Introduction to Equilibrium Powerpoint Notes
advertisement

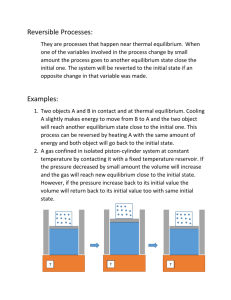
Honors/Pre-IB Chemistry NAME ________________________ Chemical Equilibrium Powerpoint Notes Sketch a graph of an “ordinary reaction” and label its parts: How does the rate of the reaction affect how the graph looks? What would happen to the graph if the rate of the reaction decreased? (Draw your answer) The rate of a reaction is dependent upon the concentration of the ________________, Is the rate constant? Explain. REVERSIBLE REACTIONS ARE: EXAMPLES (LOOK AHEAD IN THE SLIDESHOW FOR SEVERAL EXAMPLES), LIST IN DETAIL: How can you tell that a reaction is reversible? (SLIDE 9)Describe the rate of the reaction at first and why…. What happens at equilibrium? THIS DOES NOT MEAN THE REACTION IS “STUCK IN THE MIDDLE”!!! Why not? True/False – In an equilibrium reaction, all the reactants end up as products, THEN all the products convert back to reactants. Sketch the graph again, but this time label the point at which equilibrium occurs: What does “DYNAMIC” mean? Can the point of equilibrium for a reversible reaction be changed? Important Reminders: 1.) 2.) 3.) SUMMARIZING…. 4.) 5.) 6.) 7.) (SKIP AHEAD……DO SLIDES 14 & 15 FOR REVIEW) EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (SLIDE 11 – 13) **The equilibrium constant is usually represented with the ________ symbol and is expressed in units of ______________________. For an equilibrium reaction in the form…. aA + bB cC + dD The equilibrium constant would be written as: Write the equilibrium constant for the reversible reaction between hydrogen and oxygen gas to produce water: LE CHATELIER’S PRINCIPLE (Starting on SLIDE 16) What does Le Chatelier’s Principle state? There are 4 Factors that affect the Position of Equilibrium. Please explore the slideshow and fill out the table below detailing each factor: FACTOR SUMMARIZE THE BASICS EXAMPLE EQUATION