The Earth`s Atmosphere Notes
advertisement

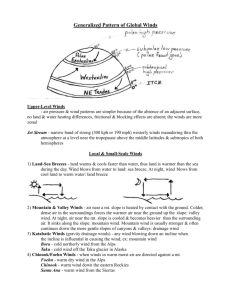
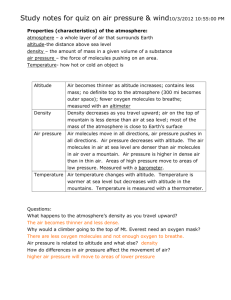
The Earth’s Atmosphere Notes 1. The Atmosphere A thin layer of air that forms a protective covering around the planet Gases found in the atmosphere o Nitrogen – 78% o Oxygen – 21% o 1% - trace amounts of other gases Solids found in the atmosphere o dust o salt o pollen Liquids found in the atmosphere o water o up to 4% water vapor 2. Layers of the Atmosphere Troposphere o Closest layer to Earth’s surface - We live here o All weather occurs here o 99% of the water vapor is found here o 75% of all atmospheric gases are found here o The temperature decreases as you go up in altitude Stratosphere o The ozone layer is found here Protects us from the Sun’s ultraviolet rays o Planes and jets fly here o The temperature increases as you go up in altitude Mesosphere o Scientists know least about this layer o Meteors burn up in this layer because of friction with the air molecules (called “shooting stars”) o Temperatures decrease as you go up in altitude o This is the coldest layer Thermosphere o Thickest layer o Contains the ionosphere A layer of electrically charged particles Allows radio waves to travel across the country Causes the Northern and Southern lights (auroras) o Temperatures increase as you go up in altitude Exosphere o Very few air molecules which have extremely high energy and temperatures o Satellites and space shuttles orbit here o Temperature increases as you go up in altitude 3. Heat Transfer Most of Earth’s energy comes from the Sun heat – energy that flows from an object with a higher temperature to an object with a lower temperature Three types of heat transfer o Radiation – heat transferred through waves or RAYS Earth is heated by radiation Dirt, rocks, water, concrete, sand, etc. absorb this energy Examples Feeling the sun on your face Sunburn Microwaving food Feeling the heat from a fire o Conduction – heat transferred by 2 objects through DIRECT contact (touching) Examples Holding a hot cup of hot chocolate Touching a hot spoon that has been sitting in a bowl of hot soup Cooking food in a frying pan (the pan sits on the burner which is heating up and then the food touches the pan) o Convection – heat transferred through the flow of material (gases and liquids) The heated material rises because it is less dense, it cools, and sinks because the material becomes more dense This is how the atmosphere gets heated Examples Lava lamps Boiling water Convection ovens Heating a room 4. Winds Wind – the movement of air from area of high pressure to an area of low pressure o cold air contracts (particles are close together), have high density, sinks o warm air expands (particles are spread out), have low density, rises Winds are named after the direction they come from Global Winds o Air moves between the equator and the poles o Coriolis Effect – the rotation of Earth causes the global winds to turn o Types of Global Winds Polar Easterlies Located at the south pole and north pole Winds come from the East Prevailing Westerlies Winds come from the West This controls our weather in the United States Trade Winds Winds come from the East Early sailors used these winds to travel from Europe to trade goods Doldrums Located around the equator Very little wind Consistent low pressure o Jet Stream Narrow bands of winds located at the top of the troposphere Winds move west to east Form between cold, dry air and warm, moist air Jets move faster when flying in the Jet Stream Local Winds o Sea Breeze The land heats up faster than the ocean causing the warm air over the land to rise. It cools and sinks over the ocean creating a cool breeze from the ocean. This happens during the day. o Land Breeze The land cools faster than the ocean causing cooler air to sink over the land. The air warm over the ocean rises. This causes a warm breeze from the land. This happens at night. 5. The Water Cycle (a.k.a. Hydrosphere – all water on the Earth and in the atmosphere) Constant cycling of water in the atmosphere Plays an important role in determining weather patterns and climate The Water Cycle o Water evaporates (change of matter from a liquid to a gas) o Plants give off moistures through the surface of their leaves transpiration o Water condenses (change of matter from a gas to a liquid) and makes clouds o The clouds can form precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, or hail) o Precipitation travels across the Earth’s surface as run off or groundwater o The cycle repeats