unit 1.4 revision questions_katie
advertisement

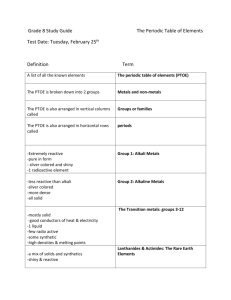
Topic: Metals, Non-Metals & Metalloids
Date: 19.10.12
1.4
1What do these words mean?
a lustrous= shine when polished and or freshly cut.
b malleable= when metals can be hammered into shapes
c ductile= they can be stretched and put into thin long wires.
2List two important metals and what they are used for.
Iron =main component of steel, and its uses include ship hulls, saucepans, car
bodies and body piercing.
Copper=Copper is used for electrical wiring and plumbing pipes.
3 Why do many metals sink in water?
Metals usually have high densities. Many metals sink in water.
4Do metal atoms form molecules or lattices?
Are generally found in nature combined with non-metals as an ionic lattice
(except the native metals).
5 What does brittle mean?
Brittle generally means ‘easily broken’
6 Draw an example of a molecule that has:
A two atoms
b four atoms
c eight atoms
Eight
Four
Two
Second option for molecule with two(2) atoms
7 Explain why most non-metals are a liquid or gas at normal room
temperatures.
This is because non-metals generally have relatively low melting and boiling
points, usually so low that they are liquids or gases at normal room
temperatures. * The way diamonds react differ*
8What is electro negativity?
The electron-attracting power of an atom is called its electro negativity.
9Which has a higher electro negativity: a metal or a non-metal?
A non metal because they are ionic & covalent. METALS don’t share
remember.
10Explain how a chemical reaction can be thought of as a robbery.
I think this is because you can use the reactions of metals and create an
explosion. For example when protons and neutrons are contributing
something to a chemical reaction they create a nuclear reaction.
11What ions can a hydrogen atom form?
Positive and or negative (ion H+)
12 Explain why H could be placed:
a
in Group I = because it is regularly stable
b in Group VII =Group VII element, depending on what it comes into
contact with.
c
by itself= because it only has 1 electron thus the electronic configuration
is k;1
13 Helium could be placed in Group II. Why?
It could be placed in Group II but is placed in Group VIII because of similar
properties to noble gases.
14 Why is helium normally placed in Group VIII?
This is because it has similar properties to inert gases.
15 List the symbols of the metalloids.
B=boron
Si=silicon
Ge= germanium
As=arsenic
Sb=antimony
Te=tellurium
Po=polonium
16 What is special about the metalloids?
They are all in a diagonal in the periodic table. The metalloids (sometimes
called semi-metals) act like non-metals in most ways. They do, however, have
some properties that are metallic: most importantly, they can conduct
electricity.
17 Separate these properties into those that belong to metals and those that
belong to non-metals:
ductile, normally gas or liquid, dense, malleable, brittle, lustrous, excellent
conductors, dull, poor conductors, normally solid at room temperature
NON –METALS= poor conductors ,brittle , dull , liquid or gas
METALS= Malleable , lustrous, excellent conductors,
METALLOIDS= N/A
18 List three non-metallic elements that:
a are gases at room temperatures= diamond
b are in Group V = Hydrogen , Carbon , Nitrogen , Oxygen , Phosphorus ,
Sulfur & Selenium
c
are in Period 2= Carbon- Neon
d would be related to chlorine= ?
e would have larger atoms than those of oxygen= Neon
19 What are the likely charges of the ions that belong in Groups I, II, III, IV, V,
VI, VII and VIII?
Mainly negatively charged.
20 What ions would these atoms form?
a Na= -2 electrons
b S= - 2 electrons { positive 6}
c I= (1+) positive 1
d P= (cation K+1) positive
e Al= -5
21 What metal/s:
a
b
c
d
is the only metal that is a liquid at 25°C= mercury (Hg)
are in Period 3? = Sodium to Aluminum
are in Group IV?= Potassium & Calcium
would form +2 ions?= Magnesium & Calcium
22 At normal room temperatures how many non-metals exist as:
a solids? = Mercury
b liquids? = Bromine
C gases? = Nitrogen , Oxygen and Chlorine