Homework 9 alcohols, aldehydes and ketones
advertisement

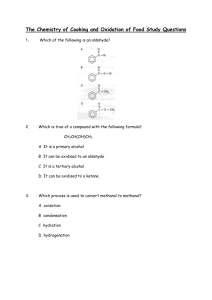
Homework 9 1. 2. Alcohols, Aldehydes and Ketones Which of the following is an aldehyde? Which is true of a compound with the following formula? CH3CH(OH)CH3 A B C D 3. Which process is used to convert methanol to methanal? A B C D 4. oxidation condensation hydration hydrogenation Which of the following alcohols can be oxidised to give a ketone? A B C D 5. It is a primary alcohol It can be oxidised to an aldehyde It is a tertiary alcohol It can be oxidised to a ketone. 2-methylbutan-1-ol 2,3-dimethylpentan-1-ol 3-methylbutan-2-ol 2-methylbutan-2-ol Ethanol vapour is passed over hot aluminium oxide. What kind of reaction occurs? A B C D Hydrogenation Dehydration Hydrolysis Dehydrogenation 6. After heating for several minutes as shown in the diagram, the pH indicator solution turned red. Liquid Q could be, A B C D 7. The dehydration on butan-2-ol can produce two isomeric alkenes, but-1-ene and but-2-ene. Which of the following alkanols can similarly produce, on dehydration, a pair of isomeric alkenes? A B C D 8. propanone paraffin propan-1-ol propan-2-ol propan-2 ol pentan-3-ol hexan –3-ol heptan-4-ol What compound is formed by the oxidation of propan-2-ol? A B C D CH3CH2CHO CH3CO CH3 CH3CH2COOH CH3CH2 CH2OH 9. CH3 – CH = CH2 reaction X CH3-CH2- CH2-OH Reaction Y CH3-CH2-COOH Which line in the table correctly describes reaction X and Y? A B C D Reaction X hydration hydration hydrolysis hydrolysis Reaction Y oxidation reduction oxidation reduction 10. Propanone is a widely used solvent. It can be made from propene. Using full structural formulae show the steps involved in this preparation and name the reagent used in each step. (2) 11. Butan – 2-ol reacts in different ways dehydration butan-2-ol oxidation condensation with ethanoic acid butanone (a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. 12. (1) (1) The compound diazomethane undergoes an unusual reaction called insertion. Under certain conditions, the CH2 group produced can insert itself into any bond which includes an atom of hydrogen. H H H H C C H H OH CH2N2 H C OH H H H C H O H C H H Nitrogen is produced in every reaction. One of the products for the reaction of diazomethane with ethanol is shown below. H H H H H C C C H H H CH2N2 H C C H H OH H OH (a) Name the product shown (1) (b) Draw the full structural formula for the other two organic products which could be formed in this reaction. (2) 13. Acreolin is a feedstock for the production of useful organic compounds, eg acrylic fibres, synthetic rubber and glycerol. Acreolin was first produced after the second world war by oxidation of propene using an antimony catalyst as shown in the diagram. H H H O2 H C C C H C3H4O Sb catalyst H H O C C C H A H H H C C C oxidation OH Acreolin H reduction H OH H B (a) Draw the structural formula for acreolin. (b) Name a possible reagent that could be used to carry out the oxidation of acreolin. 14. (1) (1) Two reactions involving a carbon compound, A, are shown. CH3-CH-CH2- CH3 A OH H+(aq)/Cr2O72Reaction 1 Reaction 2 B C4H8O CH2=CH-CH2-CH3 but-1-ene CH3-CH=CH-CH3 but-2-ene (a) Name compound A. (1) (b) Draw a structural formula for compound B. (1) (c) Name a substance used to convert compound A into but-2-ene and but-1-ene. (1) 15. Alkanols can be oxidised to alkanoic acids. CH3CH2CH2OH Propan-1-ol step 1 CH3CH2CHO propanal step 2 CH3CH2COOH propanoic acid (a) Why can step 1 be described as an oxidation reaction? (b) Acidified potassium dichromate solution can be used to oxidise propanal In step 2 . What colour change would be observed in this reaction? (1) (1)