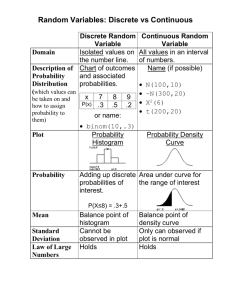
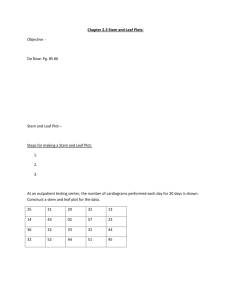
Data Analysis Project Rubric
advertisement

Name ___________________________________ Data Analysis Project Rubric Unsatisfactory (0 points) No survey Needs Improvement (1 point) Survey is of less than 20 people Satisfactory (2 points) Survey is of 20-29 people Exemplary (3 points) Survey is of 30 or more people Neither is recorded Circle Graph is done without a data statement Circle Graph is done with an incorrect data statement Circle Graph is done and a correct data statement is given Neither is recorded Histogram is done without a data statement Histogram is done with an incorrect data statement Histogram is done and a correct data statement is given Neither is recorded Stem and Leaf Plot is done without a data statement Stem and Leaf Plot is done with an incorrect data statement Stem and Leaf Plot is done and a correct data statement is given Neither is recorded Box and Whisker Plot is done without a data statement Box and Whisker Plot is done with an incorrect data statement Box and Whisker Plot is done and a correct data statement is given Individual Analysis No Individual Analysis Done 1-2 valid sentences about the individual data 3-4 valid sentences about the individual data 5 or more valid sentences about the individual data Group Analysis No Group Analysis Done 1 valid sentence about the group data 2 valid sentences about the group data 3 or more valid sentences about the group data Organizer Completed No information is in the organizer Some information is in the organizer Most information is in the organizer All information is in the organizer Name on Project No name on project Survey Complete Circle Graph and Data Statement Histogram and Data Statement Stem and Leaf Plot and Data Statement Box and Whisker Plot and Data Statement Name on Project Total Points: / 25 7.DSP.1: Understand that statistics can be used to gain information about a population by examining a sample of the population and generalizations about a population from a sample are valid only if the sample is representative of that population. Understand that random sampling tends to produce representative samples and support valid inferences. 7.DSP.2: Use data from a random sample to draw inferences about a population. Generate multiple samples (or simulated samples) of the same size to gauge the variation in estimates or predictions. 7.DSP.3: Find, use, and interpret measures of center (mean and median) and measures of spread (range, interquartile range, and mean absolute deviation) for numerical data from random samples to draw comparative inferences about two populations. 7.DSP.4: Make observations about the degree of visual overlap of two numerical data distributions represented in line plots or box plots. Describe how data, particularly outliers, added to a data set may affect the mean and/or median.