Economics Unit 3AECO – Australia and the global economy
advertisement
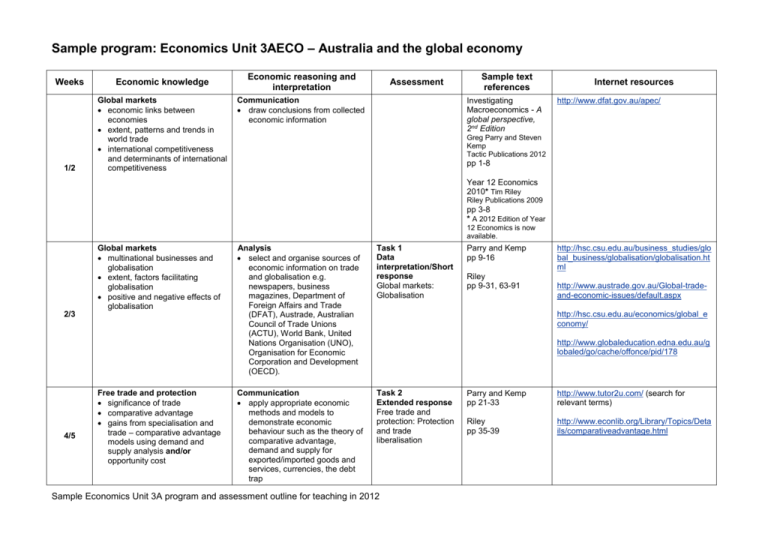
Sample program: Economics Unit 3AECO – Australia and the global economy Weeks Economic knowledge 1/2 Global markets economic links between economies extent, patterns and trends in world trade international competitiveness and determinants of international competitiveness Economic reasoning and interpretation Assessment Communication draw conclusions from collected economic information Sample text references Investigating Macroeconomics - A global perspective, 2nd Edition Internet resources http://www.dfat.gov.au/apec/ Greg Parry and Steven Kemp Tactic Publications 2012 pp 1-8 Year 12 Economics 2010* Tim Riley Riley Publications 2009 pp 3-8 * A 2012 Edition of Year 12 Economics is now available. Global markets multinational businesses and globalisation extent, factors facilitating globalisation positive and negative effects of globalisation 2/3 4/5 Free trade and protection significance of trade comparative advantage gains from specialisation and trade – comparative advantage models using demand and supply analysis and/or opportunity cost Analysis select and organise sources of economic information on trade and globalisation e.g. newspapers, business magazines, Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT), Austrade, Australian Council of Trade Unions (ACTU), World Bank, United Nations Organisation (UNO), Organisation for Economic Corporation and Development (OECD). Task 1 Data interpretation/Short response Global markets: Globalisation Communication apply appropriate economic methods and models to demonstrate economic behaviour such as the theory of comparative advantage, demand and supply for exported/imported goods and services, currencies, the debt trap Task 2 Extended response Free trade and protection: Protection and trade liberalisation Parry and Kemp pp 9-16 Riley pp 9-31, 63-91 http://hsc.csu.edu.au/business_studies/glo bal_business/globalisation/globalisation.ht ml http://www.austrade.gov.au/Global-tradeand-economic-issues/default.aspx http://hsc.csu.edu.au/economics/global_e conomy/ http://www.globaleducation.edna.edu.au/g lobaled/go/cache/offonce/pid/178 Sample Economics Unit 3A program and assessment outline for teaching in 2012 Parry and Kemp pp 21-33 http://www.tutor2u.com/ (search for relevant terms) Riley pp 35-39 http://www.econlib.org/Library/Topics/Deta ils/comparativeadvantage.html Weeks Economic knowledge Economic reasoning and interpretation Assessment Sample text references Internet resources Analysis apply mathematical techniques relevant to international economic analysis including opportunity cost ratios, calculating the terms of trade index, exchange rate calculations, completing balance of payments calculations including Balance on Current Account, Balance on Capital and Financial Account. apply appropriate methods of recording and organising economic information e.g. spreadsheet showing Australia’s net foreign liabilities, graphs showing the widening of the CAD over time, tables representing opportunity cost between the production of two goods 6 7/8 Free trade and protection forms of protection the operation of protectionist policies including tariffs and subsidies arguments for protection and trade liberalisation trade agreements, trade organisations and trading blocs Communication apply appropriate economic methods and models to demonstrate economic behaviour such as the theory of comparative advantage, demand and supply for exported/imported goods and services, currencies, the debt trap Parry and Kemp pp 33-44 Australia and the global economy the extent, composition and direction of Australia’s trade major patterns and trends in the composition and direction of Australia’s trade the structure of Australia’s Balance of Payments accounts Analysis apply effective methods for identifying relevant information within sources e.g. skimming and scanning. apply mathematical techniques relevant to international economic analysis including opportunity cost ratios, Parry and Kemp pp 55-59 pp 65-73 Sample Economics Unit 3A program and assessment outline for teaching in 2012 http://www.austrade.gov.au/ http://www.dfat.gov.au/trade/ftas.html Riley pp 35-62, 40-58, 145159 Riley pp 97-111 http://www.austrade.gov.au/ http://www.rba.gov.au/Statistics/Bulletin/s earch.asp?text=balance+of+payments&se ries=allseries http://www.mrwood.com.au/unit3/es1.asp www.abs.gov.au Weeks Economic knowledge Economic reasoning and interpretation Assessment Sample text references calculating the terms of trade index, exchange rate calculations, completing balance of payments calculations including Balance on Current Account, Balance on Capital and Financial Account. Australia and the global economy the concept of the