Unit 4 Review Key
advertisement
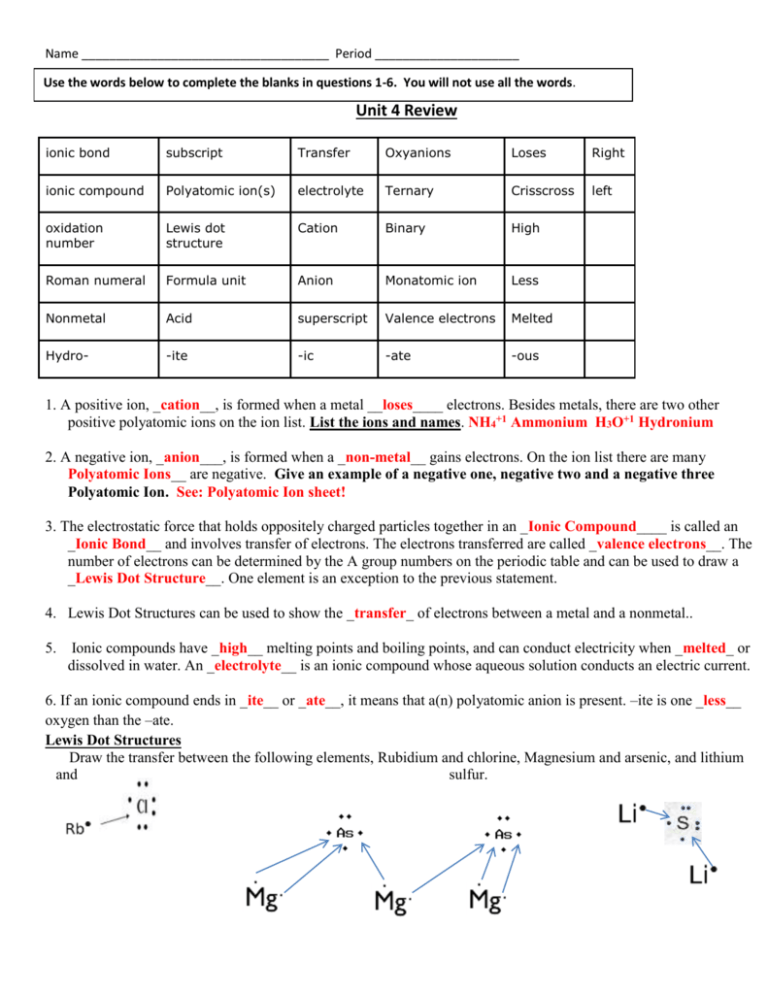
Name ____________________________________ Period _____________________ Use the words below to complete the blanks in questions 1-6. You will not use all the words. Unit 4 Review ionic bond subscript Transfer Oxyanions Loses Right ionic compound Polyatomic ion(s) electrolyte Ternary Crisscross left oxidation number Lewis dot structure Cation Binary High Roman numeral Formula unit Anion Monatomic ion Less Nonmetal Acid superscript Valence electrons Melted Hydro- -ite -ic -ate -ous 1. A positive ion, _cation__, is formed when a metal __loses____ electrons. Besides metals, there are two other positive polyatomic ions on the ion list. List the ions and names. NH4+1 Ammonium H3O+1 Hydronium 2. A negative ion, _anion___, is formed when a _non-metal__ gains electrons. On the ion list there are many Polyatomic Ions__ are negative. Give an example of a negative one, negative two and a negative three Polyatomic Ion. See: Polyatomic Ion sheet! 3. The electrostatic force that holds oppositely charged particles together in an _Ionic Compound____ is called an _Ionic Bond__ and involves transfer of electrons. The electrons transferred are called _valence electrons__. The number of electrons can be determined by the A group numbers on the periodic table and can be used to draw a _Lewis Dot Structure__. One element is an exception to the previous statement. 4. Lewis Dot Structures can be used to show the _transfer_ of electrons between a metal and a nonmetal.. 5. Ionic compounds have _high__ melting points and boiling points, and can conduct electricity when _melted_ or dissolved in water. An _electrolyte__ is an ionic compound whose aqueous solution conducts an electric current. 6. If an ionic compound ends in _ite__ or _ate__, it means that a(n) polyatomic anion is present. –ite is one _less__ oxygen than the –ate. Lewis Dot Structures Draw the transfer between the following elements, Rubidium and chlorine, Magnesium and arsenic, and lithium and sulfur. Name ____________________________________ Period _____________________ Define The Following Words Ionic bond- the electrostatic force that holds oppositely charged particles together. Monoatomic ion- a one atom ion ie: Ca+2 Cation- a positive ion; forms when an atom loses an eAnion- a negative ion; forms when an atom gains an ePolyatomic Ion- is made up of more than one atom and has an overall charge ex: SO4-2 Use parenthesis to group Binary Ionic Compound- made up of 2 elements (ions) and the second