Experiment 8: Separation of Cations
advertisement

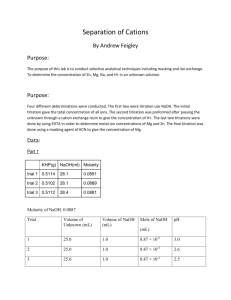
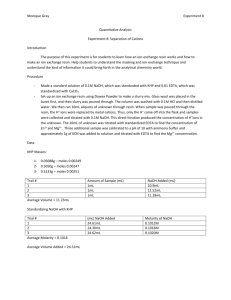
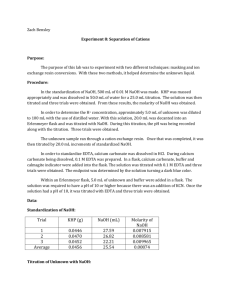
Experiment 8: Separation of Cations Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce two techniques, masking and ion exchange resins conversion. The concentrations of [H+], [Mg2-], [Zn2+], and [Na+] will be determined using these techniques. Procedure 1. Determine mass (grams) of EDTA to make a 0.1M solution. Place EDTA in 500mL of water. 2. Standardize solution with CaCO3. 3. Combine 5mL of unknown, 7mL of buffer solution, and 2mL of calmagite indicator to an Erlenmeyer flask. 4. Titrate with EDTA for three good trials. 5. Determine mass (grams) of NaOH to make a 0.1M concentration. Prepare 0.1M solution of NaOH in 500mL of water. 6. Standardize NaOH solution with KHP. 7. Dilute 5mL of unknown with 100mL of water. 8. Take 20mL aliquots of the unknown solution and add some phenolphthalein indicator to an Erlenmeyer flask and titrate. 9. Repeat for three trials for three different aliquots of unknown solution. 10. Place glass wool above the stopcock of a 50mL burette and add 10mL of dowex 50WX4200 ion exchange resin slurry to the burette. 11. Wash with 15mL of 0.1M HCl then 15mL distilled water. 12. Run 10mL of unknown through the cation exchange resin column and collect in an Erlenmeyer flask (contains H+ that exchanged with metal cations). 13. Wash column with distilled water 14. An aliquot of each sample and phenolphthalein indicator was added to an Erlenmeyer flask and titrated with 0.1M EDTA to equivalence point 15. Titrate three samples of 1mL diluted with 20mL of water with 0.1M NaOH until it turns clear 16. Directly titrate with standardized NaOH to determine [H+] 17. Obtain three 10mL samples of unknown and titrate with EDTA (find [Mg2-] and [Zn2+]). Add 5mL ammonia buffer and 1mL CaCO3 to solution and titrate with 0.1M EDTA until calmagite indicator turns blue. 18. Adjuest pH of three 10mL samples of uknown to 10 by adding ammonia buffer. 19. Add 1g KCN and titrate with EDTA until indicator turns blue (finds [Mg2-]) Data: Titration after ion exchange 1 2 mL of Unknown 10 10 mL EDTA added 11.4 12.45 3 10 10.0 Trial [H+] found via direct titration Trial mL NaOH added Equivalence Point ½ Equivalence Point 1 ~13.69 --------------- --------------- 2 15.90 15.90 7.95 3 15.40 15.40 7.70 4 14.71 14.71 7.36 Standardization of NaOH -2.0089g NaOH in 500mL Trial g KHP mL NaOH 1 0.5115 29.19 2 0.5112 31.10 3 0.5114 30.87 Titration with KCN Trial g KCN mL EDTA pH 1 1.0039 4.60 9.95 2 1.0039 4.72 9.95 3 1.0013 4.70 9.94 Calculations: Standardization of NaOH Grams of NaOH needed for 0.1M: 0.1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 39.995𝑔 × × 0.500𝐿 = 1.9995𝑔 𝐿 𝑚𝑜𝑙 Grams KHP needed for 25mL of titrant: 0.025𝐿 × 0.10𝑀 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐻𝑃 204.23𝑔 × = 0.510575𝑔 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 𝑚𝑜𝑙 Molarity of NaOH: 0.5115𝑔 𝐾𝐻𝑃 × 𝑚𝑜𝑙 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × = 0.0025 𝑚𝑜𝑙 204.24𝑔 𝐾𝐻𝑃 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐻𝑃 0.0025 𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 0.0856𝑀 0.02919𝐿 Direct Titration of [H+] Moles of NaOH: 0.0856 𝑚𝑜𝑙 × 0.01590𝐿 = 0.0013 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐿 Concentration of H+: [𝐻 + ] = 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 0.0013 𝑚𝑜𝑙 = = 0.26𝑀 𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝐴𝑑𝑑𝑒𝑑 0.005𝐿 Titration with KCN Moles of Mg2+: 𝑀𝑔 2+ 0.100 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 1𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎2+ 𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝑚𝐿 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 × × × 𝐿 1000𝑚𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 𝑀𝑔2+ 𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 4.60𝑚𝐿 × 0.100 𝑚𝑜𝑙 1𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎2+ × × = 0.00046 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐿 1000𝑚𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 Concentration of Mg2+: [𝑀𝑔2+ ] 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑀𝑔2+ 0.00046 𝑚𝑜𝑙 = = = 0.46𝑀 𝐿 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 0.001𝐿 Moles of Zn2+: 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑎𝑙 = 11.45𝑚𝐿 × 0.100 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 1𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎2+ × × = 0.001145 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐿 1000𝑚𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑍𝑛2+ = 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑎𝑙 − 𝑎𝑣𝑔. 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑀𝑔2+ 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑍𝑛2+ = 0.001145 𝑚𝑜𝑙 − 0.000467 𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 0.000678 𝑚𝑜𝑙 Concentration of Zn2+: [𝑍𝑛2+ ] = 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑍𝑛2+ 0.000678 𝑚𝑜𝑙 = = 0.027𝑀 𝐿 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 0.025𝐿 Concentration of Na+: Unable to be calculated Conclusion: The purpose of this experiment was to determine [H+], [Mg2-], [Zn2+], and [Na+] using two different techniques. The procedure was split up in class to each group since there were multiple titrations. These titrations were straightforward and we were able to calculate concentrations for magnesium, zince, and hydrogen ions. The average concentrations were 0.25M H+, 0.47M Mg2-, and 0.026M Zn2+. Two groups used the cation exchange technique, which was a more challenging technique since no one had used it before. The concentration of Na+ was unable to be calculated since the sample from the resin was titrated with EDTA instead of NaOH. Therefore, most of the error in this experiment came from the cation exchange technique since we it was new and we used the wrong titrate. Another source of error could have come from each different group. Not every one does the same techniques and one group may say a titration is done while another may say it needs another drop. To make this experiment better, it would be good for students to assign which group is doing which part the week before and for the instructor to go over the cation exchange technique beforehand.