lateral side of the forearm (thumb side) Humerus Bone Surface Markings Proximal end consists of a head that articulates with the scapula’s glenoid cavity and an anatomical neck where the epiphyseal plate used to be The body contains the deltoid tuberosity, a roughened V-shaped area where the deltoid muscle attaches At the distal end, the capitulum articulates with the head of the radius. The radial fossa is a depression that receives the head of the radius when the forearm is bent. The trochlea is a spoolshaped surface that articulates with the ulna. The coronoid fossa receives part of the ulna when the forearm is bent. The olecranon fossa is a depression on the back of the bone that receives the ulna when the forearm is straightened. Ulna Bone Surface Markings The olecranon forms the prominence of the elbow on the proximal end. The coronoid process along with the olecranon receives the trochlea of the humerus in the trochlear notch. The radial notch is a depression for the head of the radius. A styloid process is at the distal end. Radius Bone Surface Markings Disc-shaped head at the proximal end articulates with the capitulum of the humerus and radial notch of the ulna Radial tuberosity is a raised, roughened area that is where the biceps brachii muscle attaches to the bone The distal end of the radius articulates with three carpal bones There’s a styloid process at the distal end (similar to the ulna) Carpus (Wrist) 8 carpals Held together by ligaments with four bones in each row Named for their shapes Short bones The carpals in the top row are the: Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, and Pisiform The carpals in the bottom row are the: Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, and Hamate Metacarpus (Palm) 5 metacarpals Each consists of a proximal base, an intermediate body, and a distal head Numbered I-V starting with the thumb Long bones Phalanges (Fingers) 14 in each hand Thumb has two (proximal and distal) In each of the other four digits, there are three (proximal, middle, and distal) Disorders of the Upper Limb Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Narrowing of the carpal tunnel causes compression of the median nerve The nerve compression causes pain, numbness, tingling, and hand muscle weakness Rotator Cuff Injury Tears or inflammation of ligaments and tendons of the shoulder near the humerus Results in pain and loss of shoulder mobility Fractures Checkpoint Questions Which bones make up a pectoral girdle? What is the function of the pectoral girdle? With which part of the scapula does the humerus articulate? What part of the ulna is called the “elbow”? What part of which bones are commonly called the “knuckles”? What bones form the upper limb, from proximal to distal?