Yr 8 Ecology Curriculum Overview

UNIT – Ecology
Introduction
The study and understanding of interactions between organisms and their environments.
In this unit students will
Discover how animals and plants survive in their environment
Explain the how energy is transferred in a food chain
Understand how animals and plants depend on each other through food chains and food webs
Learn how living things compete against each
Differentiate between the different trophic levels in a energy pyramid
Understand how plants and animals adapt to their environment
Key Competencies
KEY SKILLS
The Key Skills that students will improve during the completion of this unit are:
Construct a food chain and identify the producer, first, second, third and fourth order consumers
Explain and identify the producers, consumers and decomposers for different types of ecosystems (coastal, dessert, rainforest, etc)
Construct food webs that show the flow of matter and demonstrate how different food chains make up a food web.
Describe the abiotic and biotic interactions in an ecosystem
Predict environmental change on living things in a local ecosystem
Explain how different plant and animal adaptations help them to survive in their habitat
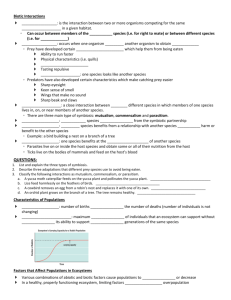
Explain the relationship of predator and prey
Differentiate between symbiosis, parasitism, commensalism and mutualism
Visit a coastal habitat and explain the relationships between the different plants and animals in it.
cod webs and predict the effects of environmental change on living things
KEY KNOWLEDGE
The key knowledge that students will obtain from this unit are
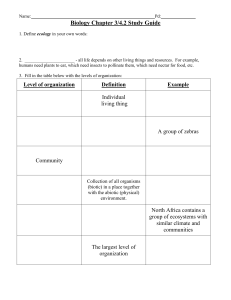
Living things in an ecosystem are called biotic (plants, animals, predators etc) factors and non-living things are called abiotic
(water, rocks, soil, sun, weather) factors.
Habitats must provide the things that animals and plants need to stay alive (food, water, shelter, space, reproduction etc)
Producers, consumers (carnivores, herbivores) and decomposers rely on each other in food chains and food webs
Predators and prey have ot fight for survival in different ways.
Animals are able to survive in harsh conditions due to their adaptations
Endangered species and the affects to the food web and ecosystem
The workings of symbiosis, parasitism, commensalism and mutualism can both hurt and help an ecosystem
KEY TERMS
The Key Terms that students will become familiar with the definition and spelling of during this unit are:
Food web Food chain producer consumer Decomposer adaptation biotic abiotic autotrophs hetrotrophs carnivores omnivores herbivores decomposers predators parasitism symbiosis biodiversity conservation Endangered species parasite scoria habitat Ecological footprint environment organism biodegradable prey plankton commensalism