Properties of Metals
advertisement

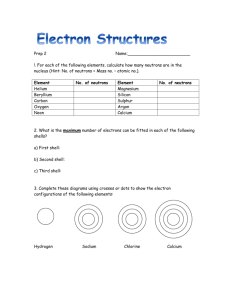
Properties of Metals, Non-Metals and Metalloids Metals – Solid at room temperature, except for mercury (a liquid). - Elements that have a high luster when clean. - Ductile (can be drawn into wires). - Malleable (can be beaten into shapes). - Left side of the periodic table. - Good conductors of heat and electricity. - Most elements are metals. Non-metals – Some gases at room temperature, some solids, one liquid (bromine). - Not very shiny. - Poor conductors of electricity. - Not ductile. - Brittle, not malleable. - Right side of the periodic table. Metalloids – Have some properties of metals and some of non-metals. (e.g. sillicon conducts electricity but isn’t lustrous). - Solids at room temperature. - Can be shiny or dull. - May conduct electricity. - Poor conductors of heat. - Brittle. - Not ductile. Bohr Models Electrons move rapidly around the nucleus in regions called shells. The atoms of different elements have different numbers of electrons. Each shell can accomidate a certain number of electrons but no more. This theory was discovered by Neils Bohr, we call electron shell diagrams Bohr models. Bohr models follow the following rules - the first shell can hold 2 electrons, the second can hold 8, the third can hold 8. After period three, the elements follow a different path. You will learn more about this in Chemistry 11. For Science 10, you are responsible for the Bohr model for the first 20 elements. Lewis Symbols In any group, all the elements have atoms with the same number of valence electrons. You can use Lewis Symbolds, to represent an atom and its valence electrons. An electron dot diagram uses the symbol of the element to replace the nucleus and inner shell electrons. The electrons in the valence shell are shown as dots placed around the symbol. Lewis symbols are a valuable tool for describing, predicting and explaining compound formations. Bonding Both Bohr models and Lewis symbols are useful in predicting chemical reactivity because they show the number of electrons in the valence shel of atoms. Knowing the valence shell structure is important in determining the chemical properties of compounds. Remember that elements in the same group, have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. Knowing the number of outer shell electrons helps you to predict the formation of compounds, name the compounds, and write their chemical formulas. A chemical bond forms between two atoms when electrons in the outer shell of each atom form a stable arrangement together. The outer shell is called the valence shell, and the electrons that form chemical bonds between two or more elements are called valence electrons. The chemical properties of elements are related to the energy changes that take place when their atoms lose, gain, or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell containing 8 electrons. Metals tend to lose their valence electrons relatively easily. The alkali metal family each have one electron in their valence shell. If the electron is moved, a particle with a single positive charge is formed. Positively Charged : Cations Any atom or group of atoms that carries an electrical charge is an ion. When a neutral atom gives up an electron, the positively charged ion that results is called a cation (pronounced “cat-eye-on”). Negatively Charged : Anions Ions can be negatively charged, as well. Since non-metals have greater numbers of valence shell electrons, they must gain electrons to fill their valence shells. Group 17 elements, the halogens, must gain one electron to obtain a nobel gas arrangement and follow the octet rule (8 electrons). When an element gains an electron, its atoms become negatively charged particles called anions (pronounced “aneye-ons”). Cations are positive and Anions are negative Forming Compounds An atom may acquire a valence shell like that of its closest noble gas in one of three ways: 1. An atom may give up electrons – forming a positive charge -- a cation. 2. An atom may gain electrons – forming a negative charge -- an anion. 3. An atom may share electrons – two atoms may share one pair of electrons, two pairs or three pairs. The bonds that are formed when atoms share electrons are single, double and triple bonds. Substances that are composted of cations and anions are called ionic compounds. The attraction between oppositely charged ions is called an ionic bond. A metal cation has the same number of electrons as an atom of the closest nobel gas with a lower atomic number. For example, neon is the closest noble gas in the periodic table to sodium, magnesium, and aluminum. The cations Na+, Mg2+, and Al3+ Atoms that share a pair of electrons are joined by covalent bonds. A neutral particle that is composed of atoms joined by covalent bonds is called a molecule. Ionic Bonding Activity – Due TOMORROW! 1a ) Draw a Bohr model of a sodium atom and a chlorine atom side by side. b) Label the atoms with their symbols below. 2. Draw the Lewis symbol for each atom in 1a. 3. Make a chart to show the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for each atom. Use a ruler. 4. What is the charge on sodium and chlorine? How did you discover this? 5. The sodium atom and the chlorine atom are not chemically alike. a) What is one physical feature which indicates chemical stability? b) How might a sodium atom gain chemical stability? How might a chlorine atom gain chemical stability? 6a) If a sodium atom looses one valence electron, what charge will the isotope have? Explain how you arrived at your answer using a complete sentence. 6b) The particle formed is called a positive ion or a cation. It is represented by the symbol and a raised + sign called a superscript. Write down the proper symbol for the sodium ion. 7a) If a chloring atom gains one valence electron, what charge will the particle have? b) Explain how you arrived at your answer. c) The particle formed is called a negative ion or anion. It is represented by the symbol and a raised – sign, called a superscript. Write down the proper symbol for the chloride ion. Not the change in the spelling of this negative ion! d) How did the spelling of the cation differ from the spelling of the anion? 8a) If a sodium atom is close to a chlorine atom, where do you think the chlorine atom will get one electron it needs for chemical stability? 8b) On the Bohr model draw an arrow from one valence electron on the sodium paricle moving to the outer most energy level (shell) of the chlorine particle. 9a) The particles formed are called ions and they have opposite charges. What happens to oppositely charged particles? b) Give an example of something that behaves in a similar way. 10. The sodium cation is now bonded to the chloride anion. Write a definition for an ionin bond and use this example in your description. 11a) What is the name of the compound formed by this ionic bond? b) When two atoms bond they have formed a compound. The compound is represented by writing the symbol of the elements involved close together. The symbols written in this fashion are called formulas. What is the formula for the compound formed from the bonding of sodium and chlorine? 12a) Repeat questions 1 to 8 and 11 for the elements Mg and O. b) Repeat the questions 1 to 8 and 11 for the elements Al and P.