Heterogeneous
advertisement

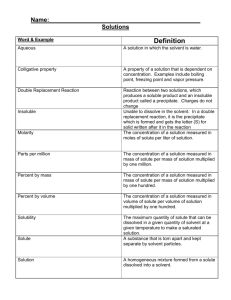
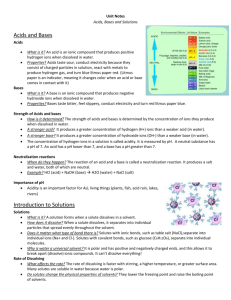
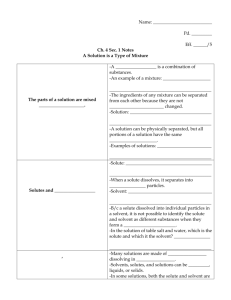
40g dissolved 20 g undissolved Dissociation Solutions Suspensions Colloids Allows continual contact between solute & solvent Heterogeneous Solutions Aerosols Foams Emulsions Gels/Sols Ions are not dissociated and the ions are not mobile since the are not in a solution Solvent Electrolyte Heating Stirring Grinding Increases the kinetic energy so molecules are moving faster so more collisions between the solute & solvent Colloid Saturated State where the solute is dissolving at the same rate that the solute is coming out of solution (crystallizing). Solubility Creates more of a surface area on the solute, so more collisions between solute & solvent will occur Solvation Saturated Solution Brownian Motion Ions are dissociated and the ions are mobile Suspension Tyndall Effect Undissolved solute would be present at the bottom of the container Solute Unsaturated Homogeneous Unsaturated water Nature of solutes/solvents Temperature Pressure 98g rule of thumb for predicting whether or not one substance dissolves in another Ex: Polar solutes will dissolve in polar solvents Aerosols Solute-solute attraction is broken up; requires energy Solvent-solvent attraction is broken up; requires energy Solute-solvent attraction is formed; releases enerty suspension Oil and water Dirt and water Colloid Heterogeneous Brownian Motion Nonelectrolyte Visibility of headbeams on a foggy night NaCl Supersaturated NaClO3 Food coloring and water Foam Dissociation Molarity = Moles of Solute Liters of Solution No charged particles are present and they are not mobile Heterogeneous