CP NT Ch 8 & 9—Covalent Compounds Why do atoms bond
advertisement

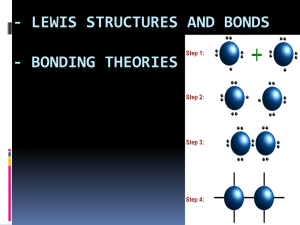
CP NT Ch 8 & 9—Covalent Compounds Why do atoms bond? Atoms want ______________—to achieve a noble gas configuration (__________) For _______________ bonds there is a _________________ of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent bonds there is a _______________ of electrons to get an octet What is a covalent bond? Covalent bond—the chemical bond that results from sharing of _______________ electrons — Occurs with elements _______________to each other on the periodic table — Between a nonmetal and a nonmetal — Molecule is two or more atoms are bonded _______________ Examples of Molecules F2 H2O NH3 (_______________) CH4 (_______________) Notice there are no _______________, only non-metals Diatomic molecules Some atoms do not exist as a _______________atom Atoms that exist as two: H2, O2, N2, Cl2, Br2, I2, F2 HONClBrIF Magnificent _____-don’t forget H 3 Types of Covalent Bonds: Single, double, triple Strength of Covalent Bond Several factors control bond strength o _______________ of shared electrons—the __________ electrons shared, the shorter the bond, and the greater the bond strength o _______________ of the atoms Single Covalent Bonds Each atom shares one _______________ (___________) of electrons _______________ bond _________________ bond of the three Double Covalent Bonds Each atom shares _______ pairs (___________) of electrons ________________ length bond ________________ strength bond Triple Covalent Bond Each atom shares _____________ pairs (___________) of electrons ______________ bond _______________ bond Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur can form double and _______________covalent bonds Covalent Molecule Properties Tend to be _______________solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature __________ melting and boiling points __________ conductors of heat and electricity Non-electrolytes – do not conduct electricity in water 1 Naming Binary Molecular Compounds 3 Rules to Name 1. Name the first element using the _______________name 2. Second element in the formula- use the root word and __________ in –ide ex: Oxygen Oxide Sulfur Sulfide Hydrogen _______________ 3. Add a prefix to ___________ words to indicate the _______________of atoms 1. mono- 6. hexa- 2. di- 7. hepta- 3. tri- 8. octa- 4. tetra- 9. nona- 5. penta- 10. deca- Exceptions to the Rules 1. When the formula contains one atom of the _______________element, omit (leave out) mono ex: CO2 ______________ ________________, not Monocarbon Dioxide 2. Drop the final letter in the prefix if the element begins with a _______________ - For prefixes 1 & 4-9 ex: CO ______________ __________________, not Carbon monooxide Example 1 S4N2 _______________ _______________ Example 2 SO3 _______________ _______________ Example 3 P4S5 _______________ _______________ Example 4 CO _______________ _______________ Example 5 NH3 _______________ _______________ common name: _______________ Example 6 CH4 _______________ _______________ Example 7 As2O3 _______________ _______________ Example 8 N2O5 _______________ _______________ Example 9 P4O10 _______________ _______________ common name: _______________ Lewis Structures 5 rules for Lewis Structures 1. Find the total # of _______________electrons for the molecule 2. Find the center atom (the element with the _______________ # of atoms) 3. Draw bonds. Connect the other atoms to the center atom. Then subtract ____ electrons from the total # of valence electrons for each bond drawn. 2 4. Distribute electrons around each atom to give a total of ____ electrons except H, Al, B, & Be 5. If there are not enough _______________to give 8 around each atom, create _______________& triple bonds. Example 1: CF4 Example 2: NH3 Example 3: H2S Ions: With Ions we add or take away _______________ . Put ions in _________________ and the charge on the outside Example 4: NH4+ Double Bonds Example 5: CO2 Triple Bond Example 6: CO Incomplete Octet Example 7: BCl3 Boron does not have 8e- around it. It is _______________but it is okay; it is one of our exceptions. 3 NT: VSEPR- V_________________ S__________ E__________________ P_________ R____________________ Lewis Structures are _________________, whereas VSEPR Molecules are _________________ VSEPR predicts the _________________ or “_________________” of the molecule ________ pairs of electrons influence the shape by pushing other atoms as far apart from each other as possible Molecular Shape Molecule Lewis Structure Number of (shared) bonding pairs of electrons Number of lone pairs of electrons Total Number of electron pairs Molecular Shapes (look at lone & bond pairs) H2 Linear CO2 Linear BH3 Trigonal planar SiF4 Tetrahedral PH3 Trigonal Pyrimidal SCl2 Bent 4 Ball and Stick Model Bond Angle Electronegativity and Polarity Electronegativity Relative ability of an atom to _______________electrons in a chemical bond _______________has the highest e.n. value. Trend: ______________ across (left to right) a period and _______________ down a group Types of Covalent bonds Non-polar covalent— _______________sharing of electrons Polar covalent—unequal _______________of electrons Non-polar covalent Sharing of electrons _______________ Usually occurs when two _______________atoms are bonded together. Examples: H2, O2, N2, Cl2, Br2, I2, F2 Polar covalent _______________ sharing of electrons unequal sharing caused by 2 elements with different ____________________ (different abilities to attract electrons) The bond is called a dipole (two poles) Creates a molecule with _____________ charges Partial charges symbolized by (delta) + and - The _______________electronegative atom is located at the partially negative end Example: + ⟼ H—Cl or H—Cl Polar molecule or not? The _______________ of a molecule usually tells if a molecule is polar or not If the VSEPR shape is _______________it is usually non-polar If the molecule is asymmetric it is _______________ 5 Name Polar example VSEPR Model Non-polar example VSEPR Model Linear HCl CO2 Trigonal planar CH2O AlH3 Tetrahedral CH3OH CH4 Trigonal pyramidal NH3 N/A N/A H2O N/A N/A (Always polar) Bent (Always polar) Intermolecular Forces The force that exists between ________________ molecules This force attracts molecules to each other 3 Types — Dispersion force or induced dipole moment between molecules; only force in ___________ molecules; _____________ force (caused by the motion of electrons) (Ex: CH4) — Dipole-dipole the force between two _____________ molecules; ______________ force (Ex: HCl) — Hydrogen bond forms between the hydrogen end of one dipole and fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen (that have at least one lone pair) end of another dipole; _______________force (Ex: H2O) _______ molecules have dispersion forces All ____________ molecules have dipole-dipole forces and dispersion forces Molecules that hydrogen bond have all 3 Solubility of polar molecules _______________ are due to intermolecular forces Like dissolves like — Polar substances will dissolve _______________molecules (and ionic compounds) — ___________________ substances will dissolve non-polar molecules 6



![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)