ULNA BONE
advertisement

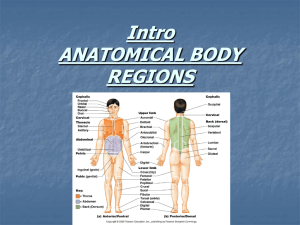
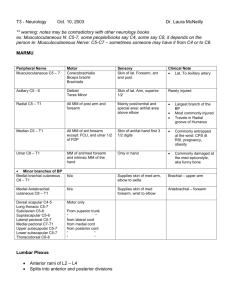
ULNA BONE LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Students should able to: • Recognize the bone. • Determine side of bone. • Identify the features of bone. • Identify the muscles attached to bone. • Identify clinical significance of bone. DETERMINATION OF SIDE • Strong Upper end. • Has hook-like projection (trochlear notch), concavity of which faces forward. • Lower end has small head. • Thin sharp crest like interosseous border of shaft lies laterally. • Styloid process projects downwards from posteriomedial aspect of head. PARTS OF BONE • • • Upper end. Shaft. Lower end. FEATURES OF UPPER END • Two processes • • • Olecranon . Coronoid. Two articular notches • • Trochear. Radial. OLECRANON PROCESS • Bent forwards, forming a beak like projection • Occupies the olecranon fossa of humerus when elbow is extended • Posses 6 surfaces • Anterior • Posterior • Lateral • Medial • Superior • Inferior CORONOID PROCESS Possess: • • 4 surfaces. • Anterior. • Lateral. • Medial surface. Two borders. • Medial border • Lateral border TROCHLEAR NOTCH The Semilunar Notch (incisura semilunaris; greater sigmoid cavity Articulates with trochlea of humerus. Formed by anterior surface of olecranon process & upper surface of coronoid process RADIAL NOTCH • Oval depression on lateral surface of coronoid process. • Articulates with head of radius • Annular ligament is attached. The Body or Shaft (corpus ulnæ) • • • • The body at its upper part is prismatic in form . its central part is straight. its lower part is rounded, smooth . has three borders and three surfaces. Borders The volar border (margo volaris; anterior border) . separates the volar from the medial surface. Prominent. begins above at the medial angle of the coronoid process ends below in front of the styloid process upper part, well-defined middle portion, smooth and rounded give origin to the Flexor digitorum profundus lower fourth serves for the origin of the Pronator quadratus The interosseous crest (crista interossea; external or interosseous border • Sharp crest like lateral border. • Upper part continuous with supinator crest. • Interosseous membrane is attached to it, except at upper part. The dorsal border (margo dorsalis; posterior border ) Begins at posterior aspect of olecranon. Ends at back of styloid process. gives attachment to an aponeurosis in upper 3\4 Apponeurosis gives a common origin to the: Flexor carpi ulnaris, the Extensor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum profundus lower fourth is smooth and rounded Surfaces The volar surface (facies volaris; anterior surface) between anterior and interosseous borders. Nutrient foramen. nutrient artery is a branch of anterior interrosseous artery. upper 3/4th gives origin to the Flexor digitorum profundus Lower 1\4 Pronator quardatus origin Medial surface • Covex. • Lies between anterior &posterior borders. • Flexor digitorum profundus from upper 3\4 MUSCLE ATTACHMENTS ON ANTERIOR SURFACE OF ULNA Brachialis Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Supinator Flexor Digitorum Profundus Posterior surface between posterior & interosseous borders. oblique line. Surface divided into a medial & a lateral part by a vertical ridge. Lateral adjoins the interosseous border; medial area adjoins the posterior border. Lateral area gives origin to • Abductor pollicis longus. • Extensor pollicis longus. • Extensor indicis. • Anconeous MUSCLES ATTACHMENT ON POSTERIOR SURFACE OF ULNA LOWER END • • PARTS. Head. Styloid process. HEAD • Articular part • Inferior surface. • Anterior & posterior margins (give attachment to capsular ligaments of wrist joint) STYLOID PROCESS • projects from posterio-medial aspect of lower end of ulna. • 1.25 cm above level of radial styloid process • gives attachment to ulnar collateral ligament of wrist joint. • Groove on dorsal surface lodges tendon of extensor carpi ulnaris. • Posterior surface gives attachment to extensor retinaculum. THANKS