Atomic structure and Nuclear Decay- Test B Study Guide
advertisement

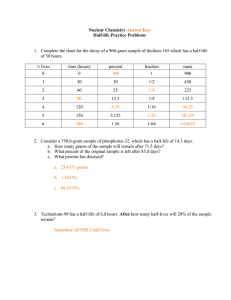
Atomic structure and Nuclear Decay- Test B Study Guide 1. The disintegration of the radioisotope radium-226 produces an isotope of the element radon and alpha radiation. Write a balanced equation for this transformation 2. The following radioisotopes are beta admitters. Write balanced nuclear equations for their decay process. a. Carbon-14 b. strontium-90 c. potassium-40 d. nitrogen-13 3. How are the mass number and atomic number of a nucleus affected by the following: a. Β- decay b. α-decay c. γ-emission d. electron capture e. positron emission 4. Complete the following table. 3 nuclear particles/ Composition Symbol Types of Radiation Alpha Beta Gamma 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Mass in amu Charge Penetrating Power Shielding 0 List three methods used to detect radiation. Define half-life Define transmutation and list two causes. List three uses for nuclear radiation What s the band of stability? Are all nuclei equally stable? What determines a nuclei’s stability? What is mass defect? Why does it occur? What happens to the mass? List the six flavors of Quarks. What is a proton made of? What is a neutron made of? Which is heavier a neutron or a proton? Why? What are electrons made of? What is the difference between fission and fusion? What unit is used to measure molar mass? What is Avegardro’s number? What is it based on? Determine the molar mass for the following: a. Al b. Mg c.H2O d. CO2 e. BaCl2 21. Determine the mass of the following in grams. a. 1.366 mol of NH3 b. 238 mol of arsenic c. 4.5 mol of NaF f. Ca(ClO3)2 d. 54 x1023 atoms of gold e. 1.20 x 1023 molecules of Na2C2O4 22. Determine the number of moles in each of the following. a. 64.1 g of Si b. 0.255 g of S c. 0.472 g of NaF d. 50 g of Ca(ClO3)2 23 19 e. 2.5 x 10 molecules of Na2C2O4 f. 7.66 x 10 molecules of H2O2 23. Determine the number of atoms/molecules/particles in the following. a. 17.0 mol of Ge b. 4.27 mol of WO3 c. 285 g of FePO4 24. Balance the following Nuclear Equations and determine what type of nuclear reaction they are. a. 49𝐵𝑒 + 42𝐻𝑒 ⟶ 126𝐶 + ________ 1 b. 235 92𝑈 + 0𝑛 ⟶ c. 31 15𝑃 + 11𝐻 ⟶ 95 42𝑀𝑜 28 ___𝑆𝑖 + 2 10𝑛 + ___________ + _____________ 0 d. 37 18𝐴𝑟 + −1𝑒 ⟶ ___________ e. 158𝑂 ⟶ 15 7𝑁 + ___________ 25. Os-182 has a half-life of 21.5 hours. How many grams of a 10.0 gram sample would have decayed after exactly three half-lives? 26. After 24.0 days, 2.00 milligrams of an original 128.0 milligram sample remain. What is the halflife of the sample? 27. Fermium-253 has a half-life of 0.334 seconds. A radioactive sample is considered to be completely decayed after 10 half-lives. How much time will elapse for this sample to be considered gone? 28. There are 10.0 grams of W-187. If the half-life is 23.9 hours, how much will be present at the end of one day? Two days? Seven days? 29. 100.0 grams of an isotope with a half-life of 36.0 hours is found. How much time will have elapsed when 5.00 grams remains? 30. If 100.0 g of carbon-14 decays until only 25.0 g of carbon is left after 11 460 y, what is the halflife of carbon-14? 31. What is 14C used for? What are its limitations? What can is sometimes used instead?