Experiment 6: EDTA Quant labs/Experiment_6Titration and the
advertisement

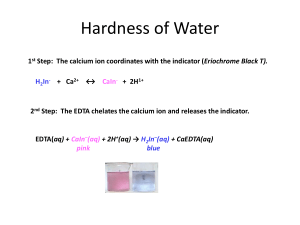
Experiment 6: EDTA Titrations and Hardness of Water John Siller Purpose: The purpose of this experiment was to use better understand EDTA titrations and use that knowledge to determine the hardness of water. It was also important to design a lab that could be repeated by our peers. Procedure 1.) Calibrate a pH meter with buffer solution until the pH of 6M ammonia buffer was confirmed 2.) Add HCl until ammonia buffer reaches a pH of 10 3.) Weigh approximately 0.93g of EDTA, add 4mL of ammonia buffer and place into a 250mL volumetric flask and diluting to get 0.01M EDTA 4.) Prepare a calcium chloride solution by reacting approximately 0.5g of calcium carbonate with 100mL 0.1M HCl 5.) Place 3mL of calcium carbonate in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask then add 5mL of ammonia buffer and some calmagite indicator 6.) Titrate with EDTA solution (3 times) 7.) Place 55mL of tap water into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask then add 3mL of ammonia buffer and calmagite indicator 8.) Titrate with EDTA solution (3 times) 9.) Crush and weigh 1 tablet then place in 100mL volumetric flask 10.) Add 5mL of ammonia buffer and then dilute with 0.1M HCl 11.) Place 5mL of new solution in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask with 2mL ammonia buffer and indicator 12.) Titrate until blue (3 times) Data Mass of CaCO3 = 0.500g Mass of EDTA = 0.9375g Mass of Antacid = 1.7258g Molarity of EDTA Trial EDTA added(mL) Molarity of EDTA(M) 1 16.12 0.0093 2 14.88 0.0101 3 15.1 0.0099 Avg 15.37 0.0098 Tap Water Titration Trial EDTA added(mL) Ca2+ Molarity(M) ppm 1 5.71 0.00102 40.88 2 5.01 0.000893 35.79 3 5.5 0.00098 39.28 Avg 5.41 0.000964 38.64 Antacid Titration Trial EDTA added(mL) % Ca2+ in sample 1 15.9 7.24 2 14.5 6.6 3 14.9 6.8 Avg 15.1 6.9 Calculations Mass of EDTA needed for 0.01 M solution molar mass EDTA disodium 0.010 mol × × 0.25 L = mass of EDTA needed 1 1L 372.24 g 0.010 mol × × 0.25 L = 0.9306 g EDTA needed 1 1L Grams Calcium Carbonate needed for CaCl2 solution Molarity of CaCl2 × mL CaCl2 used × 1 mol CaCO3 molar mass CaCO3 × = Grams Calcium Carbonate 1 mol CaCl2 1 mol CaCO3 0.1 M CaCl2 × 0.100L CaCl2 × 1 mol CaCO3 100.09 CaCO3 × = 1.0 g 1 mol CaCl2 1 mol CaCO3 Molarity of EDTA grams CaCO3 × 1 mol CaCO3 1 mol 1 × × 0.003L CaCl2 × = Molarity EDTA molar mass CaCO3 0.1 L mL of EDTA 0.500 g CaCO3 × 1 mol CaCO3 1 mol 1 × × 0.003L CaCl2 × 100.09 g CaCO3 0.1 L 0.01612mL of EDTA = 0.0093M EDTA Ca2+ concentration in tap water L of EDTA added × Molarity EDTA × 0.00571L × 0.0098M × 1 mol Ca2+ 1 × = Ca2+ Molarity 1 mol EDTA 0.055 L 1 mol Ca2+ 1 × = 0.00102 M 1 mol EDTA 0.055 L Hardness of Water Ca2+ Molarity × grams Ca2+ 1000 mg × = ppm(hardness of water) 1 mol 1g 0.00102 M × 40.078 g Ca2+ 1000 mg × = 40.88 ppm 1 mol 1g Claimed Value of Ca2+ in tablet grams CaCO3 × 1 mol CaCO3 1 mol Ca2+ grams of Ca2+ × × = Ca2+ in tablet molar mass CaCO3 1 mol CaCO3 1 mol Ca2+ 1 mol CaCO3 1 mol Ca2+ 40.078 of Ca2+ 0.500 g CaCO3 × × × = 0.2002 g of Ca2+ 100.09 CaCO3 1 mol CaCO3 1 mol Ca2+ grams Ca2+ × 100% = Amount of Ca2+ in tablet total mass of tablet 0.2002 g Ca2+ × 100% = 11.6% Ca2+ in tablet 1.7258 g Amount of 𝐂𝐚𝟐+ in sample L of EDTA added × Molarity of EDTA × 0.0159 L × 0.0098 M × 1 mol Ca2+ molar mass Ca2+ 20 parts × × = grams Ca2+ 1 mol EDTA 1 mol Ca2+ solution 1 mol Ca2+ 40.078 Ca2+ 20 parts × × = 0.1249 grams Ca2+ 1 mol EDTA 1 mol Ca2+ solution grams Ca2+ × 100% = Amount of Ca2+ in sample total mass of tablet 0.1249 g Ca2+ × 100% = 7.237% Ca2+ in sample 1.7258 g Conclusion: This lab was designed to determine the hardness of water, in other words the Ca2+ concentration. This was done to a water sample and an unknown sample. For the unknown sample it was found that it contained 7.237% Ca2+. The reported value was 11.6% so there must have been some experimental error that resulted in loss of product. Overall however the values are not significantly different enough to show a flaw in the procedure.