General Chemistry 1 Sections 7-12

Example Answers (on handout)
Soluble or Insoluble?
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
K
Fe
3
PO
3
(PO
PbCl
2
4
FeSO
4
(NH
4
)
4
)
Soluble
2
Insoluble
Insoluble (exception)
Soluble
2
S Soluble (exception)
PbS Insoluble
Announcements
• L A B T H I S W E E K - A N A L Y S I S O F S I L V E R
G R O U P I O N S
• O W L H O M E W O R K - N E W A S S I G N M E N T S
P O S T E D
•
ACID-BASE, SOLUBILITY, NET IONIC EQUATIONS
Which of the following is soluble?
1.
2.
3.
4.
AlPO
4
PbBr
2
Al(OH)
3
FeSO
4
10%
47%
29%
14%
1 2 3 4
Which of the following is insoluble?
1.
2.
3.
4.
Al(NO
3
)
3
PbC
2
O
4
NaOH
FeF
3
24%
5% 10%
1 2 3 4
61%
pH Review
What is the pH of a 0.25M solution of NaOH?
pH + pOH = 14 pOH=-log[OH ]
NaOH is a strong base [NaOH]=[OH ] pOH= -log[0.25]=0.602
pH= 14 - pOH = 14 = 0.602 = 13.4
What is the [H
3
O + ] of this solution?
[H
3
O + ] = 10 -pH = log -1 (-pH)
[H
3
O + ] = 10 (-13.4) = 3.98 x 10 -14 M
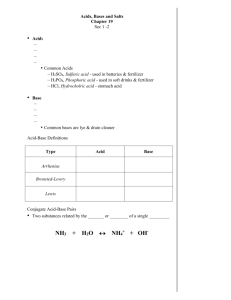
Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Anions of weak acids are weak bases
Conjugate acids and conjugate bases
Weak Acid
Example:
CH
3
COOH = weak acid
CH
3
COO = weak base
What would this look like in a reaction?
CH
3
COOH
NH
4
+
H
2
CO
3
H
2
C
2
O
4
H
2
SO
3
CH
3
COONa + HCl ?
H
2
S
H
3
PO
4
HCN
Anions of strong acids are neutral
HF
NHO
2
HClO
Weak Base
CH
3
COO -
NH
3
CO
3
2-
C
2
O
4
2-
SO
3
2-
S 2-
PO
4
3-
CN -
F -
NO
2
-
ClO -
Conjugate Acids and Bases- More Examples
HCl + NaCN ?
HNO
3
+ AlPO
4
?
Net Ionic Equations
1.
3.
Write all reactants as they exist in solution
2.
Identify acids and bases
Need both acid and base present
Look for “hidden bases” (anions of weak acids)
Ions that form insoluble compounds will form precipitates
4.
5.
6.
Look for known gas-forming reactions
Write out the products as they exist in solution
Cancel spectator ions
Precipitation Reactions
Net Ionic Equations
Pb(NO
3
)
2
+ K
2
CrO
4
?
Pb(NO
3
)
2
+ KI ?
Ba(NO
3
)
2
+ Na
2
C
2
O
4
?
Gas Forming Reactions
Special class of acid-base reactions
Gas Forming Reactions
2H + + CO
3
2 H
2
O(l) + CO
2
(g)
2H + + S 2 H
2
S(g)
2H + + SO
3
2 H
2
O(l) + SO
2
(g)
2H + + M M 2+ + H
2
(g)
Combination of double displacement (swap) and decomposition reactions
2HCl + Na
2
CO
3
?