Net Ionic Practice #1
advertisement

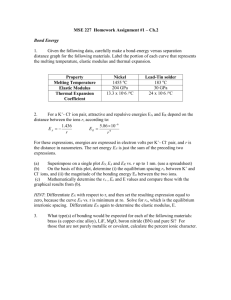
Net Ionic Reactions – Practice #1 This was excellent! You did make some mistakes (see below), but that is expected for the first one. Often I see mistakes on every single problem. So, pat yourself on the back!! FYI - This one is not graded for correctness, but will be in the future. Here is where you went wrong, followed by the correct answer. 1. Silver bromide is insoluble (see the solubility rules), so it remains as a unit (no ions). Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq) --> AgBr(s) 2. Copper II chloride is insoluble, so don’t write it as ions. 2 PO43-(aq) + 3 Cu2+(aq) --> Cu3(PO4)2(s) 3. Pb2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) --> PbSO4(s) 4. Phosphoric acid is formed as a product. It is not a strong acid (memorize the list of 7 strong acids) so it does not ionize. And, aluminum phosphate is a solid here. It can dissovle, but isn't yet. So, write it as the whole compound. 3 H+(aq) + AlPO4(s) --> Al3+(aq) + H3PO4(aq) 5. What you wrote is the correct start. But, carbonic acid is known to decompose into water and carbon dioxide. This is one to memorize. It shows up a lot! CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) --> H2O + CO2 6. Acetic acid is a weak acid (so no ions). Remember that carbonic acid forms water and carbon dioxide. Barium carbonate is listed as a solid in the problem. So, don’t write it as ions. BaCO3(s) + 2 HC2H3O2(aq) --> Ba2+(aq) + 2 C2H3O2-(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) 7. Water is a molecule (even though it is formed from ions). So, it is not written as ions. Mg(OH)2 starts off as a solid, so no ions. Mg(OH)2 + 2 H+ -> Mg+2 + 2 H2O 8. Metal oxides plus water form bases. Li2O + H2O -> 2 Li+ + 2 OH9. Sr+2 + CO3 -2 --> SrCO3 10. H+ + OH- -> H2O Write the following for each reaction: i) Molecular equation ii) Ionic equation iii) Net ionic equation 4. Since AlPO3 begins as a solid, you don’t write it as ions. All solids stay together unless and until they are dissolved! 1. Solutions of silver nitrate and potassium bromide are mixed. Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq) --> AgBr(s) 1. Silver bromide is insoluble (see the solubility rules), so it remains as a unit (no ions). Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq) → AgBr(s) 2. Solutions of potassium phosphate and copper II chloride are mixed. 2. 2 PO43-(aq) + 3 Cu2+(aq) → Cu3(PO4)2(s) Copper II chloride is insoluble, so don’t write it as ions. 3. Solutions of lead nitrate and magnesium sulfate are mixed. 3. Pb2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s) 4. Solid aluminum phosphate is added to excess nitric adic. Phosphoric acid is formed as a product. It is not a strong acid (memorize the list of 7 strong acids) so it does not ionize. 4. 3 H+(aq) + AlPO4(s) → Al3+(aq) + H3PO4(aq) 5. A solution of potassium carbonate is added to nitric acid. CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) H2CO3 5. What you wrote is the correct start. But, carbonic acid is known to decompose into water and carbon dioxide. This is one to memorize. It shows up a lot! CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) → H2O + CO2 6. Solid barium carbonate is added to excess acetic acid. Also, when you split up barium acetate into ions the acetate ion should remain intact. 6. Acetic acid is a weak acid (so no ions). Remember that carbonic acid forms water and carbon dioxide. Barium carbonate is listed as a solid in the problem. So, don’t write it as ions. BaCO3(s) + 2 HC2H3O2(aq) → Ba2+(aq) + 2 C2H3O2-(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) 7. Solid magnesium hydroxide is added to a solution of hydrobromic acid. 7. Mg(OH)2 + 2 H+ → Mg+2 + 2 H2O Water is a molecule (even though it is formed from ions). So, it is not written as ions. 8. Solid lithium oxide is added to distilled water. (i) 8. Metal oxides plus water form bases. Li2O + H2O → 2 Li+ + 2 OH9. A 100 mL sample of 1 M strontium chloride solution is mixed with a 100 mL sample of 1 M sodium carbonate solution, resulting in the formation of a precipitate. (i) 9. Sr+2 + CO3 -2 → SrCO3 10. A 0.2 M potassium hydroxide solution is titrated with a 0.1 M nitric acid solution. H3O+ + OH- -> 2 H2O 10. H+ + OH- → H2O This was excellent! You did make some mistakes (see below), but that is expected for the first one. Often I see mistakes on every single problem. So, pat yourself on the back!! FYI - This one is not graded for correctness, but will be in the future. FYI - I didn't grade this one for correctness, but will in the future. 1. Silver bromide is insoluble (see the solubility rules), so it remains as a unit (no ions). Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq) --> AgBr(s) 2. Copper II chloride is insoluble, so don’t write it as ions. 2 PO43-(aq) + 3 Cu2+(aq) --> Cu3(PO4)2(s) 3. Lead sulfate is insoluble, so don’t write it as ions. Pb2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) --> PbSO4(s) 4. Phosphoric acid is formed as a product. It is not a strong acid (memorize the list of 7 strong acids) so it does not ionize. 3 H+(aq) + AlPO4(s) --> Al3+(aq) + H3PO4(aq 5. Carbonic acid is known to decompose into water and carbon dioxide. CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) --> H2O + CO2 6. Acetic acid is a weak acid (so no ions). Remember that carbonic acid forms water and carbon dioxide. Barium carbonate is listed as a solid in the problem. So, don’t write it as ions. BaCO3(s) + 2 HC2H3O2(aq) --> Ba2+(aq) + 2 C2H3O2-(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) 7. Water is a molecule (even though it is formed from ions). So, it is not written as ions. Mg(OH)2 + 2 H+ -> Mg+2 + 2 H2O 8. Metal oxides plus water form bases. Li2O + H2O -> 2 Li+ + 2 OH9. Sr+2 + CO3 -2 --> SrCO3 10. H3O+ + OH- -> 2 H2O H+ + OH- -> H2O