Experiment 8
advertisement

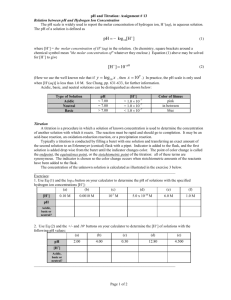
Separation of Cations Dan Palumbo Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to demonstrate two different techniques called masking and ion exchange resins conversion to identify an unknown liquid. The analyte used contains materials that could possibly interfere with analytical determination (Group lab) Procedure: Prepare a 0.1M solution of EDTA and standardize with calcium carbonate Prepare a 0.1M solution of NaOH from 6M NaOH and standardize against KHP Mass out 0.5g and add to three separate Erlenmeyer flasks with 25mL of water Calibrate a pH meter with known buffers (4, 7, 10 pH) Place a small amount of glass wool just above the stopcock of a 50mL buret and add 10mL of dowex 50WX4-200 ion exchange resin slurry. Wash with 0.1M HCl and distilled water. Run 15mL of the unknown through the cation exchange resin column and collect in an Erlenmeyer flask. Wash column with distilled water again. The exchange that went into the flask contained H+ ions that exchanged with the metal cations. First run a blank, then run samples Take an aliquot of the sample and titrate with 0.1M NaOH to the equivalence point. Determine with phenolphthalein Titrate three samples of 1mL diluted with 20 mL of water with 0.1M NaOH until the samples get clear Determine the H+ concentration through direct titration with standardized NaOH Titrate three 10mL samples of unknown with EDTA to find Mg and Zn concentrations. This is done by adding 5mL of ammonia buffer and 1mL of CaCO3 to the solution and titrating with 0.1M EDTA until calmagite indicator turns blue Adjust the pH of three 10mL samples of unknown to 10 by adding ammonia buffer. Add 1g of KCN. Titrate with EDTA to find the Mg concentration. CaCO3 does not need to be added because the indicator detects Mg and Ca. Titrate until solution turns blue Data/Calculations Titration for EDTA and sample with KCN: 0.9306 grams of EDTA KCN (grams) pH 1.0039 9.95 1.0039 9.95 1.0013 9.94 mL Unknown 10 10 10 mL EDTA 4.60 4.72 4.70 mol Mg2+ 0.00046 0.000472 0.00047 [Mg2+] 0.46 0.472 0.47 [Mg2+ ] ∶ Moles Mg 2+ = mL EDTA × Moles Mg 2+ = 4.60 mL EDTA × 0.100 mol EDTA 1L 1 mol Ca2+ × × L 1000 mL 1 mol EDTA 0.100 mol EDTA 1L 1 mol Ca2+ × × = 0.00046 mol L 1000 mL 1 mol EDTA moles Mg2+ [Mg ] = L unknown 2+ [Mg2+ ] = 0.00046 moles Mg2+ 0.001 L unknown Titration of EDTA with sample and buffer: mL Unknown mL Buffer mL EDTA 25 25 25 7 7 7 11.45 12.45 10 = 0.46M Total mol metal 0.001145 0.001245 0.0010 Mol Zn2+ [Zn2+] 0.000086 0.000014 0.000231 0.086 0.014 0.231 [Zn2+ ] ∶ Mol metal = 11.45 mL EDTA × 0.100 mol EDTA 1L 1 mol Ca2+ × × = 0.001145 L 1000 mL 1 mol EDTA mol Zn2+ = mol metal − average mol Mg2+ 0.000086 mol = 0.001145 − .001231 𝑚𝑜𝑙 moles Zn2+ L unknown 0.000086 [Zn2+ ] = = 0.086 0.001 [Zn2+ ] = Cation Exchange Titration: Trials 1 15.90 NaOH (mL) [H+] + Mol [H ] in 2 mL aliquot 2 15.40 - 3 14.71 - 0.3975 0.000795 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐻 + 1 𝐿𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 𝑎𝑑𝑑𝑒𝑑 × 𝑀𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 = [H+] 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐻 + 1 0.0159 𝐿 × 0.1 𝑀 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × 0.004 𝐿 = 0.3975 M Direct NaOH Titration of H+ NaOH used (mL) Moles NaOH [H+] 12.20 0.001187 1.187 12.08 0.001175 1.175 12.80 0.001245 1.245 *used 1 mL of unknown and diluted down with 20 mL of water Average [H+]: 1.202 [H+ ] ∶ Molarity of NaOH × Liters NaOH used = mol NaOH 0.09727 M × 0.0122 = 0.001187 mol mol NaOH Liters of acid(ammonia buffer) = M of H+ 0.001187 = 1.187 M H+ 0.001 Conclusion: The goal of the lab was to use new techniques to determine the moles and concentrations of different ions including ion exchange and masking. When calculating the total ions, the moles of H+ left after the column was run should be the total amount, but was smaller than expected. Since an aliquot was used and the total was not measured, it is unsure how much there really was. The titration of EDTA with sample and buffer also did not work because the unknown was too concentrated. This problem was fixed in the titration of NaOH with the unknown by diluting the unknown down. The ion concentrations were determined, but since only some worked, the results are not very accurate.