answer-to-chpt.-23-24-study-guide
advertisement

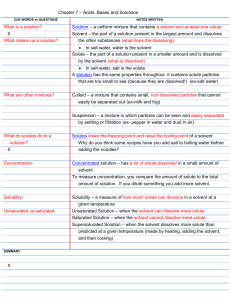
Chpt. 23-24 Review answers: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Water is unique because it doesn’t change temperature easily, has a high boiling point, high surface tension, solid ice less dense than liquid water… Water’s shape is bent, it is polar with the oxygen having a partial negative charge, the hydrogen have a partial positive charge Hydrogen bonds form between the positive hydrogen charges of one water molecule and the negative oxygen charges on another molecule, these cause water to “stick together” more, leading to high surface tension, high boiling points, low density of ice, strong capillary action. A solution is made of a solute (smaller amounts) dissolved in a solvent (larger amounts) A. 169.91 g/mol B. 303.27 g/mol, C. 76.02 g/mol, D. 129.83 g/mol, e. 17.01 g/mol, f. 270.67 g/mol, g. 135 g/mol, h. 238.7 g/mol A. 1.33 M, b. 0.33 M, c. 0.63 M, d. 4.76 x 10-4M Solubility is the property of a solute to be able to dissolve in a solvent to form a homogeneous solution. Can depend on polarity, temperature, pressure. Saturated solutions- full of solute for a given solvent at a given temperature Unsaturated solutions- have room in the solvent to dissolve more of the solute at a given temperature Supersaturated solutions- have more solute than can dissolve at a given temperature in a given solvent. Temperature normally increases the solubility of a solute in a solvent, the higher the temperature more solute can dissolve. More solute can normally dissolve at higher pressure, in the lab with the tonic water the pressure was highest at the beginning when the bottle was opened, as the pressure decreased, the amount of gas dissolved decreased. Water 23 g, 85 g, 40 g, 128 g, 22g, least soluble SO2, most soluble KNO3, NaNO3 Acids: sour, pH less than 7, hydrogen donors, corrosive turns blue litmus red. Bases: bitter, slippery, used for cleaners, pH over 7, turns red litmus blue. pH less than 7 for acids such as lemon, vinegar, cola, and rain, over 7 for bases such as drano, borax, blood. Water continuously cycled on Earth: precipitation, percolation, run-off, evaporation, condensation, precipitation 1% of Earth’s water is fresh surface water Surface water in rivers, lakes, streams, ponds. Ground water in rocks, aquifers, wells Shorter showers, less lawn watering, only run dishwasher when full, use less.. Groundwater can stay underground for hundreds to thousands of years, not easy to get to underground water to clean it. Watersheds are used for drinking, most cities get their drinking water from lakes and rivers Water supply at risk from pollution, drought, flooding, overuse Acid rain comes from sulfur dioxide pollution from factories, or from nitrates from fertilizers. Acid rain causes trees and plants to be under stress and possibly die. 23. Ocean acidification comes from excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere dissolving into the ocean 24. Oceans remove carbon dioxide by dissolving it into the water, then it reacts with calcium carbonate ions to neutralize. 25. Toxic pollutants like mercury become more concentrated as you go up the food chain, consumers at the top have higher levels than those at the bottom. 26. Coral reefs under threat from ocean warming, overfishing, logging causing siltification. 27. Producers- algae, phytoplankton, seagrass Decomposers- bacteria, fungus, worms Herbivores- damselfish, zooplankton, coral Carnivores- sharks, angelfish, snapper, stingrays 28. Energy flows up the food chain, begins with sunlight energy entering chain through producers. It costs more energy to eat tunafish than seaweed because most energy is lost as waste along the food chain.