ASSIGNMENT – JANURY 3RD – READ AND ANSWER
advertisement

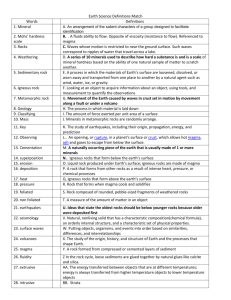
ASSIGNMENT – JANURY 3RD – READ AND ANSWER QUESTIONS ON LINED PAPER All minerals are natural resources. They are found in nature. They are not man-made. Minerals have a crystal structure. Rocks are different because they can be combinations of different minerals. They can be mixtures of different chemicals. But minerals have specific chemical and physical properties. 2 Minerals can be identified by their physical properties. A physical property is something you can see, feel, taste, or smell. You can learn to identify many common minerals. Some minerals are usually one color, but some can be different colors. 3 Some minerals have easy to see physical properties. For example, some have a crystal shape like quartz crystals. Some have grainy fibers like asbestos. 4 Some minerals are very hard. Some are soft. Talc is a mineral that is so soft you can scratch it with your fingernail. 5 The way light is reflected from the mineral is called luster. Some minerals have a shiny, metallic luster. Some look like glass. Some look dull (the opposite of shiny), and some gleam like pearls. 6 You can scrape a mineral across a porcelain tile to see what color of streak it leaves behind. Different minerals make streaks of different colors. The streak may be a different color from the mineral itself. For example, the mineral pyrite is called "fool's gold." It has a golden color, but it leaves a streak of greenishblack. This is an easy way to tell if you have found real gold or just "fool's gold." 7 Some minerals break into cubes when hit with a hammer. The way a mineral breaks is called cleavage. Some minerals break or cleave along flat, smooth planes. Other minerals leave rough, jagged lines where they break. Minerals can be identified by their cleavage. 8 Some minerals have special characteristics by which they can be identified. The mineral calcite reacts with a mild acid and will bubble. The mineral halite has a salty taste. 9 Hardness is another way to identify minerals. Diamonds are the hardest minerals found on earth. They can cut glass. A harder mineral can scratch a softer one. Your fingernail can scratch talc and gypsum but not calcite. Calcite can be scratched by a penny. Quartz can scratch steel. These are ways to test the hardness of a mineral. 10 Gemstones are minerals that are rare and beautiful. Color, luster, and hardness are properties that make a mineral valuable as a gemstone. Diamonds, rubies, opals, emeralds, and sapphires are all gemstones. 11 We use many minerals in our everyday lives. Toothpaste, salt, and baking powder used in cooking all come from minerals. Many materials used in building computers, cars, furniture, appliances, and buildings all come from minerals. In fact, the average person uses over 40,000 pounds of different minerals each year. ************************************************************************************* Rocks can be put into three main groups. They are grouped by how the rocks formed. One type is an igneous rock. This type of rock forms either above or below ground. They are called fire rocks. This is because they form from melted rock. When melted rock is below ground, it is called magma. Igneous rocks can form underground when a pocket of magma cools. When melted rock is above ground, it is called lava. Igneous rock can also form as the lava cools above ground after a volcano erupts. Granite is one type of igneous rock. Granite is very hard. It is used for structures that need to last a long time. Monuments can be made of granite. Granite can also be used as decoration. Pumice is another igneous rock. It is really a type of glass instead of crystalized minerals. It is very soft. It can be ground up and used in cleaning products. It can also be used for landscaping. Obsidian rocks are glass, too. They form when lava cools quickly on the surface. They have a shiny surface. Scoria rocks are also a type of glass. They have large pockets that show where air used to be. They are not shiny. Each of these different rocks has different traits, yet they are all formed from melted rock. Another type of rock is sedimentary rock. It is formed very slowly. It is made from tiny pieces of older rock, sand, minerals, and fossils, called sediments. Sediments are laid on the ground by water, wind, and ice. They are on the bottoms of oceans, lakes, rivers, and streams. They are on beaches and on mountains. Over many years, sediments are layered on top of each other. Chemicals or minerals in the sediment form a glue. The sediments stick together. Sedimentary rock is formed. Metamorphic (met-uh-MOR-fic) rocks are changed by the heat and pressure inside Earth. "Metamorphic" comes from a Greek word that means "change of form." Metamorphic rocks can be formed from other metamorphic rocks. They can form from sedimentary and igneous rocks, too. 2 The temperature deep inside the Earth is much hotter than temperatures near or on the surface. The weight of tons of land and rocks on top presses down on the rocks underneath. This pressure, along with heat, causes the rocks inside the Earth to go through a physical or chemical change. Movement of Earth's plates causes pressure on rocky material under the surface, resulting in folding. Water can dissolve and redeposit minerals. This can also cause a change in rocks. Minerals react with each other at high heat. Atoms rearrange, and new minerals are created from old ones. Grains in rocks are pressed and made more compact. Rocks morph into other kinds of rocks. 3 Some metamorphic rocks are slate, schist, gneiss, marble, and quartzite. Sandstone is a sedimentary rock. It is made of grains of sand pressed together. Sandstone is fairly soft. It crumbles easily. When sandstone changes into the metamorphic rock quartzite, is becomes one of the hardest rocks. 4 The sedimentary rock shale changes into slate. The mineral grains in shale change directions because of the heat and pressure. Slate, a metamorphic rock, can be changed by continued heat and pressure into a rock called schist. Schist is very different from shale. It looks different. Its structure and composition is different. Schist is made up of flaky scales and splits easily. 5 The most common type of metamorphic rock is gneiss (say "nice"). Gneiss forms from granite, an igneous rock. Granite has mineral grains of different colors. They look like grains of salt or bigger blobs of color. When granite is pressed and heated inside Earth, the minerals rearrange into layers or bands instead of grains or blobs. Granite might look like it has salt and pepper inside it, but gneiss looks like a layer cake. Squeezing pressure between two of Earth's plates sometimes causes the rocky materials to bend or fold. The layers may curve or swirl. 6 Metamorphic rocks are changed in physical or chemical form from older rocks. All three kinds of rocks may change into metamorphic rocks. Heat and pressure inside Earth cause older rocks to change into new ones. ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Questions to Answer: A. 1. 2. 3. 4. What is a mineral? How can minerals be identified? What causes other kinds of rocks to change into metamorphic rocks? How are minerals different from rocks? 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Explain the different changes and causes that the rocks inside the Earth go through. From where does the word "Metamorphic" come from? What is another name for igneous rock? What makes igneous rocks? AND How does igneous rock form below ground? Explain the different uses for igneous rocks. How do we use minerals every day? 11. How much does the average person use of different minerals each year? 12. How does sedimentary rock form? 13. Imagine that you are an igneous rock. Tell your life story. Begin as either lava or magma. Explain what type of igneous rock you "grow" up to be. B. Draw and Complete the graphic organizer using the reading and chart to help you organize the information. Describe the similarities and differences between Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic rock. Use the information from the chart and the Venn diagram to help you write your descriptive paragraph.