How to Write a Graph Using Excel
advertisement

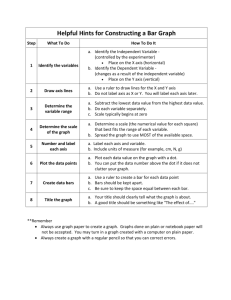
HOW TO WRITE A GRAPH USING EXCEL A graph is a picture that depicts data that have been listed in a table (refer to “What is a Table”). Because it is a picture, the graph allows us to interpret the data more easily than we might do if we were to try to read the table, especially if the table contains pages of data. In Science, we follow precise rules when we write a graph. Luckily, you no longer have to write a graph with paper and pencil, a long and tedious process; instead, you get to use an Excel spreadsheet and let the laptop do your work for you. Instead of spending five days learning how to write a graph by hand, you will only need about one class period! Directions: 1. To make the graph: a. Highlight all parts of the table EXCEPT the title. Do not highlight any empty columns. Chart Wizard b. SELECTING A LINE GRAPH: Select the following in the order presented. CHART WIZARD (it looks like a stack of books) STANDARD TYPES - LINE (Select the line graph with data points displayed at each data value. It is the graph on the left of the middle row. In this VII Science, we only make line graphs). NEXT (As an alternative, you can double click on the image) c. DELETING THE UNWANTED LINE: Open the SERIES tab. You need to remove all data lines except the ones you need. For now, you can ask your teacher if you need to remove a variable and which one to remove. Later, you will learn which curve needs to be deleted. In this case, remove Time. In the dialogue box, highlight the line you wish to remove from the Series table and then click REMOVE. d. CORRECTING THE X-AXIS At the bottom of the SERIES dialogue box, you will find Category (X) axis labels. Click the icon to the right of the entry box by this label. In the table, highlight cells A3 through A9. Do not highlight the heading. Next, click the icon to the right of the Chart Wizard – Step 2 of 4 – Chart Source Data box. You just told Chart Wizard what numbers to place on the X-axis. You may not have to do this each time you write a graph. Check to be sure the correct values appear on the X-axis. If they do, you may skip this step. Click NEXT. e. WRITING THE CHART TITLE AND AXES LABELS Skip (or Tab) down to the Category (X) Axis. We are going to begin with the X- and Y-axes labels. 1. WRITING THE CATEGORY (X) AXIS Usually, you should copy the heading from the Table and use it as the X-axis label. If you are unsure what to write, just ask and you will be told. In this graph, the X-axis would be labeled Time (seconds). Notice that the units appear in parentheses when labeling the axes. 2. WRITING THE CATEGORY (Y) AXIS The same rule applies to this axis: copy the appropriate heading from the table. In this graph, the label of the Y-axis would be Temperature (oC). Again, the units appear in parentheses. OPTION-0 produces the degree sign in Excel. 3. WRITING THE TITLE Return to Chart Title. The title should always be what you wrote for the Y- and for the X-axes, minus the units, using the format “Y vs X.” In the example we used above, the title would be Temperature vs. Time. f. Click FINISH g. MOVE THE GRAPH Drag your graph below the table so that you can read both the table and graph. h. CHANGING FROM PORTRAIT TO LANDSCAPE Sometimes you would like to move the paper sideways to give yourself more room for the graph. To do this, click on an empty cell. Open FILE - PAGE SETUP - LANDSCAPE - OK. You have just turned your spreadsheet from a vertical to a horizontal alignment. i. ADJUSTING THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF THE GRAPH Click on the white space around the graph. A black line surrounding the graph should appear. Adjust the size of the graph by grabbing a corner perimeter box and dragging it to make the graph larger. If you grab and drag a box in the middle of the border line, you can stretch out the length or the height of the graph. This may become necessary to allow all (or most of the) axis variables to appear. j. READJUSTING THE LOCATION OF THE LEGEND Sometimes you will want to drag the graph and fill the space inside the white box. You can click on the gray graph itself and change its proportions, and you can drag the legend to a new location, as shown in the next illustration. the graph was widened inside the white box, and the legend was dragged to a new location on top of the graph k. PRINTING If you click on the graph, you will print only the graph. But graphs should always be accompanied by their tables To print both the table and the graph, click on an empty cell outside of the graph and the table. [REMEMBER: type your name in an empty cell so you will know which graph belongs to you when you go to the printer]. l. IMPROVING THE GRAPH’S APPEARANCE 1. Double click on the gray area inside the graph. Under FILL, click on a color and click OK. 2. Double click on the graph, again, but this time, click on FILL EFFECTS under the color choices. Select the GRADIENT tab. Play around with two colors. Some words of advice are in order. First, dark colors print out as dark gray or even black on a black and white printer, and that could obscure the curve on your graph. If you intend to print your graph, I suggest that you use only light colors. Second, fancy colors and other effects might distract from your basic intent of trying to give understanding to a string of numbers. While glitz is fun, it may not be wise to use it. 3. Would you like to add a background picture inside of the graph? For example, maybe you think a picture of a thermometer would be an appropriate image. Double click on the graph, choose FILL EFFECTS and open the PICTURE tab. A picture should be related to the subject of the graph. A picture of your favorite vacation spot might be confusing when the graph has to do with the effects of temperature. 4. To change the color of the title’s font, double click on the title. You can also change the color of the X and Y labels. 5. To change the color of the line, double click on the curve (the line in the graph) and change its color. 6. Similarly, you can change the color of the data points. 7. Can you change the color of the white field around the graph? m. TO ERASE A GRAPH Sometimes it is easier simply to re-write a graph if you make a mistake. There are two ways to erase a graph. You can click in the white area around the graph and press the DELETE key or you can press EDIT CLEAR - ALL. n. TO CREATE TWO Y-AXES Sometimes, you will have two columns of very different data for the Yaxes. For example, for the homework exercise called DO in the Snake River, you will be asked to graph both Water Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen (quite different variables). To do this, start to graph the data in the usual way, highlighting all three columns. Prepare the title and the Category (X) axis as usual. The Value (Y) axis is the heading of the first column of “Y” data in the table. Click on FINISH. Refer to the legend to identify the line for the Y-axis that you labeled. Click on the line of the second Y-axis variable in the graph. Click: FORMAT - SELECTED DATA SERIES. Open the AXIS tab and select SECONDARY AXIS OK Open CHART - CHART OPTIONS - TITLE. Type in the name of the heading of the second Y-axis under Second Value (Y) Axis. CAUTION: be sure you type this name in the correct location! You do not want this label appearing as a second X-axis label.