Chapter 7

X
CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS
Chapter 7 – Acids, Bases and Solutions
NOTES WRITTEN
What is a solution?
X
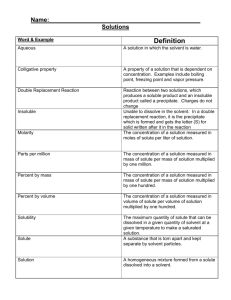
Solution
Solvent
– a uniform mixture that contains a solvent and at least one solute
– the part of a solution present in the largest amount and dissolves
What makes up a solution?
the other substances (what does the dissolving)
In salt water, water is the solvent
Solute – the part of a solution present in a smaller amount and is dissolved
by the solvent (what is dissolved)
In salt water, salt is the solute
A solution has the same properties throughout. It contains solute particles
that are too small to see (because they are dissolved!) (ex-salt water)
What are other mixtures?
What do solutes do to a
solution?
X
Concentration-
Solubility-
Unsaturated vs saturated-
SUMMARY
Colloid – a mixture that contains small, non-dissolved particles that cannot
easily be separated out (ex-milk and fog)
Suspension – a mixture in which particles can be seen and easily separated
by settling or filtration (ex- pepper in water and dust in air)
Solutes lower the freezing point and raise the boiling point of a solvent
Why do you think some recipes have you add salt to boiling water before
adding the noodles?
Concentrated solution – has a lot of solute dissolved in a small amount of
solvent
To measure concentration, you compare the amount of solute to the total
amount of solution. If you dilute something you add more solvent.
Solubility – a measure of how much solute can dissolve in a solvent at a
given temperature
Unsaturated Solution – when the solvent can dissolve more solute
Saturated Solution – when the solvent cannot dissolve more solute
Supersaturated Solution – when the solvent dissolves more solute than
predicted at a given temperature (made by heating, adding the solvent,
and then cooling)
X
CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS
What are acids?
X
What are bases?
What is the pH scale?
X
What is a neutral solution?
What is neutralization?
SUMMARY
NOTES WRITTEN
Acids – something that tastes sour , reacts with metals (is corrosive) and
carbonates and turns blue litmus paper red
Has a pH of 0-6 on the pH scale
Hydrogen Ion (H+) – an atom of hydrogen that has lost its electron
An acid produces hydrogen ions in water
HCL H+ + Cl-
Bases – something that tastes bitter , feels slippery and turns red litmus paper
blue
Has a pH of 8-14 on the pH scale
Hydroxide Ion (OH-) – an atom of hydrogen that has lost its electron
A base produces hydroxide ions in water
NaOH Na+ + OH-
Knowing the concentration of hydrogen ions is the key to knowing how acidic
or basic a solution is – scientists use a pH scale pH Scale – range of values from 0-14 used to express the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution
Neutral Solution – a solution that is neither acidic nor basic…has a pH of 7
Acid- low pH means high concentration of H+
Base high pH means low concentration of H+
Neutralization – reaction between an acid and a base
In a neutralization reaction- an acid reacts with a base to produce salt and
water (and so has a pH of 7)
HCl + NaOH H
2
O + Na+ + Cl-