element (ion) ends in -ide Determine if each suffix/ prefix is for a non-metal ion, Polyatomic Ion or an Acid, -ate= Polyatomic Ion -ide= non-metal (anion) -ic= Acid -ite= Polyatomic Ion -ous Acid Hydro- = Binary Acid Fill in the appropriate oxidation numbers for each family Oxidation Numbers Transition Metals 1. What groups are transition metals found in on the periodic table? Groups 3-12 2. Give the charge (oxidation #) of the following transition metals. Lead II +2 Iron III +3 Au II +2 Name ____________________________________ Period _____________________ Ionic Compounds 1. List three characteristics of Ionic compounds. High melting points, high boiling points, conduct electricity in aqueous solutions, form salts 2. _Valence__ electrons are involved in the formation of a chemical bond. 3. Cations _lose_ electrons and have a _positive__ charge. 4. Anions __gain__ electrons and have a _negative___ charge. 5. **Most Ionic compounds are made of a _metal_ and a _non-metal_ Element Oxidation # Ion Formula Sodium +1 Na +1 Bromide -1 Br-1 Oxide -2 O-2 Lithium +1 Li+1 Phosphide -3 P-3 Potassium +1 K+1 Element Oxidation # Ion Formula Iron (II) +2 Fe+2 Mercury (I) +1 Hg+1 Gold (III) +3 Au+3 Silver +1 Ag+1 Nickel (II) +2 Ni+2 Copper (I) +1 Cu+1 Zinc +2 Zn+2 Name of Compound Formula Name of Compound Formula Potassium Phosphate K+1 PO4-3 = K3PO4 Ammonium Phosphide NH4+1 P-3 = (NH4)3P Calcium Chloride Ca+2 Cl-1 = CaCl2 Copper (II) Sulfate Lithium Fluoride LiF Magnesium Iodide MgI₂ CuSO4 = Cu+2SO4-2 Was Reduced Pb(CrO4)2 = Pb+4(CrO4) -2 Was Reduced Cs+1 C2H3O2 = CsC2H3O2 Copper (I) Oxide Iron(III) acetate Fe+3 C2H3O2-1 Cobalt (III) Carbonate Cu+1 O-2 = Cu20 Lead (IV) Chromate Cesium Acetate Iron (III) Oxide Sr+2 CrO4-2 = SrCrO4 Was Reduced Fe2O3 = Fe+3O-2 Lithium Hydroxide Li+1 OH-1 = LiOH Strontium Chromate Fe (C2H3O2)3 Co₂(CO₃)₃ Name ____________________________________ Period _____________________ Write the formula for each TA – Ternary Acid BA – Binary Acid TC – Ternary Compound BC – Binary Compound 1. Nitrous Acid TA; Acid H+ Nitrous Nitrite (NO2) = HNO2 2. Aluminum Hydroxide TC; Al+3 OH-1 = Al(OH)3 (Remember OH is a BASE) 3. Hydroselenic Acid BA ; Acid H+ Selenic Selenide Se-2 = H2Se 4. Phosphoric Acid TA; Acid H+ phosphoric phosphate (PO4)-3 =H3PO4 5. Strontium Hydroxide TC; Sr+2 OH-1 = Sr(OH)2 (Remember OH is a BASE) Write the name for each 6. 7. 8. 9. HCl BA; Hydrochloric Acid HNO3 TA ; NO3 is Nitrate ic Nitric Acid H2CO3 TA; CO3 is Carbonate ic = Carbonic Acid Ca(OH)2 TC; Calcium Hydroxide (Remember OH is a BASE)