Worksheet 5: Enzyme Kinetics
advertisement

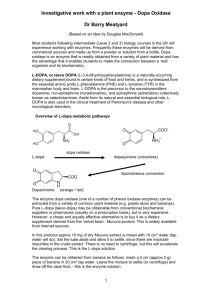
Worksheet 6 Enzymes 25 points Name: Section: Date Turned in: Introduction: 1. (2 pts) What role, if any, does the “active site” play in “enzyme specificity”? 2. (2 pts) Why do we need to reach enzyme saturation to measure the maximum velocity? Materials and Methods: 3. (2.5 pts) If a mixture of tyrosinase and L-DOPA was occurring at its Vmax, and you added 3 more drops of substrate, do you think the overall reaction velocity would increase, decrease, or stay the same? Assume the reaction has unlimited substrate. Explain your reasoning. 4. (2.5 pts) If the L-DOPA happened to be colored and the dopachrome was clear, could you measure the decrease in substrate concentration over time and get to a similar reaction velocity? Why or why not? 5. (2 pts) If the L-DOPA was the same color as Dopachrome, how would that change the methods of this experiment? Results: 5. (5 pts) Using Prism, construct a substrate concentration v. reaction velocity curve based on our class data. Draw one or two arrows showing the Vmax and Km on the graph in their approximate locations! Make sure the axes are properly labeled. Provide a descriptive figure legend that includes the quantitative values for Vmax and Km! note: contact your instructor if Prism has “ambiguous” on the results page or you find a ~ symbol before the Vmax or Km 6. (2 pts) Which of the following Km values indicates the most efficient enzyme? Explain your answer. a. Km = 0.15 M c. Km = 150 mM 5 b. Km = 1.5 x 10 nM d. Km = 15 M Discussion: 7. (2 pts) What effect did the inhibitor PTU (phenylthiourea) have on the reaction velocity of tyrosinase? Explain WHY it had this effect. 8. (2 pts) Using your data and the concept of “structure is related to function”, explain the velocity results as the temperature changed from very low to very high. 9a. (3 pts) Follow the link to the review article. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00094.x/pdf Read the Introduction only. The peptidoglycan cell wall is constructed, in part, by an enzyme called transpeptidase. The antibiotic ampicillin is an inhibitor of transpeptidase. As you will read, enzyme inhibition can lead to cell lysis. a. What is cell lysis and why does it result in the inability of bacteria to reproduce? b. Why would inhibition only be effective “during cell growth”? c. Why are human cells unaffected by this antibiotic?