Answer Key - biology4friends
advertisement
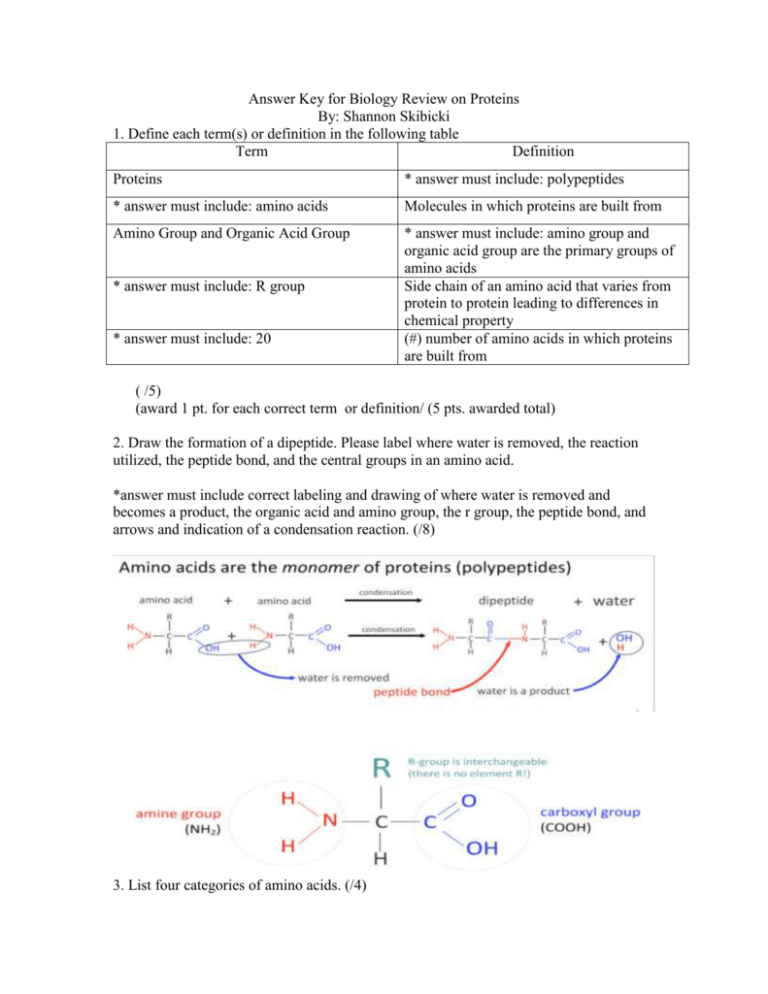
Answer Key for Biology Review on Proteins By: Shannon Skibicki 1. Define each term(s) or definition in the following table Term Definition Proteins * answer must include: polypeptides * answer must include: amino acids Molecules in which proteins are built from Amino Group and Organic Acid Group * answer must include: amino group and organic acid group are the primary groups of amino acids Side chain of an amino acid that varies from protein to protein leading to differences in chemical property (#) number of amino acids in which proteins are built from * answer must include: R group * answer must include: 20 ( /5) (award 1 pt. for each correct term or definition/ (5 pts. awarded total) 2. Draw the formation of a dipeptide. Please label where water is removed, the reaction utilized, the peptide bond, and the central groups in an amino acid. *answer must include correct labeling and drawing of where water is removed and becomes a product, the organic acid and amino group, the r group, the peptide bond, and arrows and indication of a condensation reaction. (/8) 3. List four categories of amino acids. (/4) Answer must include: 1 pt. for each item (/4) o Acidic amino acids o Basic amino acids o Amino acids with hydrophobic properties o Amino acids with hydrophilic properties 4. Which of the following are components the secondary protein structure? I. polypeptide chains II. protein stabilization via hydrogen bonding III. coiling to produce a helix or B sheets IV. vesicles budding off the rough ER a) I. b) I., IV. c) I., II. III. d) IV. (1 pt. each) 5. Distinguish between tertiary and quaternary proteins. (/3) * Answer could include: Tertiary protein is when the molecule unique to the protein is folded into a complex shape o Complex shape of the tertiary bond is maintained by the four types of bond at adjacent parts of the polypeptide chain: Hydrogen bonds (between atoms) Ionic bonds (electrostatic interaction between opposite charges) Disulphide bonds (strong covalent bond formed by the oxidation of SH groups) Van der Waals forces bonds – comes into play when atoms are very close o Lysozyme is an example of a protein with a tertiary structure While the quaternary protein also takes on a complex shape, it has the following components which make it unique: o Two or more proteins are held together o Biologically active molecule o Hemoglobin is an example of quaternary structure (4 polypeptide chains held around non-protein haem group an atom of iron occurs) 6. Draw and label a diagram of the phospholipid bilayer indicating the non polar and polar amino acid residues. *Answer should include phosphate head, hydrophilic and hydrophobic tails, clear labeling polarity of channel proteins, receptor proteins (proteins on the side of the membrane) to indicate the polar and non polar amino acid residues. (/8) 7. Identify the type of protein or the role of the protein with an example in the following table. Protein Structural protein Enzymes Muscle/ movement proteins Transport Defence against infectious disease proteins Membrane proteins Role/ Example Insoluble, often long coiled tertiary structures, that provide structural support, especially in bones and hair. /collagen Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions/ pepsin Bring about muscle contractions by reaction with ATP, triggered by calcium ions. (myosin or actin) Involved with transport and respiratory gasses/ hemoglobin Serve as antibodies secreted by b lymphocytes Component of structure, also can serve as enzymes, pumps, and receptors. Major component of phospholipid bilayer.