Genetics Test Review KEY
advertisement
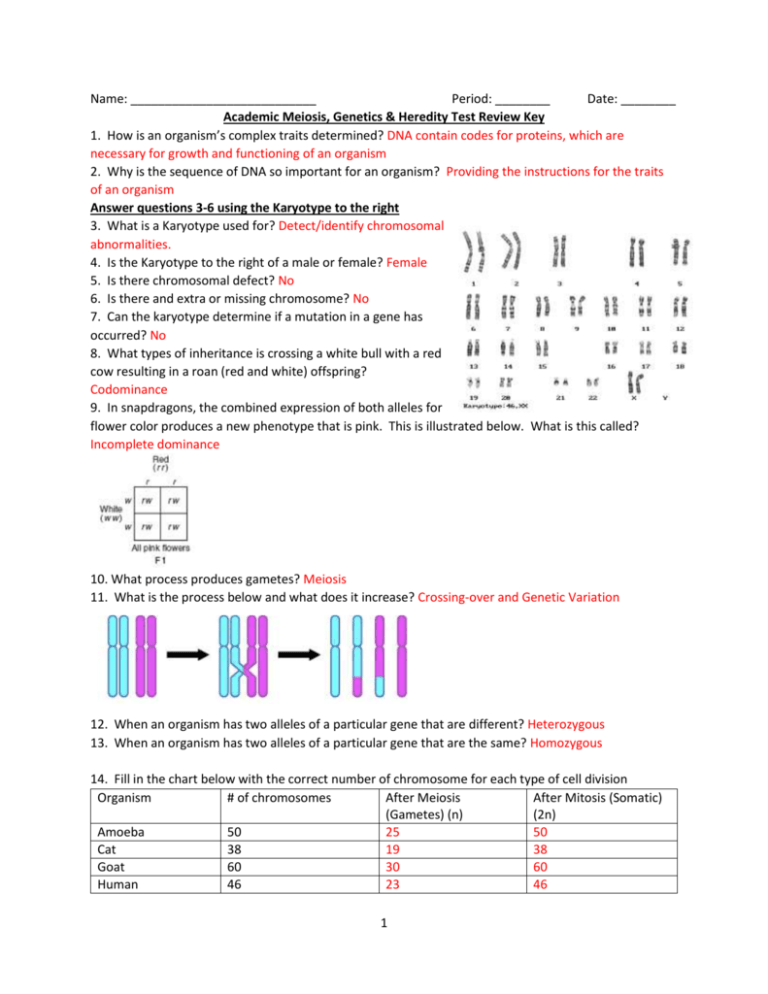
Name: ___________________________ Period: ________ Date: ________ Academic Meiosis, Genetics & Heredity Test Review Key 1. How is an organism’s complex traits determined? DNA contain codes for proteins, which are necessary for growth and functioning of an organism 2. Why is the sequence of DNA so important for an organism? Providing the instructions for the traits of an organism Answer questions 3-6 using the Karyotype to the right 3. What is a Karyotype used for? Detect/identify chromosomal abnormalities. 4. Is the Karyotype to the right of a male or female? Female 5. Is there chromosomal defect? No 6. Is there and extra or missing chromosome? No 7. Can the karyotype determine if a mutation in a gene has occurred? No 8. What types of inheritance is crossing a white bull with a red cow resulting in a roan (red and white) offspring? Codominance 9. In snapdragons, the combined expression of both alleles for flower color produces a new phenotype that is pink. This is illustrated below. What is this called? Incomplete dominance 10. What process produces gametes? Meiosis 11. What is the process below and what does it increase? Crossing-over and Genetic Variation 12. When an organism has two alleles of a particular gene that are different? Heterozygous 13. When an organism has two alleles of a particular gene that are the same? Homozygous 14. Fill in the chart below with the correct number of chromosome for each type of cell division Organism # of chromosomes After Meiosis After Mitosis (Somatic) (Gametes) (n) (2n) Amoeba 50 25 50 Cat 38 19 38 Goat 60 30 60 Human 46 23 46 1 15. What is an allele considered to be if one allele is express and the other is not? Dominant 16. Using the genetic key chart to write in the correct genotype Pea Plants T=tall Y-yellow t= short Cocker Spaniels y-green B=black coat color b=brown coat color Guinea Pigs Tomato plants B=black fur F=short fur b=brown fur f=long fur H=hairy stems h=hairless stems Organism Homozygous tall, heterozygous yellow pea plant Heterozygous black cocker spaniel Brown cocker spaniel Possible genotypes TTYy Bb bb Guinea pig that is Heterozygous for both traits Heterozygous hairy tomato plants Heterozygous black, long fur Guinea Pig BbFf Hh Bbff 17. If a two guinea pigs with the genotype BBFf x bbff, what percentage of the offspring would be heterozygous for both traits? 18. What is the expected outcome of two tomato plants that are heterozygous for hairy stems? 2 19. The segregation that occurs during meiosis results in a… Reduction in the number of chromosomes per cell 20. If pea plants with the genotype TTYy is crossed with a pea plant with genotype Ttyy, what percentage of offspring will be expected to have TtYy? 21. What are the components of DNA that are referred to as the genetic code. Nitrogen Bases 22. If a brown cocker spaniel is crossed with a homozygous black cocker spaniel. What is the expected outcome? 23. If you cross a pink snapdragon with a white snapdragon. What percentage would be red? (rr) red, (ww) white, (rw) pink 3 24. What are all the possible blood types for the offspring produced by a type “O” mother and an a Type “AB” father 25. Why is sexual reproduction important? Meiosis ensures that there is genetic variation within the offspring that results from two parents. 26. A woman that is heterozygous for normal blood clotting is cross with a man that has normal blood clotting. What are the chances that their offspring will have hemophilia? H= normal blood clotting h=hemophilia 27. Name the processes in the diagrams below as Mitosis or Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis 4 F=Free earlobes f= Attached earlobes 28. Predict the genotype of individual #14 ff=Attached 5