Uddingston Grammar School Nat.6 Chemistry Unit 2 : Oxidation of

Uddingston Grammar School
Nat.6 Chemistry
Unit 2 : Oxidation of Food
Homework
1.
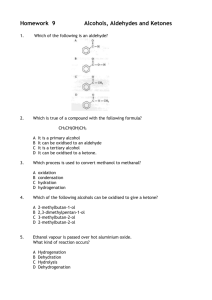
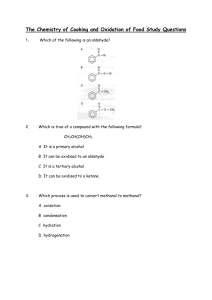
Which is true of a compound with the following formula?
CH
3
CH(OH)CH
3
A.
It is a primary alcohol
B.
It can be oxidised to an aldehyde
C.
It is a tertiary alcohol
D.
It can be oxidised to a ketone.
2.
Which process is used to convert methanol to methanal?
A.
Oxidation
B.
Condensation
C.
Hydration
D.
Hydrogenation
3.
Which of the following alcohols can be oxidised to give a ketone?
A.
2-methylbutan-1-ol
4.
Ethanol vapour is passed over hot aluminium oxide.
What kind of reaction occurs?
A.
Hydrogenation
B.
Dehydration
C.
Hydrolysis
D.
Dehydrogenation
B.
2,3-dimethylpentan-1-ol
C.
3-methylbutan-2-ol
D.
2-methylbutan-2-ol
5.
The dehydration on butan-2-ol can produce two isomeric alkenes, but-1-ene and but-2-ene. Which of the following alkanols can similarly produce, on dehydration, a pair of isomeric alkenes?
A.
propan-2 ol
B.
pentan-3-ol
C.
hexan –3-ol
D.
heptan-4-ol
6.
CH
3
– CH = CH
2
Reaction X
CH
3
-CH
2
- CH
2
-OH
Reaction Y
CH
3
-CH
2
-COOH
Which line in the table correctly describes reaction X and Y?
A
B
C
D
Reaction X
Hydration
Hydration
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Reaction Y
Oxidation
Reduction
Oxidation
Reduction
7.
Oxidation of 4-methylpentan-2-ol using copper (II) oxide results in the alcohol
A.
losing 2g per mole
B.
gaining 2g per mole
C.
gaining 16g per mole
D.
not changing in mass
8.
Which compound has isomeric forms?
A.
C
2
H
3
Cl
B.
C
2
H
5
Cl
C.
C
2
HCl
3
D.
C
2
H
4
Cl
2
9.
Which line in the table shows the correct functional group for each homologous series?
10.
Which two isomers would each produce an acid when warmed with acidified potassium dichromate solution?
A.
1 and 2
B.
2 and 3
C.
1 and 4
D.
3 and 4
11.
Butan – 2-ol reacts in different ways
oxidation butanone dehydration butan-2-ol condensation with
ethanoic acid a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (1) b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. (1)
12.
Although aldehydes and ketones have different structures, they both contain the carbonyl functional group.
In the reaction of propanal with Tollens’ reagent, silver ions are reduced to form silver metal.
Complete the following ion-electron equation for the oxidation.
C
3
H
6
O C
2
H
5
COOH
13.
Alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of carbonyl compounds with methyl
(1) magnesium bromide. The reaction takes place in two stages.
Stage 1 : Methyl magnesium bromide reacts with methanal in an addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Stage 2: Reaction of the product with water produces ethanol a) Suggest a name for the type of reaction which takes place in stage 2. (1) b) Draw a structural formula for the product obtained if propanone had been used
(1) instead of methanal.
14.
Butan-1-ol reacts in different ways.
butanal butanoic acid butan-1-ol
X
Condensation with ethanoic acid a) Name a reagent that could be used to oxidise butan-1-ol to butanal. b) Name an isomer of butanal that cannot be oxidised to butanoic acid.
(1)
(1) c) Draw a structural formula for ester X produced by the condensation of butan-1ol with ethanoic acid. (1)
15.
The quantity of alcohol present after a fermentation reaction is called the % alcohol by volume.
This can be calculated from measurements taken using an instrument called a hydrometer. The hydrometer is floated in the liquid sample, before and after fermentation, to measure its specific gravity.
%alcohol by volume = change in specific gravity of liquid x ƒ
Where ƒ is a conversion factor, which varies as shown in the table.
The hydrometer readings are shown below.
Calculate the % alcohol by volume for this sample. (2)
16.
The element boron forms many useful compounds.
Borane (BH
3
) is used to synthesis alcohols from alkenes.
The reaction occurs in two stages
Stage 1 Addition Reaction
The boron atom bonds to the carbon atom of the double bond which already has the most hydrogens directly attached to it.
Stage 2 Oxidation Reactions
The organoborane compound is oxidised to form the alcohol. a) Name the alcohol produced in Stage 2. b) Draw a structural formula for the alcohol which would be formed from the alkene shown below.
(1)
(1)
17.
Hydrogels are used in disposable nappies. They are fine powders that can absorb up to 500 times their own weight in water.
A hydrogel is a very long molecule with carboxyl groups at regular intervals along its length. A short section of a hydrogel molecule is shown below.
Hydrogels are extremely good at soaking up water because the water molecules are strongly attached to them.
Using your knowledge of chemistry, comment on how suitable hydrogels would be for absorbing liquids or solutions spilled in a chemistry lab. (3)
18.
The table shows the boiling points of some alcohols.
a) Using information from the table, describe two ways in which differences in the structures affect boiling point of isomeric alcohols. (2) b) Predict a boiling point for hexan-2-ol. (1)
19.
Many carbon compounds containing oxygen are very flammable.
The table shows information about two families of isomers.
The lowest temperature at which a compound will ignite is called its flash point. a) A compound with the molecular formula C
6
H
14
O has a boiling point of 158 o C.
Draw a structural formula for this compound. (1) b) For a family of isomers in the table, write a general statement linking the flash points of the compounds to their structures. (1)
30 marks