Anatomical Boundaries Doc.
advertisement

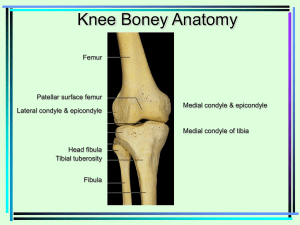
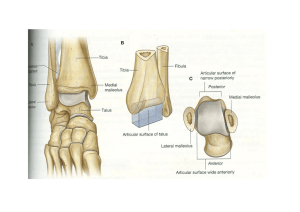
Important anatomical bounties for ESA 2 Anatomical snuff box: (brevis between 2 longus) Medial- EPL Lateral-EPB/APL Contents- Radial artery, cephalic vein, scaphoid. Axilla : Apex: Clavicle, Coracoid process, 1st rib (CCR) Anterior: pectoralis major & minor Posterior: lats dorsi, teres major, subscapularis Medial: serratus anterior, ribs, intercostals Lateral: tendon of long head of biceps brachii Base: Axillary fascia, Runs between latissimus dorsi and pectoralis major, ie. Hairy armpit Cubital fossa: The cubital fossa is the triangular area on the anterior view of the elbo Superior: (proximal) boundary - an imaginary horizontal line connecting the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus Medial (ulnar) boundary - lateral border of pronator teres muscle Lateral (radial) boundary - medial border of brachioradialis muscle apex- formed by the meeting point of the lateral and medial boundaries Contents: medial to lateral median nerve, biracial artery, bicep brachii tendon, radial nerve. (My bum turns red) .The ulnar nerve is also in the area, but is not in the cubital fossa; it occupies a groove on the posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle of the humerus. Posterior triangle of the neck: Apex: Union of the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius muscles at the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone Anterior: Posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus Posterior: Anterior border of the trapezius Base: Middle one third of the clavicle Anterior triangle of the neck: Anterior- Midline of neck from chin to manubrium Posterior- anterior margin of SCM Apex- jugular notch in manubrium of sternum Base- lower border of body of mandible to mastoid process (along chin) Femoral canal: Anterosuperiorly-inguinal ligament Posteriorly-pectineal ligament lying anterior to the superior pubic ramus Medially -lacunar ligament Laterally- femoral vein Inguinal canal (Starting from superior):MALT Superior wall (roof): 2 Muscles: · internal oblique Muscle · transverse abdominus Muscle Anterior wall: 2 Aponeuroses: · Aponeurosis of external oblique · Aponeurosis of internal oblique Lower wall (floor): 2 Ligaments: · inguinal Ligament · lacunar Ligament Posterior wall: 2Ts: · Transversalis fascia · conjoint Tendon Carpel tunnel: Roof- flexor retinaculum (fibrous band) Floor & walls - carpal bones Contents- flexor tendons & median nerve Hesselbach's triangle: Medial border: Lateral border of rectus abdominis. Superolateral border: Inferior epigastric vessels Inferior border: Inguinal ligament, sometimes referred to as Poupart's ligament This can be remembered by the mnemonic RIP (as direct inguinal hernias rip directly through the abdominal wall). Popliteal fossa: Superior and medial: the semitendinosus muscle and semimembranosus muscle Superior and lateral: the biceps femoris muscle Inferior and medial: the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle Inferior and lateral: the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle and plantaris muscle