Word
advertisement

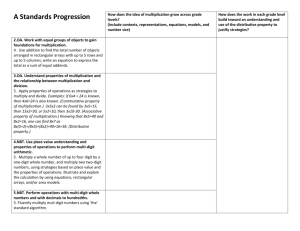
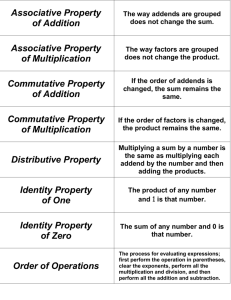
A Standards Progression How does the idea of multiplication grow across grade levels? (include contexts, representations, equations, models, strategies, and number size) How does the work in each grade level build toward an understanding and use of the distributive property to justify strategies? 2.OA. Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication. 4. Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays with up to 5 rows and up to 5 columns; write an equation to express the total as a sum of equal addends. Uses addition to find the total Models: objects and rectangular arrays Equations are repetition of equal addends (2+2+2+2=8) Begins the concrete experiences of multiplication 3.OA. Understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division. 5. Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Examples: if 6x4 = 24 is known, then 4x6=24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3x5x2 can be found by 3x5=15, then 15x2=30, or 5x2=10, then 3x10-30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8x5=40 and 8x2=16, one can find 8x7 as 8x(5+2)=(8x5)+(8x2)=40+16=56. (Distributive property.) (Please note: There are many other standards that develop multiplication. This is one standard that directly identifies the Properties of Operations.) Commutative Associative Distributive 4.NBT. Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 5. Multiply a whole number of up to four digit by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. Number size increases from 4-digit x 1 digit, to 2-digit by 2digit. 5.NBT. Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths. 5. Fluently multiply muli-digit numbers using ‘the’ standard algorithm. Students work in whole numbers. Uses place value to support properties of the operations. Models might include: open arrays, arrays, equations and partial product notation Gr. 3 Builds on understanding of arrays to deepen thinking about commutative property and distributive property. Provides a scaffold from the concrete array to the equation. Gr. 4 Builds on a concrete understanding of single digit numbers to expand to larger whole numbers. Uses models more abstractly to scaffold use of properties to support strategies. Gr. 5 Fluency expectation in multiplication of whole numbers. Uses place value to support properties of the operations. Models might include: open arrays, arrays, equations and partial product notation