Unpacking Outcomes
advertisement
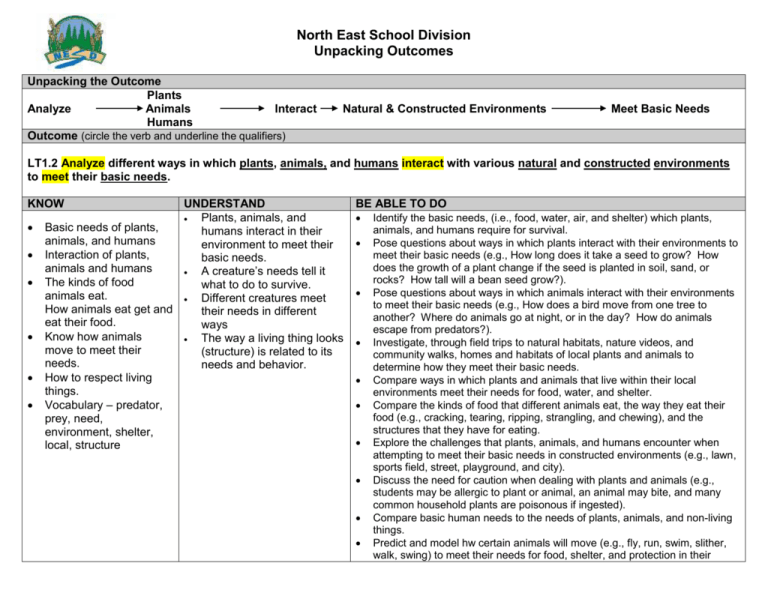
North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Plants Analyze Animals Interact Humans Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) Natural & Constructed Environments Meet Basic Needs LT1.2 Analyze different ways in which plants, animals, and humans interact with various natural and constructed environments to meet their basic needs. KNOW UNDERSTAND Plants, animals, and Basic needs of plants, humans interact in their animals, and humans environment to meet their Interaction of plants, basic needs. animals and humans A creature’s needs tell it The kinds of food what to do to survive. animals eat. Different creatures meet How animals eat get and their needs in different eat their food. ways Know how animals The way a living thing looks move to meet their (structure) is related to its needs. needs and behavior. How to respect living things. Vocabulary – predator, prey, need, environment, shelter, local, structure BE ABLE TO DO Identify the basic needs, (i.e., food, water, air, and shelter) which plants, animals, and humans require for survival. Pose questions about ways in which plants interact with their environments to meet their basic needs (e.g., How long does it take a seed to grow? How does the growth of a plant change if the seed is planted in soil, sand, or rocks? How tall will a bean seed grow?). Pose questions about ways in which animals interact with their environments to meet their basic needs (e.g., How does a bird move from one tree to another? Where do animals go at night, or in the day? How do animals escape from predators?). Investigate, through field trips to natural habitats, nature videos, and community walks, homes and habitats of local plants and animals to determine how they meet their basic needs. Compare ways in which plants and animals that live within their local environments meet their needs for food, water, and shelter. Compare the kinds of food that different animals eat, the way they eat their food (e.g., cracking, tearing, ripping, strangling, and chewing), and the structures that they have for eating. Explore the challenges that plants, animals, and humans encounter when attempting to meet their basic needs in constructed environments (e.g., lawn, sports field, street, playground, and city). Discuss the need for caution when dealing with plants and animals (e.g., students may be allergic to plant or animal, an animal may bite, and many common household plants are poisonous if ingested). Compare basic human needs to the needs of plants, animals, and non-living things. Predict and model hw certain animals will move (e.g., fly, run, swim, slither, walk, swing) to meet their needs for food, shelter, and protection in their environment, based on personal observations, pictures, or videos. Explore how people demonstrate respect for living thing by caring for domestic plants and animals (e.g., growing a plant, hatching eggs, and keeping a pet). ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How do plants interact with their environment? How do animals interact with their environment? What challenges do plants, animals, and humans encounter when attempting to meet their basic needs? How are human’s needs different from the needs of animal, plants, and non-living things? How do animals know what to do to live? How do creatures act differently? How do they act the same? What makes each living thing unique? How does a living thing’s needs affect its behavior and appearance?