Current Account Deficit (CAD) reasons for, and trends in, Australia’s CAD implications and different views re the significance of Australia’s CAD Analysis apply mathematical techniques relevant to international economic analysis including opportunity cost ratios, calculating the terms of trade index, exchange rate calculations, completing balance of payments calculations including Balance on Current Account, Balance on Capital and Financial Account. apply appropriate methods of recording and organising economic information e.g. spreadsheet showing Australia’s net foreign liabilities, graphs showing the widening of the CAD over time, tables representing opportunity cost between the production of two goods Australia and the global economy the Terms of Trade (ToT) and the ToT index recent trends in Australia’s ToT significance of changes in the ToT Analysis apply mathematical techniques relevant to international economic analysis including opportunity cost ratios, calculating the terms of trade index, exchange rate calculations, completing balance of payments calculations including Balance on Current Account, Balance on Capital and Financial Account. 9 10 Internet resources www.dfat.gov.au/publications/stats.html Task 3: Data interpretation/Short response Australia and the global economy: Australia’s current account deficit Sample Economics Unit 3A program and assessment outline for teaching in 2012 Parry and Kemp pp 73-80 www.rba.gov.au www.abs.gov.au Riley pp 108-111, 115, 217-221, 369 Parry and Kemp pp 91-97 http://www.mrwood.com.au/unit3/es1.asp www.rba.gov.au Riley pp 112-114 www.abs.gov.au Weeks 11/12 13/14 15 Economic knowledge Economic reasoning and interpretation Australia and the global economy exchange rates and the Trade Weighted Index (TWI) determination of freely floating exchange rates appreciation and depreciation relationship between the Balance of Payment (BoP) and the exchange rate the factors that affect the exchange rate effects of movements in the exchange rate on sectors of the economy recent trends in Australian exchange rates Analysis apply mathematical techniques relevant to international economic analysis including opportunity cost ratios, calculating the terms of trade index, exchange rate calculations, completing balance of payments calculations including Balance on Current Account, Balance on Capital and Financial Account. Australia and the global economy foreign liabilities i.e. foreign investment and foreign debt relationship between the current account outcome and foreign liabilities extent of and recent trends in Australia’s foreign investment and foreign debt benefits and costs of foreign investment and foreign debt Communication apply appropriate economic methods and models to demonstrate economic behaviour such as the theory of comparative advantage, demand and supply for exported/imported goods and services, currencies, the debt trap Revision/preparation for examination Assessment Task 4: Extended response Australia and the global economy: Exchange rates Sample text references Parry and Kemp pp 103-115 Internet resources www.rba.gov.au www.mrwood.com.au Riley pp 123-141 http://www.abc.net.au/money/currency/fea tures.htm http://www.anz.com/aus/corporate/econo mics-markets-research/ http://www.stgeorge.com.au/corporatebusiness/report-centre Communication apply appropriate economic methods and models to demonstrate economic behaviour such as the theory of comparative advantage, demand and supply for exported/imported goods and services, currencies, the debt trap Task 5: Data interpretation/Short response Australia and the global economy: Balance of payments and foreign liabilities Task 6: Examination Sample Economics Unit 3A program and assessment outline for teaching in 2012 Parry and Kemp pp 125-138 http://www.mrwood.com.au/unit3/es1.asp www.abs.gov.au Riley pp 219-225 www.rba.gov.au Sample assessment outline: Economics 3AECO – Australia and the global economy Assessment Type Data interpretation/ Short response Assessment Type Weighting When Task weighting Outcome 2 The operation of the economy Outcome 3 Economic policy and action Week 3 Task 1 Global markets: Globalisation 10% Week 9 Task 3 Australia and the global economy: Australia’s current account deficit 10% Week 14 Task 5 Australia and the global economy: Balance of payments and foreign liabilities 15% Week 5 Task 2 Free trade and protection: Protection and trade liberalisation 20% Week 12 Task 4 Australian and the global economy: Exchange rates 15% Week 16 Task 6 3A Examination End of year - Mock Examination (3A and 3B) 20% 10% 35% (CC weighting 3050%) 35% Extended response Task Outcome 1 Economic inquiry (CC weighting 3050%) 30% Examination (CC weighting 2030%) Sample Economics Unit 3A program and assessment outline for teaching in 2012