Atoms Notes Part 1 Models and Parts
advertisement

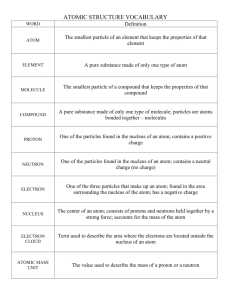
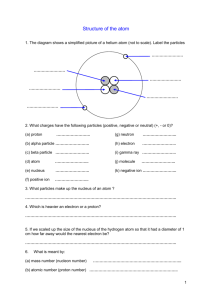
Democritus 1st used the word atom, said they were small hard particles, made of single material, all different shapes/sizes atom smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element Dalton -said all things are made of atoms, which can’t be created or destroyed -atoms of the same element are the same. atoms of different elements are different -atoms can join together to form new substances Thompson Rutherford -discovered particles inside the atom, called the negative ones electrons. -His model is called the plum pudding model. -He used a cathode ray tube and electric charge to see the particles move towards the positive charge -discovered positively charged nucleus. said most of atom is empty space. -shot particles into gold foil. Some of the particles bounced back, some deflected, most went straight through. Bohr -said that electrons move in certain paths or levels. His model is still used today Modern Atomic Theory -electrons are found in electron clouds, regions where electrons are likely to be. The exact location of electrons cannot be found. What are the 3 main parts of the atom? proton- positive, found in nucleus, mass of 1 AMU neutron- no charge, found in nucleus, mass of 1 AMU electron- negative charge, found in cloud around nucleus, no mass Atomic Mass Unit (AMU) Unit of mass for measuring atoms. 1 AMU is equal to the mass of 1 proton or neutron Ion particle that is charged because of an unequal number of protons & neutrons Atomic Number the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotope an atom that has the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes usually have the same properties, some are radioactive. Mass Number the sum of the protons and neutrons. This will always be a whole number atomic mass the average mass of an atom expressed in atomic mass units (AMU). This is usually a decimal b/c it’s an average Describe the 4 forces inside an atom gravitational force- gravity exists between the parts of an atom electromagnetic force- like charges repel, opposite charges attract strong force- the forces that hold the positively charged nucleus together weak force- the force that can change a neutron into a proton or electron.