Acids, Bases & Salts (B)
advertisement

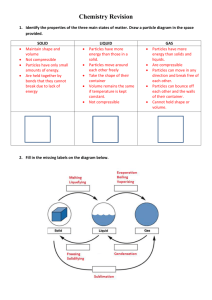
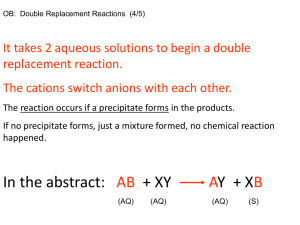
Page |1 Acids, Bases & Salts (B) Q.1. From the list of the substances given below, choose the pair required to prepare the salts (i) to (iii) in the laboratory and write down the relevant equations. The substances are : Iron, Chlorine, Lead Nitrate solution, Sodium Nitrate solution, Iron (III) Carbonate, Lead Carbonate, Iron (III) Hydroxide, Sodium Hydroxide and dilute Hydrochloric acid. (i) Sodium Chloride (ii) Lead Chloride (iii) Anhydrous Iron (III) Chloride. Ans.: - (i) NaOH + HCl (dil) → NaCl + H2O (ii) Pb(NO3)2+ 2HCl (dil) → PbCl2 + 2HNO3 (iii) 2Fe (heated) + 3Cl2 (dry) → 2FeCl3. Q.2. All Ammonium salts are decomposed on heating. What other property do Ammonium salts have in common? Ans.: - All Ammonium salts are soluble in water. Q.3. Answer the following questions, relating your answers only to salts in the list given below : Anhydrous Calcium Chloride, Copper Sulphate-5-water, Sodium Carbonate-10 – water. (a) Which compound is efflorescent? (b) Which compound is blue in colour? (c) Which compound is deliquescent? (d) What would be seen on mixing a solution of Calcium chloride with a solution of Sodium carbonate? (e) Write the balanced equation for occurring when a solution of Calcium chloride is mixed with a solution of Sodium carbonate. Ans : - (a) SodiumCarbonate – 10 – water. (b) Copper sulphate – 5 – water. (c) Anhydrous Calcium chloride. (d) A white precipitate of Calcium carbonate is formed. (e) CaCl2 + Na2CO3 → CaCO3 ↓ + 2NaCl Q.4. In this question, you are required to supply the word (or words) that will make the following sentence into correct statement which is to be written down in full. Calcium nitrate reacts with Sodium sulphate to form Calcium sulphate. Ans.: - Calcium nitrate solution reacts with Sodium sulphate solution to form Calcium sulphate. Q.5. Describe in each case, one chemical test that would enable you to distinguish between the following pairs of chemicals. Describe what happens with each chemical or state “no visible reason”. (a) Sodium chloride solution and sodium nitrate. (b) Sodium sulphate solution and Sodium chloride solution. Ans : - (a) Sodium chloride solution Sodium nitrate solution When sodium chloride When sodium nitrate solution Page |2 solution is treated with Silver nitrate solution, a white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess of Ammonium hydroxide. is treated with Silver nitrate solution, no visible reaction is observed. b) Sodium sulphate solution Sodium chloride solution When Sodium sulphate solution is treated with Barium chloride solution, a white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in all the mineral acids. When Sodium chloride solution is treated with Barium chloride solution, no visible reaction is observed. Q.6. Write balanced equations for each of the following reactions : (a) Action of heat on Copper nitrate. (b) Zinc and dilute Sulphuric acid. Ans.: - (a) 2Cu(NO3)2 + Δ → 2CuO + 4NO2 + O2. (b) Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2. Q.7. (a) Choose the correct word or phrase from the brackets to complete the following sentences : (i) Ammonium chloride is a soluble salt prepared by (precipitation, neutralization). (ii) When Ammonium chloride is heated, it undergoes (thermal decomposition, thermal dissociation). (b) Write correctly the balanced equations for each of the reactions mentioned in the above statements. Ans.: - (a)(i) Neutralization. (ii) Thermal dissociation. (b) NH4OH + HCl → NH4Cl + H2O Δ NH4Cl ↔ NH3 + HCl cool Q.8. Define the following terms : (i) pH-scale (ii) Neutralization. Ans.: - (i) pH-scale – It is a scale to tell whether a given solution