Cell Revision Questions - IBDPBiology-Dnl
advertisement

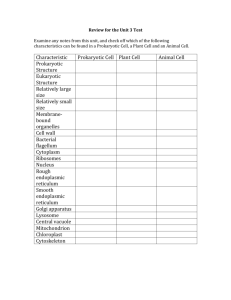
THE CELL: Review Questions 1. (a) State the cell theory [5] (b) Outline the process of endocytosis. [5] (c ) Compare, with the aid of a diagram, the structure of generalised prokaryotic and eukaryotic animal cells. [8] 2. (a) Using a table, compare the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. [5] (b) Draw a labelled diagram showing the main features of the ultra-structure of an animal. (c) Explain the process of passive transport across the cell membrane. (5) (8) 3. (a) List two functions of membrane proteins. [1] (b) Oxygen (O2) moves across the membrane by diffusion. Define the term diffusion. [1] (c) Potassium can move across the membrane by passive or active transport. Distinguish between active transport and facilitated diffusion of ions. [2] (d) The hormone insulin leaves the cell by exocytosis. Describe the process of exocytosis. [2] 4. Diffusion (passive transport) can be studied using bags made of an artificial permeable membrane. In an experiment, equal volumes of each of the following solutions were placed into separate bags: 6 mol dm -3 sodium chloride -3 6 mol dm sucrose The bags, each of the same size, were placed in distilled water at constant temperature. At regular intervals over a period of 160 minutes, both the volume and mass of each bag was measured. The data collected is shown below. (a) Compare the rates of change in mass and volume for the two bags. [2] (b) Calculate the rates of increase in mass and in volume for the bag containing sodium chloride solution during the first 30 minutes. [2] (c) Explain why the volume of both bags increases. [2] 1 (d) Suggest why for a short time, there is a decrease in mass while the volume is still increasing for the bag containing sodium chloride solution. [2] Paramecium caudatum is a freshwater protist with contractile vacuoles that expel water. A culture of P. caudatum was exposed to different concentrations of salt and the numbers of vacuole contractions per minute were counted. The data is shown in the table below. (e) Suggest a reason for the vacuole responses shown by this data. [1] (f) If a substance which prevents contractile vacuole activity was introduced into the environment of P. caudatum, predict what you would see. [1] 5. (a) Outline the structure of cell membranes, including substances contained in them and how they are arranged. [5] (b) Explain how properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membrane. [8] (c) Compare active transport across membranes with passive transport across membrane. [5] 6. (a) Outline the significance to organisms of the different properties of water. [5] (b) Describe the process of active transport across membranes. [5] (c) (a) Draw a diagram of the ultrastructure of an animal cell as seen in an electron micrograph. [6] 7. (a) Draw a labelled diagram of the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane. [5] (b) Describe passive transport across a biological membrane. [5] (c) Explain, with reference to its properties, the significance of water as a coolant, a means of transport and as a habitat. [8] 8. (a) Outline the advantages of using a light microscope instead of an electron microscope. (b) Explain the importance of the surface area to volume ratio as a factor limiting cell size. (c) Define the term organelle and state one function for each of these organelles: ribosome, golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, lysosome, rough endoplasmic reticulum. [5] [7] [6] 2 9. A study was carried out to determine the relationship between the diameter of a molecule and its movement through a membrane. The graph below shows the results of the study. (a) From the information in the graph alone, describe the relationship between the diameter of a molecule and its movement through a membrane. [2] A second study was carried out to investigate the effect of passive protein channels on the movement of glucose into cells. The graph below shows the rate of uptake of glucose into erythrocytes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. (b) Identify the rate of glucose uptake at an external glucose concentration of 4 mmol dm 3 by (i) simple diffusion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ……………………………………………………... . . . [1] 3 (ii) facilitated diffusion. . . . . . …………………………………………………. . . . . . . . . . . . . [1] (c) (i) Compare the effect of increasing the external glucose concentration on glucose uptake by facilitated diffusion and by simple diffusion. [3] (ii) Predict, with a reason, the effect on glucose uptake by facilitated diffusion of increasing the external concentration of glucose to 30 mmol dm 3. [2] 10.(a) Outline the advantages of using light microscopes in comparison with electron microscopes. [3] (b) Distinguish between the structure of plant and animal cells. [6] (c) Explain how the structure and properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes. [9] 11. (a) Distinguish between diffusion and osmosis. [1] (b) Explain how the properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of the cell surface membrane. [2] (c) State the composition and the function of the plant cell wall. [2] (d) Animal and plant cells can be seen under light and electron microscopes. Complete the chart below using a tick ( √) for observation and a cross ( % ) when this observation is not possible using this type of microscope. [3] 4 12. (a) Draw a diagram of a plasma membrane. (b) List the functions of membrane proteins. (c) Explain the role of vesicles in transportation of materials within cells. [5] [5] [8] 13. (a) Distinguish between the terms resolution and magnification when applied to electron microscopy. [2] 14. (a) Explain how the surface area to volume ratio influences cell sizes. [3] (b) State one function for each of the following organelles. [3] (i) Ribosomes (ii) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (iii) Golgi apparatus (c) Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in regards to three different features. (d) Discuss possible exceptions to the cell theory. [3] [4] 5 The electron micrograph below shows part of a cell. [2] (b) Identify the structures labelled I and II. 6 15. (a) Label the following electron micrograph of a prokaryotic cell. [2] (b) Calculate the magnification of the prokaryotic cell. [1] (c) State two advantages of using a light microscope over an electron microscope. [2] (d) State one function of each of the following organelles. * Lysosome * Golgi apparatus * Rough endoplasmic recticulum * Nucleus * Mitochondrion [5] 7