Biotic interactions 1.3-Section 1.3 Student`s Copy
advertisement

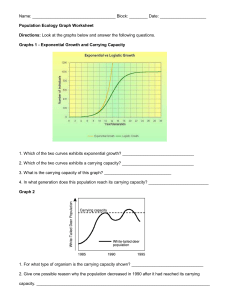
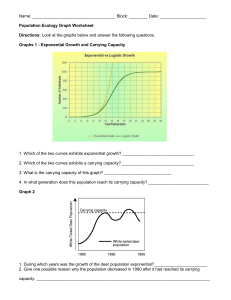
Biotic Interactions _________________: is the interaction between two or more organisms competing for the same ___________________ in a given habitat. ◦ Can occur between members of the ___________ species (i.e. for right to mate) or between different species (i.e. for _____________) _________________: occurs when one organism _________ another organism to obtain _____________ ◦ Prey have developed certain _______________________ which help them from being eaten Ability to run faster Physical characteristics (i.e. quills) _______________________ Tasting repulsive ___________________: one species looks like another species ◦ Predators have also developed certain characteristics which make catching prey easier Sharp eyesight Keen sense of smell Wings that make no sound Sharp beak and claws ___________________: a close interaction between ________ different species in which members of one species lives in, on, or near members of another species. ◦ There are three main type of symbiosis: mutualism, commensalism and parasitism. __________________: ____________ species ________________ from the symbiotic partnership __________________: _________ species benefits from a relationship with another species ___________ harm or benefit to the other species ◦ Example: a bird building a nest on a branch of a tree __________________: one species benefits at the ____________________ of another species ◦ Parasites live on or inside the host species and obtain some or all of their nutrition from the host ◦ Ticks live on the bodies of mammals and feed on the host’s blood QUESTIONS: 1. 2. 3. List and explain the three types of symbiosis. Describe three adaptations that different prey species use to avoid being eaten. Classify the following interactions as mutualism, commensalism, or parasitism. a. A yucca moth caterpillar feeds on the yucca plant and pollinates the yucca plant. ________________________________ b. Lice feed harmlessly on the feathers of birds. __________________________________ c. A cowbird removes an egg from a robin’s nest and replaces it with one of its own. _____________________________ d. An orchid plant grows on the branch of a tree. The tree remains healthy. _______________________________ Characteristics of Populations __________________: number of births ________________ the number of deaths (number of individuals is not changing) ________________________: maximum ________________ of individuals that an ecosystem can support without ________________ its ability to support ________________ generations of the same species Factors that Affect Populations in Ecosystems Various combinations of abiotic and biotic factors cause populations to ________________ or decrease In a healthy, properly functioning ecosystem, limiting factors __________________ overpopulation _________________________: an environmental factor that _________________ an increase in the number of organisms in a population or prevents them from moving into new habitats Population Size Abiotic Factor Biotic Factor Competition Extreme climate changes Parasitism QUESTIONS: 4. Explain what is meant by the following terms. a. Limiting factor b. Carrying capacity c. Equilibrium 5. Identify the following limiting factors as either abiotic or biotic. a. Wind blows the seeds of a dandelion into a pond. The seeds fail to grow. ___________________________ b. A population of grasshoppers eats all the available food, and their numbers drop dramatically. _________________________ c. A bacterium causes a deadly disease in a herd of reindeer, and some of them die. _____________________________ d. Plants growing beneath the trees in a forest are unable to get enough sunlight. __________________________ 6. Does the success of a prey population depend on its predators? Explain. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Population Growth Equation: _________________: the _____________ of offspring of a species ____________ in an ecosystem in one year _________________: the number of individuals of a species that ________ in an ecosystem in one year. _________________: the number of individuals of a species moving _________ an existing population _________________: the number of individuals of a species moving __________ of an existing population Population Growth = ________________________________________________________________________ Sample Question: 7. Calculate the change in population and the new population in a population of 1000 swans after the following data were collected: births = 300, deaths = 200, immigration = 4, emigration = 5. Practice Question: 8. Calculate the change in population and the new population in a population of 60 hares after the following data were collected: births = 20, deaths = 25, immigration = 3, emigration = 7. Population histograms: - graphs used to study populations of long-lived organisms. Looks at the male-female ratio and compares it to age. A pyramid with a _________ base indicates that there is a rapid ___________ in population. A pyramid with ______ changes in its population distribution means that the population growth is close to __________. A pyramid with a _____________ base shows that population may be on a ________________. Use the following information to construct a population histogram: Age Distribution of Humans in a Shopping Mall (Wednesday at 5 pm) Ages Females 0–4 8 5–9 6 10 – 14 8 15 – 19 5 20 – 24 3 25 – 29 9 Males 7 4 2 1 5 3 Wolf and Moose Populations on Isle Royale – Activity 1. Can an ecosystem support an infinite number of moose? Why or why not? _______________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. If wolves did not live on Isle Royale, what main factor would determine the amount of moose the island could support? ______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What other factors may influence population numbers? ________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Is predation an abiotic or biotic limiting factor? _________________________________________ On Isle Royale, the moose have a predator – the wolf. Using the graph provided below, answer the following questions. 5. When the moose (prey) population increases, what happens to the wolf (predator) population? Why? _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ 6. What may have caused the moose population to decline? When this happens, what happens to the wolf population? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Why is this interaction between predator and prey called a cycle? ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Why is this cycle so easily studied on Isle Royale? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________