is acidic, alkaline or neutral in nature. (ii) Neutralization – It is a process when Hydrogen ions, derived from an acid, combine with Hydroxyl ions, derived from base, forming unionized water molecule. Q.9. (i) Outline the steps that would be necessary to convert insoluble Lead (II) oxide into insoluble Lead chloride. (ii) Write the balanced equations for the reaction required to convert insoluble Lead (II) oxide into insoluble Lead chloride. (iii) If iron reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, what will be the products of sulphuric acid? (iv) A solution of Iron (III) chloride has a pH less than 7.Is the solution acidic or alkaline? Page |3 Ans.: - (i) Lead oxide is treated with dilute nitric acid to get soluble Lead nitrate. This Lead nitrate is treated with soluble Metallic chloride or dilute hydrochloric acid to get insoluble Lead chloride. (ii) PbO + 2HNO3 (dil) → Pb(NO3)2 + H2O Pb(NO3)2 + 2NaCl → PbCl2 + 2NaNO3. (iii) The product will be Ferrous sulphate / Iron (II) Sulphate. Fe + H2SO4 (dil) → FeSO4 + H2. (iv) Acidic. Q.10. From the following list of substances, choose the one substance in each case which matches the description (a) to (f) given below : (Write down the names exactly as they are given in the list. Do not write formulae.) Ammonium nitrate, Calcium Hydrogen carbonate, Copper Carbonate, Lead carbonate, Lead nitrate, Potassium nitrate, Sodium carbonate, Sodium Hydrogen carbonate, Zinc carbonate. (a) A Hydrogen carbonate which exists in the solid state. (b) A carbonate not decomposed by heat. (c) A green coloured Carbonate which turns black on heating. (d) a nitrate which gives off only Oxygen when heated. (e) A nitrate which on heating decomposes into Dinitrogen oxide (Nitrous oxide) and steam. (f) A nitrate which gives off Oxygen and Nitrogen dioxide when heated. Ans.: - (a) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (b) Sodium carbonate (c) Copper carbonate (d) Potassium nitrate (e) Ammonium nitrate (f) Lead nitrate. Q.11. Some methods used for the laboratory preparation of salt are A – Metal + acid B – Carbonate + acid C – Precipitation D – Direct combination E – Titration Copy and complete the following table : Salt Method of Preparation mmonium sulphate Titration Calcium carbonate Iron (III) chloride Lead nitrate Zinc sulphate Ans.: Salt Method of Preparation Ammonium sulphate Titration Calcium carbonate Precipitation Page |4 Iron (III) chloride Direct combination Lead nitrate Carbonate + acid / Metal + acid Zinc sulphate Metal + acid Q.12. What do you see when concentrated Sulphuric acid is added to Copper sulphate-5-water. Ans.: - When concentrated Sulphuric acid is added to blue coloured crystalline Copper sulphate-5-water, it crumbles down to a white amorphous powder by loosing water of crystallization. Q.13. Name (formula not acceptable) the gas produced in the following reaction: Warming Ammonium sulphate solution with Sodium Hydroxide solution. Ans.: - Ammonia. Q.14. State what do you observe when : (a) Neutral litmus solution is added to an alkaline solution. (b) Lead nitrate solution and Sodium chloride solution are mixed. Ans.: - (a) The colour of litmus changes to blue. (b) A white precipitate soluble in hot water and insoluble in cold water is formed. Q.15. Copy and complete the table. The table summarizes the observations following the addition of Barium chloride solution and Lead nitrate solution to solution of Zinc salt. If nothing happens write no reaction as shown or write white precipitate. Barium chloride solution Lead nitrate solution Zinc chloride solution Zinc nitrate solution No reaction Zinc sulphate solution Ans.: Barium chloride solution Lead nitrate solution Zinc chloride solution No reaction White precipitate