HPLC/LCMS
advertisement

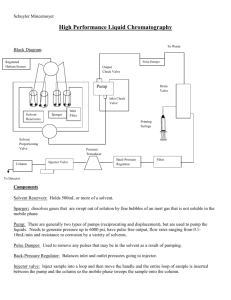
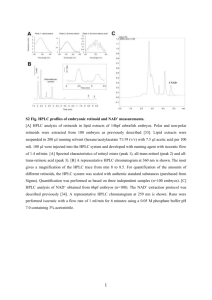
LC-MS and HPLC Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to learn the basic functions of the HPLC, and the LC-MS and to understand the separation techniques. Unknown and known samples will be tested with both instruments. Introduction: The HPLC is known as high performance liquid chromatography, this is commonly used to water-based sample. A liquid mobile phase and a solid or liquid mobile phase are utilized. The instrument consists of a solvent pump, helium source, pump, pulse damper, drain valve, pressure regular and an injector chamber and column. The LC-MS is similar to the HPLC in parts however it uses a mass spectrometer as the detector, which provides qualitative and quantitative data. Such as molar mass and information about the compounds structure. Procedure: LC-MS 1. Prepare the samples by weighing out a range of concentrations in ppm of caffeine 2. Once standards are created in a range fill the small vials up the 1.5 mL mark 3. Make sure all sections of the instrument are on 4. Turn the nitrogen gas on in the gas room to the about 40psi 5. Open the nitrogen on the bench top 6. On the desktop click the Analyst Software icon 7. In the vertical menu, click on the hardware configuration then LC-MS then activate profile 8. In the vertical menu now click Build Acquisition Batch. In the window that appears fill in the set name (file name) 9. Select the method “caffeine10” 10. Click add set then add sample the bottom of the window you select the number of your samples 11. Under Vial position enter the numbers where the vials reside in the LC tray 12. Click on the submit tab then submit then view select “sample queue” then acquire then ready then acquire then start 13. After a graph appears right click on the graph and click List Data 14. In the new window click on the peak list tab this is where needed data is recorded 15. Print data 16. In the vertical menu, click on hardware configuration 17. The window from the startup will appear, click on LC-MS once more and then click on deactivate profile this will shut down the instrument 18. Shut the nitrogen gas off at the desk and in the gas room HPLC 1. Make sure to degas the methanol and water 2. Turn on the computer 3. Check the pump lines A and B for gas bubbles 4. If there are bubbles execute the purge with the pump 5. Purge the lines by opening the valve and hitting the purge button 6. Close the valve and hit the purge button again 7. Turn the pump back on 8. Turn on detector 9. Select method and run all the parameters 10. Run the standards and the unknowns Data: HPLC: The HPLC was down during our lab time LC-MS: The data is inconclusive and no calibration curve can be drawn because of problems with the MS detector during our lab time. However chromatograms are in lab notebook. Conclusion: The HPLC was down during our lab thus we don’t have any data or experience on it. However it is fixed and running now. So when I get a chance I plan on investigating the operation of the HPLC by using the SOP and background information. The LC-MS was easy to use in that setting up sample vials and running the program were straightforward. However there was a problem with the MS and its ability to detect the caffeine therefore our results had no identifiable use. After the LCMS I wish to try to run samples on it again to see if we get better results.