The Middle Ages-Crusades and Church (14.1, 14.2)
advertisement
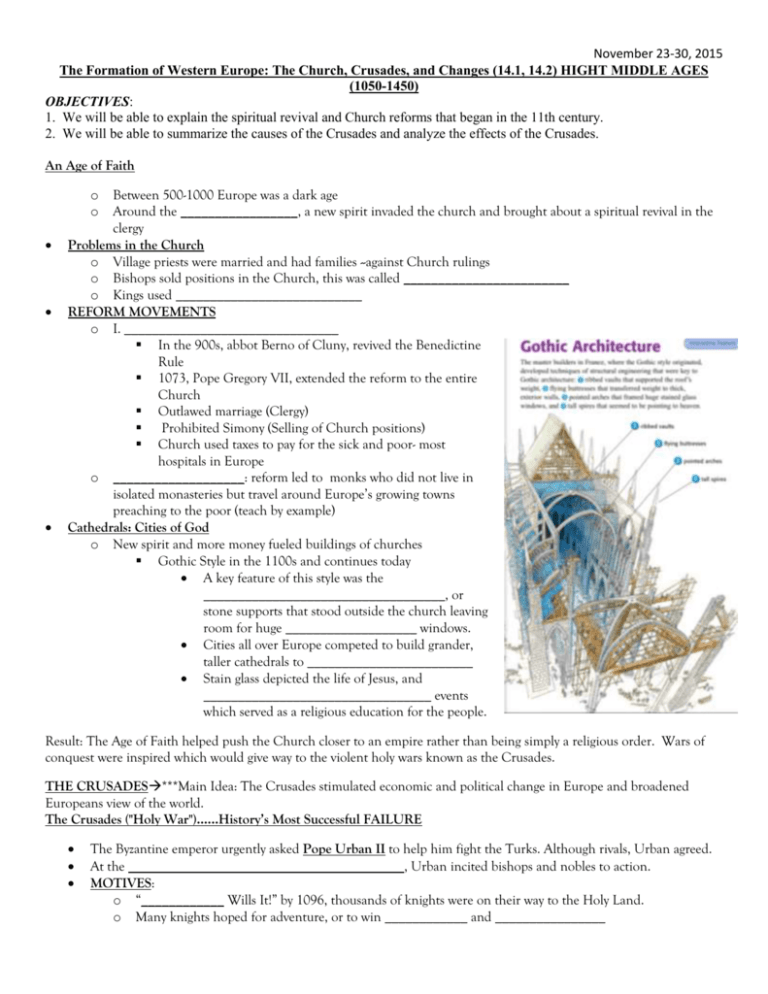
November 23-30, 2015 The Formation of Western Europe: The Church, Crusades, and Changes (14.1, 14.2) HIGHT MIDDLE AGES (1050-1450) OBJECTIVES: 1. We will be able to explain the spiritual revival and Church reforms that began in the 11th century. 2. We will be able to summarize the causes of the Crusades and analyze the effects of the Crusades. An Age of Faith Between 500-1000 Europe was a dark age Around the _________________, a new spirit invaded the church and brought about a spiritual revival in the clergy Problems in the Church o Village priests were married and had families --against Church rulings o Bishops sold positions in the Church, this was called ________________________ o Kings used ___________________________ REFORM MOVEMENTS o I. _______________________________ In the 900s, abbot Berno of Cluny, revived the Benedictine Rule 1073, Pope Gregory VII, extended the reform to the entire Church Outlawed marriage (Clergy) Prohibited Simony (Selling of Church positions) Church used taxes to pay for the sick and poor- most hospitals in Europe o ___________________: reform led to monks who did not live in isolated monasteries but travel around Europe’s growing towns preaching to the poor (teach by example) Cathedrals: Cities of God o New spirit and more money fueled buildings of churches Gothic Style in the 1100s and continues today A key feature of this style was the ___________________________________, or stone supports that stood outside the church leaving room for huge ___________________ windows. Cities all over Europe competed to build grander, taller cathedrals to ________________________ Stain glass depicted the life of Jesus, and _________________________________ events which served as a religious education for the people. o o Result: The Age of Faith helped push the Church closer to an empire rather than being simply a religious order. Wars of conquest were inspired which would give way to the violent holy wars known as the Crusades. THE CRUSADES***Main Idea: The Crusades stimulated economic and political change in Europe and broadened Europeans view of the world. The Crusades ("Holy War")......History’s Most Successful FAILURE The Byzantine emperor urgently asked Pope Urban II to help him fight the Turks. Although rivals, Urban agreed. At the ________________________________________, Urban incited bishops and nobles to action. MOTIVES: o “____________ Wills It!” by 1096, thousands of knights were on their way to the Holy Land. o Many knights hoped for adventure, or to win ____________ and ________________ November 23-30, 2015 Pope Urban also hoped to increase his power and perhaps heal the ____________________ or split between the Roman and Byzantine Churches o Opportunity to get rid of knights that caused ___________________ o ________________________ made money by loaning to finance The First Crusade o Pope called on Christians to fight and recover the __________________________ (Jerusalem) persecuted _________________________, as they were blamed for killing Jesus o Pope promised glory, riches, titles, and forgiveness of sins if people fought (ie. ticket to heaven) o Only the _____________________________ (1097-1099) came close to achieving its goal. In 1099, Christian Knights captured Jerusalem The Crusades...All Together (2-8) o The Crusades continued, off and on, for over 200 years (8 Total) o The Third Crusade led by Kings (Particularly _________________________________________ of England) Europe against Muslim leader _____________________. Truce or agreement after battles that unarmed Christians could visit holy land o During the ___________________________________, the crusaders were diverted from fighting Muslims to fighting Christians because Venetian merchants and crusaders in ___________________ – captured and looted Constantinople, the Byzantine capital. o By 1291, Muslim armies captured the last Christian outpost, the victors massacred their defeated enemies, this time they were Christians Effects of the Crusades o Example of Church power o _______________ was expanded between Europe and Southwest Asia o Failure of later crusades lessened the power of the _________________ o The Crusades weakened the power of the feudal nobility Increased power of __________________ o Thousands of __________________ and other participants lost their lives o Began a legacy of bitterness and hatred of Christians for the Muslims o Persecution of __________________ o Those who survived brought back culture to ____________________ Reconquista (1100-1492) (The Reconquest of Spain) o Christians sought to take over Muslim held lands (Starting in 1100) o In 1469, Isabella of Castile married Ferdinand of Aragon, both made a final push against the Muslim strong hold of Granada, and in 1492, the Reconquista was complete. o The religious ______________ ended with Isabella. o With support from the ____________________________-- A Church court set up to try people accused of heresy: Isabella launched a brutal crusade against Jews and Muslims. o Achieves religious unity but 150k left Spain o











