Redox Reactions - ThinkChemistry
advertisement

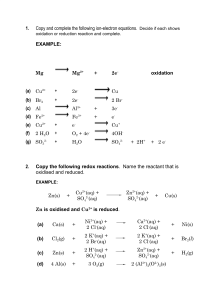
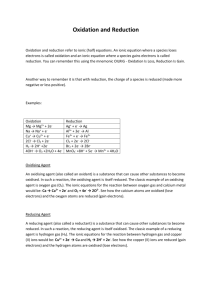
Redox Reactions Chemical Reactions There are 3 major classes of chemical reaction: 1. Precipitation 2. Acid-base 3. Redox Oxidation Refers to the gain of oxygen in a chemical reaction EXAMPLE: Iron + oxygen Iron(II) oxide Write the chemical equation (unbalanced) Fe + O2 FeO The iron has gained oxygen and has been oxidised Reduction Is the opposite of oxidation This means that it involves the lose of oxygen Write a chemical equation for the reduction of calcium oxide. Balance the equation 2CaO 2Ca + O2 Redox reactions Whenever a chemical is oxidised, another chemical must be reduced, and vise vera EXAMPLE: Mg + CuO MgO + Cu Write a similar equation for the reaction of zinc and iron oxide. Label the oxidation and reaction steps Introducing electrons Mg + CuO MgO + Cu The oxidation and reduction steps can be written out separately: OXIDATION REDUCTION Mg 2+O2CuO Cu MgO Mg2+O2Cu Re-write the above two steps, but add charges to the ions involved In the oxidation step: Mg + O2 Mg2+O2The magnesium atoms have turned into magnesium ions Have they gained or lost electrons? OXIDATION IS ALWAYS LOSS of electrons O.I.L. Where have the electrons gone to? They have been taken by the copper: Cu2+O2Cu The copper has turned from ions into atoms 2+ + 2- Cu2+ + 2e NEUTRAL Cu REDUCTION IS ALWAYS GAIN of electrons R.I.G. Practice Write similar ion-electron equations for: Calcium ions turning into calcium atoms Sodium ions turning into sodium atoms Aluminium ions turning into aluminium atoms All of these REDUCTIONS can be found in the data booklet Potassium atoms turning into potassium ions Nickel atoms turning into nickel(II) ions Writing ion-electron equations All reductions are found in data booklet To write the oxidation, reverse the equation Cu2+ + 2e Cu Cu Cu2+ + 2e Both sides of the equation should be neutral when the charges are added together REMEMBER: OIL RIG Problems 1. (a) (b) (c) 2. Look at the following equation: Zn + Ag2O ZnO + Ag Which chemical is being oxidised? Write an ion-electron equation for the oxidation step. Write an ion-electron equation for the reduction step. Assessment tests 10.3 and 10.4