Zinc nitrate solution No No Page |5 reaction Zinc sulphate solution reaction White White precipitate precipitate Q.16. Write the balanced equations for the following reactions: (a) Dilute hydrochloric and Sodium sulphite. (b) An acid and an alkali. (Yoy must first write : “The acid is ______ and the alkali is _______. “ then write the equation) Ans.: - (a) Na2SO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 (b) The acid is – Sulphuric acid or Nitric acid or Hydrochloric acid. The alkali is – Sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. H2SO4 (dil) + 2KOH → K2SO4 + 2H2O HNO3 (dil) + KOH → KNO3 + H22O HCl (dil) + NaOH → NaCl + H2O Q.17. Write the terms defined by the following sentences : (a) A soluble base. (b) The insoluble solid formed when two solutions are mixed together. (c) An acidic solution in which there is only partial ionization of the solute molecules. Ans.: - (a) Alkali (b) Precipitate (c) Weak acid. Q.18. Differentiate between the chemical nature of an aqueous solution of Hydrogen chloride and an aqueous solution of Ammonia. Ans.:Aqueous solution of Hydrogen chloride Aqueous solution of Ammonia It is acidic in nature It is basic in nature It turns blue litmus to red It turns red litmus to blue It gives Hydronium ions in It gives hydroxyl ions in the solution the solution Q.19. Write the balanced equations for the following reactions: (a) Dilute Nitric acid producing Carbon dioxide. (b) Dilute Sulphuric acid producing Hydrogen. (c) Between Lead nitrate solution and dilute Sulphuric acid. Ans : - (a) CaCO3 + 2HNO3 (dil) → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2 Na2CO3+ 2HNO3(dil) → 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2 (b) Mg + H2SO4 (dil) → MgSO4 + H2 Zn + H2SO4 (dil) → ZnSO4 + H2 (c) Pb(NO3)2 + H2SO4 → PbSO4 ↓ + 2HNO3 Q.20. Choosing substances from the list given below, write equations for the reactions which you would use in the laboratory to obtain in the box given below the list: (i) Sodium sulphate (ii) Copper sulphate (iii) Iron (II) sulphate (iv) Zinc carbonate. Page |6 Dilute sulphuric acid Copper Copper sulphate Iron Sodium carbonate Sodium Zinc Ans : - (i) Na2CO3+ H2SO4 (dil) → Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2 (ii) CuCO3 + H2SO4 (dil) → CuSO4 + H2O + CO2 (iii) Fe + H2SO2 (dil) → FeSO4 + H2 (iv) Zn + H2SO4 (dil) → ZnSO4 + H2 ZnSO4+ Na2CO3→ ZnCO2 + Na2SO4 Q.21. From the formulae listed below, choose one, in each case, corresponding to the salt having the given description : AgCl, CuCO3, CuSO4.5H2O, KNO3, NaCl, NaHSO4, Pb(NO3)2, ZnCO3, ZnSO4.7H2O. (i) An acid salt. (ii) An insoluble Chloride. (iii) On treating with concentrated Sulphuric acid, this salt changes from blue to white. (iv) On heating, this salt changes from green to black. (v) This salt gives Nitrogen dioxide on heating. Ans : - (i) NaHSO4 (ii) AgCl (iii) CuSO4.5H2O (iv) CuCO3 (v) Pb(NO3)2 Q.22. The following table shows the tests a student performed on two aqueous solutions A, B. Write down on your answer script the observation (i) and (ii) that were made. Test Observation Conclusion (i) To solution A, Barium chloride solution and dilute Hydrochloric acid were added. (i) A contains SO4-2 ions (ii) To solution B,Silver nitrate solution and dilute Nitric acid were added. (ii) B contains Cl- ions Ans : - (i) A white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in all mineral acids. (ii) A white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess of Ammonium hydroxide. Q.23. The salt which in solution gives a pale green precipitate with NaOH solution and a white precipitate with BaCl2solution : (a) Iron [III] sulphate (b) Iron [II] sulphate (c) Iron [II] chloride (d) Iron [III] chloride. Ans : - (b) Iron (II) sulphate. Page |7