Lab #8: Separation of Cations
advertisement

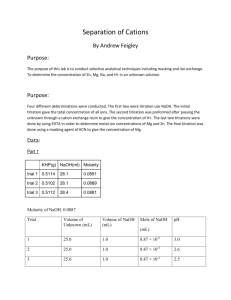
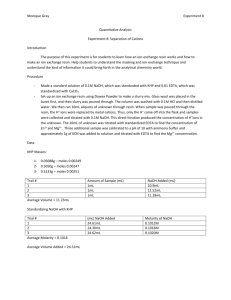
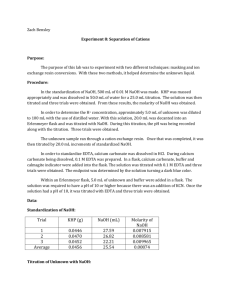
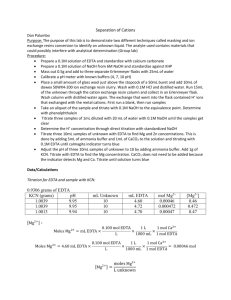
Lab 8: Separation of Cations (Group Lab) Purpose: Two techniques commonly used for selectivity in analytical chemistry will be tested. The analyte of interest is in a sample containing other materials that could potentially interfere with analytical determination. Different selectivity methods include: masking, trapping, conversion, extraction, gas diffusion, dialysis, and chromatographic separation. Masking and ion exchange conversion will be explored in this lab. Procedure: EDTA (0.9061 g) was massed and placed in a volumetric flask ( 250 mL). DH2O was added to the dilution point making an approximate 0.002M EDTA solution. Glass wool was placed in a 50mL burette just above the stopcock. A resin slurry (~10mL) was made and added to the burette. The resin slurry was washed 3 times with HCl (~0.01M) and then an additional 3 times with dH2O. An unknown sample (20 mL) was pipetted and loaded onto the column and run through the cation exchange resin column into an Erlenmeyer flask(250mL). Distilled H2O was then pushed through the column and collected in the same flask. The solution was transferred into a volumetric flask (100 mL) and diluted to the mark. The solution from the cation exchange column was titrated with NaOH (0.095 M) until it reached the equivalence point. An NaOH solution (~100mL) was made to adjust the pH of the samples. The pH meter was calibrated using 4.01, 7.00, and 10.01 buffer solutions. The pH of the unknown samples was adjusted to approximately a pH of 10. The unknown sample (10 mL) was pipetted into three Erlenmeyer flasks (250mL). The pH of each sample was adjusted to approximately 10. KCN (~1g) was added to each sample. The concentration of the [H+] was found by titrating an unknown sample using standardized NaOH. To standardize the NaOH, KHP (0.0996 g) was dissolved in dH2O and titrated with NaOH. The unknown solution (~20mL, pH 10) was titrated using a standardized EDTA solution. Calmagite indicator (pink/ violet to blue) was used to determine the end point of the titration. Data: Moles of EDTA Molarity EDTA Standardization of NaOH: Start of titration (mL) 3.55 End of titration (mL) 8.45 Total (mL) 4.90 Titration with Zn2+ masked with KCN: Sample KCN Added (g) 1 1.0040 2 1.0048 3 1.0029 Average: 0.0174 M Example: Titration of H+: pH 10.40 9.70 9.90 mL EDTA Added 17.3 17.4 17.4 [Mg2+] 0.0173 0.0174 0.0174 Start Volume 8.50 10.00 13.00 mL Unknown 10.0 20.0 20.0 End Volume 10.00 13.00 16.10 Total 1.50 3.00 3.10 [H+] 0.0149 +/- .0003 0.0149 +/- .0003 0.0154 +/- .0003 Example: Sample 1 2 3 mL Unknown 20 20 20 Volume EDTA 48.1 45.4 45.2 Average:0.0231 M [Mg2+] +[Zn2+] Example: Cation Exchange: Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 mL Unknown 20 20 20 mL NaOH used 3.0 2.98 3.05 + [H ] 0.0143 0.0142 0.0145 Average [H+]: 0.0143 M Zn2+ Concentration: [Mg2+] + [Zn2+] 0.0241 M 0.0227 M 0.0226 Average: 0.0151 M [H+] [Zn2+ +Mg2+]-[Mg2+]=[Zn2+] 0.0231-0.0174=0.0057 M Zn2+ Na+ Concentration [H+]-[Zn2+ + Mg2+]=[Na+] Inconclusive Conclusion: The purpose of this experiment was to demonstrate two types of techniques commonly used for selectivity in analytical chemistry: masking and ion exchange resin conversion. This experiment was separated into several parts and each was completed by different lab groups. Due to this separated nature, the procedures were difficult to follow, and the data was difficult to analyze to form conclusions. The titrations of Mg2+, Zn2+, and H+ ions were successful. However, when the solution was passed through the cation exchange column in an attempt to determine the total metal ion concentration (replacing the metal ions with H+ ), a lower concentration of H+ than the original solution was found. It is believed that some H+ was lost in the cation exchange resin. This error prevented an accurate calculation of the Na+.