Domain - Images

Classification & Taxonomy
What does it mean to classify?
• Classification is when you put objects or things into groups, based on their traits/characteristics, in order to make them easier to find and understand.
Why do we group things?
What are some other examples of classification you can think of?
Biology reasons to classify:
• 1.8 million named species in the world today
• Grouping living organisms means we can learn more about them as a group
• So that we can talk about the same living thing with other people and scientists.
Ex. Cougar / Mountain Lion
On the next slide I want you to find all of the plants
How could we have made that task easier?
Now find all of the plants on the next slide.
Activity
• Using a pair of scissors and the handout sheet, I want you to:
Divide up the organisms into 4-6 groups. Based on some logic.
On your left hand page record your grouping criteria.
Switch notebooks with another pair and categorize your pictures based on their criteria.
Taxonomy and Taxons
• Taxonomy is basically the science of putting living things into groups.
Taxons are the groups we put them into
All Living things.
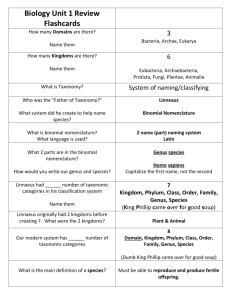
• In order to help us understand all 1.8 million organisms scientists divided them up, based on similarities, into 3 gigantic groups.
• Domain – This is the absolute largest division of living things. All living things can be put into 1 of the 3 Domains.
3 Domains
1. Eukarya – This is the domain for all living things with eukaryotic cells, such as animals, including humans, plants, fungi and protists.
3 Domains
2. Archaea – This domain contains the extreme bacteria. These are bacteria that can live in boiling water, or acid lakes. Some even live in your intestines
(but not many).
3 Domains
3. Bacteria – This domain contains all of the rest of the bacteria, like E. coli ,
Strep , Staph , etc.
Inside the 3 Domains
• Inside each of the Domains there are 1 to 4
Kingdoms.
Domain
• For Example:
Eukarya
Kingdoms Animalia Plantae Fungi Protista
Inside each of the kingdoms there are further subdivisions and so on until you get to a single species.
The Taxons and Taxonomy
Domain
There is only one kind of thing at this taxon.
Kingdoms
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Activity
• Copy the information from page 459 onto your domains and kingdoms chart.
• Cut out the chart and glue it into your notebook.
Classification
• What is classification?
It is when you put things into groups based on certain characteristics.
Understanding Check: Taxonomy
• What is the largest taxon?
Domain
• What is the smallest taxon?
Species
Understanding Check: Taxonomy
• How many types of organisms can be found in the taxon species?
One
Understanding check: Kingdoms
Understanding check: Kingdoms
The Eight Taxons
Domain -----------------------------------------------
Largest
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species ------Smallest
Remembering the Eight taxons
• “Dear King Phillip Called Out For Good S oup”
• Domain
• Kingdom
• Phylum
• Class
• Order
• Family
• Genus
• Species
Practice
• What are the taxons from largest to smallest?
• Domain
• Kingdom
• Phylum
• Class
• Order
• Family
• Genus
• Species
Binomial Nomenclature
• Binomial = “Two Name”
• Nomenclature = “Naming System”
• Uses Genus and Species
Examples:
• Homo sapiens = Humans
• Felis concolor = Mountain Lion
Binomial Nomenclature Cont’
• Ursus arctos = Grizzly Bear
• Ursus sort of like its last name
• arctos - sort of like its first name
• Which of the following organisms are most closely related?
Picea abies
Pinus sylvestris
Picea glauca
Thuja plicata
• Which of the following organisms are most closely related?
Rana temporaria
Codium fragile
Bryopsis plumosa
Rana malculosa
Cladogram
• A cladogram shows how closely related several species are.
• For Example - See .pdf of page 452
Example: Which two are most closely
Related?
Frog
Turtle Rabbit Cow
Root
Branching
Point
Assignment
• Work with the person next to you and try to make a cladogram using the information and instructions on page 453
(Quick Lab)
Use a separate piece of paper and turn it in when finished.