Atomic Origins Unit Plan | 30.4KB
advertisement
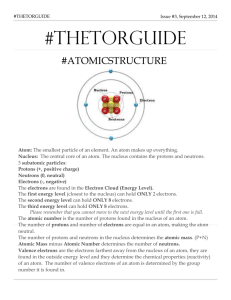
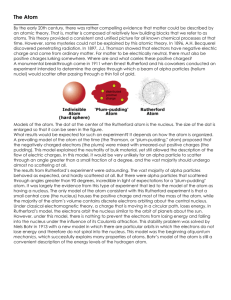
Unit Lesson Plan – Atomic Origins Teacher: Click here to enter text. Time Frame: 10 Grade: Subject: 16 days School: PSI Chemistry Next Generation Science Standard(s) AP Essential Knowledge HS-PS1-8 Develop models to illustrate the changes in the composition of the nucleus of the atom and the energy released during the processes of fission, fusion, and radioactive decay. EK 1.B.1 The atom is composed of negatively charged electrons, which can leave the atom, and a positively charged nucleus that is made of protons and neutrons. The attraction of the electrons to the nucleus is the basis of the structure of the atom. Coulomb’s law is qualitatively useful for understanding the structure of the atom. EK 1.D.2 An early model of the atom stated that all atoms of an element are identical. Mass spectrometry data demonstrate evidence that contradicts this early model. Essential Questions (What questions will the student be able to answer as a result of the instruction?) 1. Where did matter come from? Knowledge & Skills (What skills are needed to achieve the desired results?) By the end of this unit, students will know: By the end of this unit, students will be able to: Each atom has a charged substructure consisting of a nucleus, surrounded by electrons. Nuclear processes, including fusion, fission, and radioactive decays of unstable nuclei, involve release or absorption of energy. The total number of neutrons plus protons does not change in any nuclear process. Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the relationships between systems or between components of a system. Assessment (What is acceptable evidence to show desired results (rubrics, exam, etc.)? After a brief lesson using the SMART Board to introduce concepts, students will be questioned on these concepts using the SMART Response system. The teacher will demonstrate the problem solving skills needed for the topic and again, students will be questioned using the SMART Response system. Students will convene in small groups to complete problems. Then some students may volunteer to write their solutions on the board and explain their problem solving process. www.njctl.org Chemistry Atomic Origins (What is the sequence of activities, learning experiences, etc, that will lead to desired results (the plan)? Topic Presentation CW/HW 1 The Big Bang Slides 4-26 Practice Questions 1-5 Syllabi, Lab Safety Contract Practice Questions 6-10 2 Lab Safety Lab Safety Presentation Lab Safety Quiz 3 Chemical Reactions Lab Lab Lab Analysis 4 Electrons & Protons Slides 27-46 Practice Questions 11-15 Practice Questions 16-20 5 The Nucleus – Nucleus & Neutrons Slides 47-71 Practice Questions 21-25 Practice Questions 36-41 6 The Nucleus Nomenclature Slides 72-81 Practice Questions 26-35 Practice Questions 42-50 7 Formation of Elements – Binding Energy Quiz Slides 82-92 Practice Questions 51-53 Practice Questions 62-64 8 Formation of Elements – Fusion/Fission Slides 93-112 Practice Questions 54-61 Practice Questions 65-72 9 Isotopes – Atomic Symbols Quiz Slides 113-119 Practice Question 73-76 Practice Questions 81-86 10 Atomic Masses Activity Activity Activity Analysis Day www.njctl.org Chemistry Atomic Origins 11 Isotopes – Atomic Mass Slides 120-127 Practice Questions 77-80 Practice Questions 87-90 12 Radioactive Decay Slides 128-139 Practice Questions 91-95 Practice Questions 96-100 13 Half-Life Slides 140-145 Practice Questions 101105 Practice Questions 106110 14 Review Quiz Multiple Choice Review MC/FR Review Questions 15 Review Free Response Review MC/FR Review Questions 16 Test Unit Test www.njctl.org Chemistry Atomic Origins