11. Weather Part 4 – The Water Cycle
advertisement

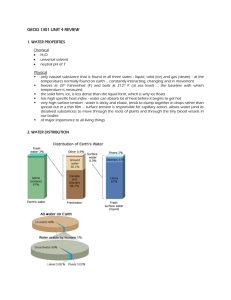
The Water Cycle Think About It: Why is there humidity? There is moisture in the air. Why is there moisture in the air? It evaporates from lakes and oceans. Solar radiation causes it to change its state. Remember: Water takes longer to warm and cool because of its high heat capacity. Lots of solar energy is needed to change the state of water! Solid Ice Liquid Water Gas Vapour Changing States of Water Melting – solid to liquid Evaporating – liquid to gas Endothermic – absorption of heat. A lot of energy is needed for these changes. This is why it takes a long time for the temperature in the spring to rise significantly even when the days are longer and there is more sunlight. Most of the Sun’s energy is used to melt the snow and ice. Changing States of Water Condensing – gas to liquid Solidifying (freezing) – liquid to solid Exothermic – the release of heat. A lot of energy is released during these changes. This is why the temperature falls slowly in autumn even though there is significantly less sunlight. The freezing water is releasing heat. The Water Cycle The hydrologic cycle. Water continually cycles through the biosphere. It circulates, continuously, through the oceans, atmosphere, and land in different forms. This About It: Describe the processes of the water cycle. Water vapour condenses to form clouds, which result in precipitation when the conditions are suitable. Precipiation falls to the surface and infiltrates the soil or flows to the ocean as runoff. Surface water evaporates, returning moisture to the atmosphere, while plants return water to the atmosphere by transpiration. The Water Cycle Condensation: Water vapour in the air rises because of convection. As it rises, the water vapour loses energy. This causes its temperature to drop, causing it to change from gas to liquid (water droplets) or solid (ice or snow). The Water Cycle Precipitation: The water droplets or ice pellets are too heavy to remain in the atmosphere. They fall. The Water Cycle Infiltration: Some precipitation reaches land and seeps into the ground. This is now groundwater. The Water Cycle Runoff: Precipitation that does not infiltrate will drain into creeks, streams, and rivers, which eventually add to the water levels of lakes and oceans. Some runoff will evaporate or infiltrate during its travels. The Water Cycle Evaporation: Solar radiation heats the water on Earth. This causes it to gain energy. This causes it to rise into the atmosphere as vapour. The Water Cycle Transpiration: Plants take in water through their roots and release it through their leaves. It is released into the atmosphere. The Water Cycle Heat Transfers in the Water Cycle: page 21 EXOTHERMIC ENDOTHERMIC